Italian Americans
This article may be too long to read and navigate comfortably. (October 2024) |
Italo-americani (Italian) | |
|---|---|
 Italian American ancestry by state according to the U.S. Census Bureau's American Community Survey in 2019 | |
| Total population | |
| Alone (one ancestry) 6,629,993 (2020 census)[1] 2.00% of the total US population Alone or in combination 16,813,235 (2020 census)[1] 5.07% of the total US population | |
| Languages | |
| Religion | |
| Predominantly Catholicism with small minorities practicing Greek Orthodoxy, Protestantism and Judaism | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Corsican Puerto Ricans, Maltese Americans, Sammarinese Americans and other Italians |
Italian Americans (Italian: italoamericani) are Americans who have full or partial Italian ancestry. According to the Italian American Studies Association, the current population is about 18 million, an increase from 16 million in 2010, corresponding to about 5.4% of the total population of the United States. The largest concentrations of Italian Americans are in the urban Northeast and industrial Midwestern metropolitan areas, with significant communities also residing in many other major U.S. metropolitan areas.[4]
Between 1820 and 2004, approximately 5.5 million Italians migrated to the United States during the Italian diaspora, in several distinct waves, with the greatest number arriving in the 20th century from Southern Italy. Initially, most single men, so-called birds of passage, sent remittance back to their families in Italy and then returned to Italy.
Immigration began to increase during the 1880s, when more than twice as many Italians immigrated than had in the five previous decades combined.[5][6] Continuing from 1880 to 1914, the greatest surge of immigration brought more than 4 million Italians to the United States.[5][6] The largest number of this wave came from Southern Italy, which at that time was largely agricultural and where much of the populace had been impoverished by centuries of foreign rule and heavy tax burdens.[7][8] This period of large-scale immigration ended abruptly with the onset of World War I in August 1914. In the 1920s, 455,315 immigrants arrived.[9] They came under the terms of the new quota-based immigration restrictions created by the Immigration Act of 1924.[10] Italian-Americans had a significant influence on American society and culture, making contributions to visual arts, literature, cuisine, politics, sports, and music.[11]
History
[edit]Before 1880
[edit]Italians in the United States before 1880 included a number of explorers, starting with Christopher Columbus, and a few small settlements.[12]
Age of Discovery and early settlement
[edit]
Italian[13] navigators and explorers played a key role in the exploration and settlement of the Americas by Europeans. Genoese explorer Christopher Columbus (Italian: Cristoforo Colombo [kriˈstɔːforo koˈlombo]) completed four voyages across the Atlantic Ocean for the Catholic monarchs of Spain, opening the way for the widespread European exploration and colonization of the Americas.
Another Italian, John Cabot (Italian: Giovanni Caboto [dʒoˈvanni kaˈbɔːto]), together with his son Sebastian, explored the eastern seaboard of North America for Henry VII in the early 16th century. In 1524, the Florentine explorer Giovanni da Verrazzano (Italian: [dʒoˈvanni da (v)verratˈtsaːno]) was the first European to explore the Atlantic coast of North America between Florida and New Brunswick in 1524.[14] The Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci (Italian: [ameˈriːɡo veˈsputtʃi]) first demonstrated in about 1501 that the New World was not Asia as initially conjectured but a different continent (America is named after him).[15]
A number of Italian navigators and explorers in the employ of Spain and France were involved in exploring and mapping their territories and in establishing settlements, but their work did not lead to the permanent presence of Italians in America. In 1539, Marco da Nizza explored the territory that later became the states of Arizona and New Mexico.



The first Italian to be registered as residing in the area corresponding to the current United States was Pietro Cesare Alberti,[19] commonly regarded as the first Italian American. Alberti was a Venetian seaman who, in 1635, settled in the Dutch colony of New Amsterdam, which would eventually become New York City.
A small wave of Protestants, known as Waldensians, immigrated during the 17th century. They were of French and northern Italian heritage (specifically Piedmontese), The first Waldensians began arriving around 1640, with the majority coming between 1654 and 1663.[20] They spread out across what was then called New Netherland and what would become New York, New Jersey, and the Lower Delaware River regions. The total American Waldensian population that immigrated to New Netherland is currently unknown; however, a 1671 Dutch record indicates that in 1656 alone the Duchy of Savoy near Turin, Italy, had exiled 300 Waldensians because of their Protestant faith.
Enrico Tonti (Henri de Tonti), together with the French explorer René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle, explored the Great Lakes region. De Tonti founded the first European settlement in Illinois in 1679 and in Arkansas in 1683, known as Poste de Arkansea, making him "The Father of Arkansas."[17][18] With LaSalle, he co-founded New Orleans and was governor of the Louisiana Territory for the next 20 years. His brother Alphonse de Tonty (Alfonso de Tonti), with French explorer Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac, was the co-founder of Detroit in 1701, and was its acting colonial governor for 12 years.
Spain and France were Catholic countries and sent many missionaries to convert the native American population. Included among these missionaries were numerous Italians. In 1519–25, Alessandro Geraldini was the first Catholic bishop in the Americas, at Santo Domingo. Father François-Joseph Bressani (Francesco Giuseppe Bressani) labored among the Algonquin and Huron peoples in the early 17th century. The southwest and California were explored and mapped by Italian Jesuit priest Eusebio Kino (Chino) in the late 17th and early 18th centuries. His statue, commissioned by the state of Arizona, is displayed in the United States Capitol Visitor Center.
The Taliaferro family (originally Tagliaferro), believed to have roots in Venice, was one of the First Families to settle Virginia. The Wythe House, a historic Georgian home built in Williamsburg, Virginia, in 1754, was designed by architect Richard Taliaferro for his son-in-law, American Founding Father George Wythe, who married Richard's daughter Elizabeth Taliaferro. The elder Taliaferro designed much of Colonial Williamsburg, including the Governor's Palace, the Capitol of the Colony of Virginia, and the President's House at the College of William & Mary.[21]
Francesco Maria de Reggio, an Italian nobleman of the House of Este who served under the French as François Marie, Chevalier de Reggio, came to Louisiana in 1747 where King Louis XV appointed him Captain General of French Louisiana, until 1763.[22] Scion of the de Reggios, a Louisiana Creole first family of St. Bernard Parish, Louisiana, Francesco Maria's granddaughter Hélène Judith de Reggio would give birth to famed Confederate General P. G. T. Beauregard.[23]
A colonial merchant, Francis Ferrari of Genoa, was naturalized as a citizen of Rhode Island in 1752.[24] He died in 1753, and in his will speaks of Genoa, his ownership of three ships, a cargo of wine, and his wife Mary,[25] who went on to own one of the oldest coffee houses in America, the Merchant Coffee House of New York on Wall Street at Water Street. Her Merchant Coffee House moved across Wall Street in 1772, retaining the same name and patronage.[26]
Today, the descendants of the Alberti-Burtis, Taliaferro, Reggio, and other early families are found all across the United States.[27]
1776 to 1880
[edit]This period saw a small stream of new arrivals from Italy. Some brought skills in agriculture and the making of glass, silk and wine, while others brought skills as musicians.[28]

In 1773–1785, Filippo Mazzei, a physician, philosopher, diplomat, promoter of liberty, and author, was a close friend and confidant of Thomas Jefferson. He published a pamphlet containing the phrase, "All men are by nature equally free and independent,"[29] which Jefferson incorporated essentially intact into the Declaration of Independence.
Italian Americans served in the American Revolutionary War both as soldiers and officers. Francesco Vigo aided the colonial forces of George Rogers Clark by serving as one of the foremost financiers of the Revolution in the frontier Northwest. Later, he was a co-founder of Vincennes University in Indiana.
After American independence, numerous political refugees arrived, most notably Giuseppe Avezzana, Alessandro Gavazzi, Silvio Pellico, Federico Confalonieri, and Eleuterio Felice Foresti. Giuseppe Garibaldi resided in the United States in 1850–51. At the invitation of Thomas Jefferson, Carlo Bellini became the first professor of modern languages at the College of William & Mary, in the years 1779–1803.[30][31]
In 1801, Philip Trajetta (Filippo Traetta) established the nation's first conservatory of music in Boston, where, in the first half of the century, organist Charles Nolcini and conductor Louis Ostinelli were also active.[32] In 1805, Thomas Jefferson recruited a group of musicians from Sicily to form a military band, later to become the nucleus of the U.S. Marine Band. The musicians included the young Venerando Pulizzi, who became the first Italian director of the band and served in this capacity from 1816 to 1827.[33] Francesco Maria Scala, an Italian-born naturalized American citizen, was one of the most important and influential directors of the U.S. Marine Band, from 1855 to 1871, and was credited with the instrumental organization the band still maintains. Joseph Lucchesi, the third Italian leader of the U.S. Marine Band, served from 1844 to 1846.[34] The first opera house in the country opened in 1833 in New York through the efforts of Lorenzo Da Ponte, Mozart's former librettist, who had immigrated to America and had become the first professor of Italian at Columbia College in 1825.

During this period, Italian explorers continued to be active in the West. In 1789–91, Alessandro Malaspina mapped much of the west coast of the Americas, from Cape Horn to the Gulf of Alaska. In 1822–23, the headwater region of the Mississippi was explored by Giacomo Beltrami in the territory that was later to become Minnesota, which named a county in his honor.
Joseph Rosati was named the first Catholic bishop of St. Louis in 1824. In 1830–64, Samuel Mazzuchelli, a missionary and expert in Indian languages, ministered to European colonists and Native Americans in Wisconsin and Iowa for 34 years and, after his death, was declared Venerable by the Catholic Church. Father Charles Constantine Pise, a Jesuit, served as Chaplain of the Senate from 1832 to 1833,[35][36] the only Catholic priest ever chosen to serve in this capacity.
In 1833, Lorenzo Da Ponte, formerly Mozart's librettist and a naturalized U.S. citizen, founded the first opera house in the United States, the Italian Opera House in New York City, which was the predecessor of the New York Academy of Music and of the New York Metropolitan Opera. Missionaries of the Jesuit and Franciscan orders were active in many parts of America. Italian Jesuits founded numerous missions, schools, and two colleges in the west. Giovanni Nobili founded the Santa Clara College (now Santa Clara University) in 1851. The St. Ignatius Academy (now University of San Francisco) was established by Anthony Maraschi in 1855. The Italian Jesuits also laid the foundation for the winemaking industry that would later flourish in California. In the east, the Italian Franciscans founded hospitals, orphanages, schools, and St. Bonaventure College (now St. Bonaventure University), established by Pamfilo da Magliano in 1858.
In 1837, John Phinizy (Finizzi) became the mayor of Augusta, Georgia. Samuel Wilds Trotti of South Carolina was the first Italian American to serve in the U.S. Congress (a partial term, from December 17, 1842, to March 3, 1843).[37] In 1849, Francesco de Casale began publishing the Italian American newspaper L'Eco d'Italia in New York, the first of many to eventually follow. In 1848, Francis Ramacciotti, piano string inventor and manufacturer, immigrated to the U.S. from Tuscany.
Beginning in 1863, Italian immigrants were one of the principal groups of unskilled laborers, along with the Irish, that built the Transcontinental Railroad west from Omaha, Nebraska.[38] In 1866, Constantino Brumidi completed the frescoed interior of the United States Capitol dome in Washington, D.C., and spent the rest of his life executing still other artworks to beautify the Capitol. The first Columbus Day celebration was organized by Italian Americans in New York City on October 12, 1866.[39]

Giovanni Martino or Giovanni Martini, also known as John Martin, was a soldier and trumpeter who served both in Italy with Giuseppe Garibaldi and in the United States Army, famously in the 7th Cavalry Regiment under George Armstrong Custer. He was the only survivor from Custer's company at the Battle of the Little Bighorn.

An immigrant, Antonio Meucci, brought with him a concept for the telephone. He is credited by many researchers with being the first to demonstrate the principle of the telephone in a patent caveat he submitted to the U.S. Patent Office in 1871; however, considerable controversy existed relative to the priority of invention, with Alexander Graham Bell also being accorded this distinction. (In 2002, the U.S. House of Representatives passed a resolution on Meucci (H.R. 269) declaring that "his work in the invention of the telephone should be acknowledged.")[40]
During this period, Italian Americans established a number of institutions of higher learning. Las Vegas College (now Regis University) was established by a group of exiled Italian Jesuits in 1877 in Las Vegas, New Mexico. The Jesuit Giuseppe Cataldo, founded Gonzaga College (now Gonzaga University) in Spokane, Washington in 1887. In 1886, Rabbi Sabato Morais, a Jewish Italian immigrant, was one of the founders and first president of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America in New York. Also during this period, there was a growing presence of Italian Americans in higher education. Vincenzo Botta was a distinguished professor of Italian at New York University from 1856 to 1894,[41] and Gaetano Lanza was a professor of mechanical engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology for over 40 years, beginning in 1871.[42]
Anthony Ghio became the mayor of Texarkana, Texas in 1880. Francis B. Spinola, the first Italian American to be elected to the United States House of Representatives, served as a representative from New York from 1887 to 1891. He also served as a general in the Union Army during the American Civil War. Following the war, Spinola was a banker and insurance agent and became an influential figure among the rapidly growing Italian immigrant community in the New York City area. He was again a member of the State Assembly (New York Co., 16th D.) in 1877, 1881, and 1883.
Civil War
[edit]
Between 5,000 and 10,000 Italian Americans fought in the American Civil War.[43] The great majority of Italian Americans, for both demographic and ideological reasons, served in the Union Army (including generals Edward Ferrero and Francis B. Spinola). Some Americans of Italian descent from the disbanded Army of the Two Sicilies, which was defeated by Giuseppe Garibaldi after the Expedition of the Thousand, fought in the Confederate Army. They included Confederate generals William B. Taliaferro (of English-American and Anglo-Italian descent) and P. G. T. Beauregard.[23] Six Italian Americans received the Medal of Honor during the war, including Colonel Luigi Palma di Cesnola, who later became the first director of the Metropolitan Museum of Arts in New York (1879–1904).
The Garibaldi Guard recruited volunteers for the Union Army from Italy and other European countries to form the 39th New York Infantry.[44] At the outbreak of the American Civil War, Giuseppe Garibaldi was a very popular figure. The 39th New York Volunteer Infantry Regiment, with 350 Italian members, was nicknamed Garibaldi Guard in his honor. The unit wore red shirts and bersaglieri plumes. They carried with them both a Union Flag and an Italian flag with the words Dio e popolo, meaning "God and people."[45] In 1861, Garibaldi himself volunteered his services to President Abraham Lincoln. Garibaldi was offered a major general's commission in the U.S. Army through the letter from Secretary of State William H. Seward to H. S. Sanford, the U.S. minister at Brussels, July 17, 1861.[46]
The great Italian diaspora (1880–1914)
[edit]




From 1880 to 1914, 13 million Italians migrated out of Italy,[47] making Italy the scene of one of the largest voluntary emigrations in recorded world history.[48] During this period of mass migration, 4 million Italians arrived in the United States, 3 million of them between 1900 and 1914.[49] They came for the most part from southern Italy (the regions of Abruzzo, Campania, Apulia, Basilicata, and Calabria) and from the island of Sicily.[50] Most planned to stay a few years, then take their earnings and return home. According to historian Thomas J. Archdeacon, 46 percent of the Italians who entered the United States between 1899 and 1924 permanently returned home.[51]
Padrone system
[edit]Immigrants without industrial skills found employment in low-wage manual labor jobs. Instead of finding jobs on their own, most used the padrone system whereby Italian middlemen (padroni) found jobs for groups of men and controlled their wages, transportation, and living conditions for a fee.[52][53]
According to historian Alfred T. Banfield:
- Criticized by many as slave traders who preyed upon poor, bewildered peasants, the "padroni" often served as travel agents, with fees reimbursed from paychecks, as landlords who rented out shacks and boxcars, and as storekeepers who extended exorbitant credit to their Italian laborer clientele. Despite such abuse, not all "padroni" were dastardly and most Italian immigrants reached out to their "padroni" for economic salvation, considering them either as godsends or necessary evils. The Italians whom the "padroni" brought to Maine generally had no intention of settling there, and most were sojourners who either returned to Italy or moved on to another job somewhere else. Nevertheless, thousands of Italians did settle in Maine, creating "Little Italies" in Portland, Millinocket, Rumford, and other towns where the "padroni" remained as strong shaping forces in the new communities.[54]
Push and pull
[edit]In terms of the push-pull model of immigration,[55] America provided the pull factor by the prospect of jobs that unskilled and uneducated Italian peasant farmers could do. Peasant farmers accustomed to hard work in the Mezzogiorno, for example, took jobs building railroads and constructing buildings, while others took factory jobs that required little or no skill.[56]
The push from southern Italy
[edit]The push factor came primarily from the harsh economic conditions in southern Italy. Major factors that contributed to the large exodus included political and social unrest, the weak agricultural economy of the South modeled on the outdated latifundist system dating back to the feudal period, a high tax burden, soil exhaustion and erosion, and military conscription lasting seven years.[8] The poor economic situation in the 19th century became untenable for many sharecroppers, tenant farmers, and small business and land owners. Multitudes chose to emigrate rather than face the prospect of a deepening poverty. A large number of these were attracted to the United States, which at the time was actively recruiting workers from Italy and elsewhere to fill the labor shortage that existed in the years following the Civil War. Often the father and older sons would go first, leaving the mother and the rest of the family behind until the male members could afford their passage.
The pull of high wages
[edit]By far the strongest "pull" factor was money.[57] Migrants expected to make large sums in a few years of work, enabling them to live much better when they returned home, especially by buying a farm. Real life was never so golden: the Italians earned well below average rates. Their weekly earnings in manufacturing and mining in 1909 came to $9.61, compared to $13.63 for German immigrants and $11.06 for Poles.[58] The result was a sense of alienation from most of American culture and a lack of interest in learning English or otherwise assimilating.[59] Not many women came, but those who did became devoted to traditional Italian religious customs.[60] When the World War I broke out, European migrants could not go home. Wages shot up, and the Italians benefited greatly. Most decided to stay permanently, and they flourished in the 1920s.[61]
"Little Italys"
[edit]Many sought housing in the older sections of the large Northeastern cities—districts that became known as "Little Italys." Such housing was frequently in overcrowded, substandard tenements, which were often dimly lit and had poor heating and ventilation. Tuberculosis and other communicable diseases were a constant health threat for the immigrant families that were compelled by economic circumstances to live in these dwellings. Other immigrant families lived in single-family abodes, which was more typical in areas outside of the enclaves of the large northeastern cities and other parts of the country as well.
"Birds of passage" return to Italy
[edit]An estimated 49 percent of Italians who migrated to the Americas between 1905 (when return migration statistics began) and 1920 did not remain in the United States.[62] These so-called birds of passage intended to stay in the United States for only a limited time, followed by a return to Italy with enough in savings to reestablish themselves there. While many did return to Italy, others chose to stay or were prevented from returning by the outbreak of World War I in 1914.[63]
Employment opportunities
[edit]The Italian male immigrants in the Little Italys were most often employed in manual labor and were heavily involved in public works, such as the construction of roads, railroad tracks, sewers, subways, bridges, and the first skyscrapers in the northeastern cities. As early as 1890, it was estimated that around 90 percent of New York City's and 99 percent of Chicago's public works employees were Italians.[64] The women most frequently worked as seamstresses in the garment industry or in their homes. Many established small businesses in the Little Italys to satisfy the day-to-day needs of fellow immigrants.
A New York Times article from 1895 provides a glimpse into the status of Italian immigration at the turn of the century:
- Of the half million Italians that are in the United States, about 100,000 live in the city, and including those who live in Brooklyn, Jersey City, and the other suburbs the total number in the vicinity is estimated at about 160,000. After learning our ways they become good, industrious citizens.[65]
The New York Times in May 1896 sent its reporters to characterize the Little Italy/Mulberry neighborhood:
- They are laborers; toilers in all grades of manual work; they are artisans, they are junkmen, and here, too, dwell the rag pickers. . . . There is a monster colony of Italians who might be termed the commercial or shop keeping community of the Latins. Here are all sorts of stores, pensions, groceries, fruit emporiums, tailors, shoemakers, wine merchants, importers, musical instrument makers. . . . There are notaries, lawyers, doctors, apothecaries, undertakers. . . . There are more bankers among the Italians than among any other foreigners except the Germans in the city.[66]
The masses of Italian immigrants that entered the United States (1890–1900) posed a change in the labor market, prompting Fr. Michael J. Henry to write a letter in October 1900 to the Bishop John J. Clancy of Sligo, Ireland, warning[67]
- [that unskilled young Irishmen] would have to enter into competition with their pick-axe and shovel against other nationalities—Italians, Poles etc. to eke out bare existence. The Italians are more economic, can live on poor fare and consequently can afford to work for less wages than the ordinary Irishman.
The Brooklyn Eagle, in a 1900 article, addressed the same reality:[67]
- The day of the Irish hod-carrier has long been past. . . . But it is the Italian now that does the work. Then came the Italian carpenter and finally the mason and the bricklayer.
In spite of the economic hardship of the immigrants, civil and social life flourished in the Italian American neighborhoods of the large northeastern cities. Italian theater, band concerts, choral recitals, puppet shows, mutual aid societies, and social clubs were available to the immigrants.[68] An important event, the festa, became for many an important connection to the traditions of their ancestral villages in Italy. The festa involved an elaborate procession through the streets in honor of a patron saint or the Virgin Mary in which a large statue was carried by a team of men, with musicians marching behind. Followed by food, fireworks, and general merriment, the festa became an important occasion that helped give the immigrants a sense of unity and common identity.
Pull of California and the South
[edit]The destinations of many of the Italian immigrants were not only the large cities of the East Coast, but also more remote regions of the country, such as Florida and California. They were drawn there by opportunities in agriculture, fishing, mining, railroad construction, lumbering, and other activities under way at the time. Often the immigrants contracted to work in these areas of the country as a condition for payment of their passage. It was not uncommon, especially in the South, for the immigrants to be subjected to economic exploitation, hostility, and sometimes even violence.[69] The Italian laborers who went to these areas were in many cases later joined by wives and children, which resulted in the establishment of permanent Italian American settlements in diverse parts of the country. A number of towns, such as Roseto, Pennsylvania,[70] Tontitown, Arkansas,[71] and Valdese, North Carolina,[72] were founded by Italian immigrants during this era.
Pull of business opportunities
[edit]A number of major business ventures were founded by Italian Americans. Amadeo Giannini originated the concept of branch banking to serve the Italian American community in San Francisco. He founded the Bank of Italy, which later became the Bank of America. His bank also provided financing to the film industry developing on the West Coast at the time, including the financing for Walt Disney's Snow White, the first full-length animated motion picture to be made in the United States. Other companies founded by Italian Americans—such as Ghirardelli Chocolate Company, Progresso, Planters Peanuts, Contadina, Chef Boyardee, Italian Swiss Colony wines, and Jacuzzi—became nationally known brand names in time. An Italian immigrant, Italo Marciony (Marcioni), is credited with inventing the earliest version of an ice cream cone in 1898. Another Italian immigrant, Giuseppe Bellanca, brought with him in 1912 an advanced aircraft design, which he began producing. One of Bellanca's planes, piloted by Cesare Sabelli and George Pond, made one of the first nonstop trans-Atlantic flights in 1934.[73] Several families, including the Grucci, Zambelli, and Vitale families, brought with them expertise in fireworks displays, and their preeminence in this field has continued to the present day.
Pull of artistic opportunity
[edit]Following in the footsteps of Constantino Brumidi, others were commissioned to help create Washington's impressive monuments. An Italian immigrant, Attilio Piccirilli, and his five brothers carved the Lincoln Memorial, which they began in 1911 and completed in 1922. Italian construction workers helped build Washington's Union Station, considered one of the most beautiful stations in the country. Work on Union Station began in 1905 and was completed in 1908. The six statues that decorate the station's facade were carved by Andrew Bernasconi between 1909 and 1911. Two Italian American master stone carvers, Roger Morigi and Vincent Palumbo, spent decades creating the sculptural works that embellish Washington National Cathedral.[74]
Italian conductors contributed to the early success of the Metropolitan Opera of New York (founded in 1880), but it was the arrival of impresario Giulio Gatti-Casazza in 1908, who brought with him conductor Arturo Toscanini, that made the Met internationally known. Many Italian operatic singers and conductors were invited to perform for American audiences, most notably, tenor Enrico Caruso. The premiere of the opera La Fanciulla del West on December 10, 1910, with conductor Toscanini and tenor Caruso, and with the composer Giacomo Puccini in attendance, was a major international success as well as an historic event for the entire Italian American community.[75] Francesco Fanciulli (1853–1915) succeeded John Philip Sousa as the director of United States Marine Band, serving in this capacity from 1892 to 1897.[76]
Italian Americans became involved in entertainment and sports. Rudolph Valentino was one of the first great film icons. Dixieland jazz music had a number of important Italian American innovators, the most famous being Nick LaRocca of New Orleans, whose quintet made the first jazz recording in 1917. The first Italian American professional baseball player, Ping Bodie (Francesco Pizzoli), began playing for the Chicago White Sox in 1912. Ralph DePalma won the Indianapolis 500 in 1915.
Public roles
[edit]Italian Americans became increasingly involved in politics, government, and the labor movement. Andrew Longino was elected governor of Mississippi in 1900. Charles Bonaparte was secretary of the Navy and later attorney general in the Theodore Roosevelt administration, and he founded the Federal Bureau of Investigation.[77]

Joe Petrosino was a New York City Police Department (NYPD) officer who was a pioneer in the fight against organized crime. Crime-fighting techniques that Petrosino pioneered are still practiced by law enforcement agencies. Salvatore A. Cotillo was the first Italian American to serve in both houses of the New York State Legislature and the first who served as Justice of the New York State Supreme Court.
Fiorello La Guardia was elected to Congress from New York in 1916. He served as mayor of New York City from 1934 to 1946 as a Republican. A 1993 survey of historians, political scientists and urban experts conducted by Melvin G. Holli of the University of Illinois at Chicago saw La Guardia ranked as the best American big-city mayor to serve between the years 1820 and 1993.[78]
Numerous Italian Americans were at the forefront in fighting for worker's rights in industries such as the mining, textiles, and garment industries, the most notable among these being Arturo Giovannitti, Carlo Tresca, and Joseph Ettor.[79][80]
Society for the Protection of Italian Immigrants
[edit]An American teacher who had studied in Italy, Sarah Wool Moore, was so concerned with grifters luring immigrants into rooming houses or employment contracts in which the bosses got kickbacks that she pressed for the founding of the Society for the Protection of Italian Immigrants (often called the Society for Italian Immigrants). The society published lists of approved living quarters and employers. Later, the organization began establishing schools in work camps to help adult immigrants learn English.[81][82] Wool Moore and the society began organizing schools in the labor camps that employed Italian workers on various dam and quarry projects in Pennsylvania and New York. The schools focused on teaching phrases that workers needed in their everyday tasks.[83] Because of its success in helping immigrants, the society received a commendation from the commissioner of emigration for the Italian Ministry of Foreign Affairs in 1907.[84]
World War I and interwar period
[edit]
The United States entered World War I in 1917. The Italian American community wholeheartedly supported the war effort and its young men, both American born and Italian born, enlisted in large numbers in the American Army.[85] It was estimated that during the two years of the war (1917–18) Italian American servicemen made up approximately 12 percent of the total American forces, a disproportionately high percentage of the total.[86] An Italian-born American infantryman, Michael Valente, was awarded the Medal of Honor for his service. Another 103 Italian Americans (83 Italian born) were awarded the Distinguished Service Cross, the second highest decoration.[87] Italian Americans also accounted for more than 10 percent of war casualties World War I, despite making up less than 4 percent of the U.S. population.[88]
Restricted immigration
[edit]The war, together with the restrictive Emergency Quota Act of 1921 and Immigration Act of 1924, heavily curtailed Italian immigration. Total annual immigration was capped at 357,000 in 1921 and lowered to 150,000 in 1924. Quotas were allotted on a national basis in proportion to a nationality's existing share of the population. The National Origins Formula, which sought to preserve the existing demographic makeup of the United States and generally favored northwestern European immigration, computed Italians to be the fifth-largest national origin of the U.S. population in 1920, to be assigned 3.87 percent of annual quota immigrant spots.[89][90] Despite implementation of the quota, the inflow of Italian immigrants remained between 6 or 7 percent of all immigrants.[91][92][93] And when the restrictive quota system was abolished by the Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965, Italians had already grown to be the second largest immigrant group in America, with 5,067,717 immigrants from Italy admitted between 1820 and 1966—constituting 12 percent of all immigrants to the United States—more than from Great Britain (4,711,711) and from Ireland (4,706,854).[5]




Employment and unemployment
[edit]In the interwar period, jobs as policemen, firemen, and civil servants became increasingly available to Italian Americans. Others found employment as plumbers, electricians, mechanics, and carpenters. Women found jobs as civil servants, secretaries, dressmakers, and clerks. With better-paying jobs, Italian Americans moved to more affluent neighborhoods outside of the Italian enclaves. The Great Depression (1929–1939) had a major impact on the Italian American community and temporarily reversed some of the earlier gains made. Many unemployed men and some women found jobs on President Franklin Roosevelt's New Deal work programs, such as the Works Progress Administration and the Civilian Conservation Corp.
Politics
[edit]By 1920, numerous Little Italys had stabilized and grown considerably more prosperous as workers were able to obtain higher-paying jobs, often in skilled trades. In the 1920s and 1930s, Italian Americans contributed significantly to American life and culture, politics, music, film, the arts, sports, the labor movement, and business.
In politics, Al Smith (Anglicized form of the Italian surname Ferraro) became the first governor of New York of Italian ancestry—although the media characterized him as an Irish. He was the first Catholic to receive a major party presidential nomination, as Democratic candidate for president in 1928. He lost Protestant strongholds in the South but energized the Democratic vote in immigrant centers across the entire North. Angelo Rossi was mayor of San Francisco from 1931 to 1944. In 1933–34, Ferdinand Pecora led a Senate investigation of the Wall Street Crash of 1929, which exposed major financial abuses, and spurred Congress to rein in the banking industry.[94] Pecora's work later inspired a play, The Reckoning: Pecora for the Public.[95] Liberal leader Fiorello La Guardia served as Republican and Fusion mayor of New York City from 1934 to 1945. On the far left, Vito Marcantonio was first elected to Congress in 1934 from New York.[96] Robert Maestri was mayor of New Orleans from 1936 to 1946.[97]
Music, Hollywood, and arts
[edit]The Metropolitan Opera continued to flourish under the leadership of Giulio Gatti-Casazza, whose tenure continued until 1935. Rosa Ponselle and Dusolina Giannini, daughters of Italian immigrants, performed regularly at the Metropolitan Opera and became internationally known. Arturo Toscanini returned in the United States as the main conductor of the New York Philharmonic Orchestra (1926–1936) and introduced many Americans to classical music through his NBC Symphony Orchestra radio broadcasts (1937–1954). Ruggiero Ricci, a child prodigy born of Italian immigrant parents, gave his first public performance in 1928 at the age of 10 and had a long international career as a concert violinist.
Popular singers of the period included Russ Columbo, who established a new singing style that influenced Frank Sinatra and other singers that followed. On Broadway, Harry Warren (Salvatore Guaragna) wrote the music for 42nd Street, and received three Academy Awards for his compositions. Other Italian American musicians and performers, such as Jimmy Durante, who later achieved fame in movies and television, were active in vaudeville. Guy Lombardo formed a popular dance band, which played annually on New Year's Eve in New York City's Times Square.
The film industry of this era included Frank Capra, who received three Academy Awards for directing and Frank Borzage, who received two Academy Awards for directing. Italian American cartoonists were responsible for some of the most popular animated characters: Donald Duck was created by Al Taliaferro, Woody Woodpecker was a creation of Walter Lantz (Lanza), Casper the Friendly Ghost was co-created by Joseph Oriolo, and Tom and Jerry were co-created by Joseph Barbera. The voice of Snow White was provided by Adriana Caselotti, a 21-year-old soprano.
In public art, Luigi Del Bianco was the chief stone carver at Mount Rushmore from 1933 to 1940.[98] Simon Rodia, an immigrant construction worker, built the Watts Towers over a period of 33 years, from 1921 to 1954.
Sports
[edit]
In sports, Gene Sarazen (Eugenio Saraceni) won both the Professional Golf Association and U.S. Open Tournaments in 1922. Pete DePaolo won the Indianapolis 500 in 1925. Tony Lazzeri and Frank Crosetti started playing for the New York Yankees in 1926. Tony Canzoneri won the lightweight boxing championship in 1930, and Rocky Marciano is the only undefeated heavyweight champion in history. Lou Little (Luigi Piccolo) began coaching the Columbia University football team in 1930. Joe DiMaggio, who was destined to become one of the most famous players in baseball history, began playing for the New York Yankees in 1936. Hank Luisetti was a three time All-American basketball player at Stanford University from 1936 to 1940. Louis Zamperini, the American distance runner, competed in the 1936 Olympics and later became the subject of the bestselling book Unbroken by Laura Hillenbrand, published in 2010 and a 2014 movie of the same title.
Economy
[edit]Italian American businessmen specialized in growing and selling fresh fruits and vegetables, which were cultivated on small tracts of land in the suburban parts of many cities.[99][100] The produce was trucked into the nearby cities and often sold directly to the consumer through farmers' markets. In California, the DiGiorgio Corporation was founded, which grew to become a national supplier of fresh produce in the United States. Italian Americans in California were leading growers of grapes and producers of wine. Many well known wine brands, such as Mondavi, Carlo Rossi, Petri, Sebastiani, and Gallo emerged from these early enterprises. Italian American companies were major importers of Italian wines, processed foods, textiles, marble, and manufactured goods.[101]
Italian Americans continued their significant involvement in the labor movement during this period. Well-known labor organizers included Carlo Tresca, Luigi Antonini, James Petrillo, and Angela Bambace.[102]
Organized crime
[edit]Italian organized crime emerged in the late 19th century in New York as an offshoot of the Sicilian Mafia. It evolved into a separate entity partially independent of the original Mafia in Sicily, and it eventually encompassed or absorbed other Italian gangsters and crime groups (such as the American Camorra) active in the United States and Canada that were not of Sicilian origin.[103][104]
Al Capone was the nation's most infamous organized crime boss in the 1920s. He attained notoriety during the Prohibition era as the co-founder and boss of the Chicago Outfit. Their most famous single crime was the Saint Valentine's Day Massacre of 1929, when Capone's men, dressed as policemen, massacred seven members of a rival gang. Capone's seven-year reign as a crime boss ended when he went to federal prison at the age of 33. Some ethnic Americans viewed him a hero, seeing him as the epitome of self-made success, a defender of American ideals, a family man, and a philanthropist. His stature helped them justify their own violations of the prohibition laws against liquor.[105]
Mussolini for and against
[edit]Benito Mussolini's Fascist regime in Italy sought to build a base of popular support in the United States, focusing on the Italian community. His supporters far outnumbered his opponents, both inside the Italian American community and among all Catholics, as well as among the wider American leadership.[106][107])
According to Stefano Luconi, in the 1920s and 1930s "numerous Italian Americans became US citizens, registered for the vote, and cast their ballots in order to lobby Congress and the Presidency on behalf of fascism and to support Mussolini's goals in foreign policy."[108]
According to Fraser Ottanelli, Rome also worked to enhance Italy's reputation through a series of highly visible moves. They included participating in the Century of Progress (1933–1934) world fair in Chicago; supporting Italo Balbo's dramatic transatlantic flights; and donating a statue to Chicago. A small minority of Italian Americans who fervently opposed fascism did not support Rome's moves. They promoted an unsuccessful measure in Congress that condemned Italy's meddling in U.S. internal affairs and called for the revocation of U.S. citizenship from people who swore allegiance to Mussolini. Alberto Tarchiani, Italy's first ambassador to the United States after World War II, requested the removal of any displays that honored the fascist regime, but with little success. Many memorials remain in the 21st century.[109]
World War II
[edit]



As a member of the Axis powers, fascist Italy declared war on the United States on December 11, 1941, four days after Japan attacked Pearl Harbor. As a consequence, Executive Order 9066 called for the compulsory relocation of more than 10,000 Italian Americans and restricted the movements of more than 600,000 Italian Americans nationwide.[113] They were targeted despite a lack of evidence that Italians were conducting spy or sabotage operations in the United States.[114][115][116][117]
Although the great majority of Italian Americans admired Mussolini in the 1930s, very few if any demonstrated any desire to transfer fascist ideology to America.[88] When Italy entered the war on the side of Nazi Germany in 1940, "most Italian Americans distanced themselves from Fascism."[118]
Anti-fascist Italian expatriates in the United States founded the Mazzini Society in Northampton, Massachusetts, in September 1939 to work toward ending fascist rule in Italy. These political refugees from Mussolini's regime disagreed among themselves whether to ally with communists and anarchists or to exclude them. The Mazzini Society joined with other anti-fascist Italian expatriates in the Americas at a conference in Montevideo, Uruguay in 1942. They unsuccessfully promoted one of their members, Carlo Sforza, to become the post-fascist leader of a republican Italy. The Mazzini Society dispersed after the fall of Mussolini as most of its members returned to Italy.[119][120]
Between 750,000 and 1.5 million people of Italian descent are thought to have served in the U.S. armed forces during the war, about 10 percent of the total, and 14 Italian Americans received the Medal of Honor for their service.[121][122] Among these was Sgt. John Basilone, one of the most decorated and famous servicemen in World War II, who was later featured in the HBO series The Pacific. Army Ranger Colonel Henry Mucci led one of the most successful rescue missions in U.S. history—the 1945 mission that freed 511 survivors of the Bataan Death March from a Japanese prison camp in the Philippines. In the air, Capt. Don Gentile became one of the war's leading aces, with 25 German planes destroyed. Film director, producer, and writer Frank Capra made a series of wartime documentaries known as Why We Fight, for which he received the U.S. Distinguished Service Medal in 1945 and the Order of the British Empire Medal in 1962.
Biagio (Max) Corvo, an agent of the U.S. Office of Strategic Services (OSS), drew up plans for the invasion of Sicily and organized operations behind enemy lines in the Mediterranean region during World War II. He led the Italian Secret Intelligence branch of the OSS, which was able to smuggle hundreds of agents behind enemy lines, supply Italian partisan fighters, and maintain a liaison between Allied field commands and Italy's first post-fascist Government. Corvo was awarded the Legion of Merit for his efforts during the war.[123] Other Italian Americans such as Edward E. Boccia ≤https://ghostarmy.org/roster/Edward-Eugene-Boccia/≥ served in the Ghost Army ≤https://ghostarmy.org/≥. The Headquarters Special Troops and the 3133rd Signal Company Special, composed of visual arts students, architects, designers, and other creatives, carried out 25 battlefield deceptions in France, Luxembourg, Belgium, Germany, and Italy and were all awarded the Congressional Medal of Honor.
The work of Enrico Fermi was crucial in developing the atom bomb. Fermi, a Nobel Prize laureate nuclear physicist, who immigrated to the United States from Italy in 1938, led a research team at the University of Chicago that achieved the world's first sustained nuclear chain reaction, which clearly demonstrated the feasibility of an atom bomb. Fermi later became a key member of the team at Los Alamos Laboratory that developed the first atom bomb. He was subsequently joined at Los Alamos by Emilio Segrè, one of his colleagues from Italy, who was also destined to receive the Nobel Prize in physics.
Three United States World War II destroyers were named after Italian Americans: USS Basilone (DD-824) was named for Sgt. John Basilone; USS Damato (DD-871) was named for Corporal Anthony P. Damato, who was awarded the Medal of Honor posthumously for his valor during World War II; and USS Gherardi (DD-637) was named for Rear Admiral Bancroft Gherardi, who served during the Mexican–American War and the American Civil War.
World War II ended the mass unemployment and relief programs that characterized the 1930s, opening up new employment opportunities for large numbers of Italian Americans, who significantly contributed to the nation's war effort. Much of the Italian American population was concentrated in urban areas where the new war materiel plants were located. Many Italian American women took war jobs, such as Rose Bonavita, who was recognized by President Franklin D. Roosevelt with a personal letter commending her for her performance as an aircraft riveter. She, together with a number of other women workers, provided the basis of the name, "Rosie the Riveter", which came to symbolize the millions of American women workers in the war industries.[124] Chef Boyardee, the company founded by Ettore Boiardi, was one of the largest suppliers of rations for U.S. and allied forces during World War II. For his contribution to the war effort, Boiardi was awarded a gold star order of excellence from the United States War Department.
Wartime violation of Italian-American civil liberties
[edit]From the onset of the Second World War, and particularly following Pearl Harbor attack, Italian Americans were increasingly placed under suspicion. Groups such as The Los Angeles Council of California Women's Clubs petitioned General John L. DeWitt to place all enemy aliens in concentration camps immediately, and the Young Democratic Club of Los Angeles went a step further, demanding the removal of American-born Italians and Germans—U.S. citizens—from the Pacific Coast.[125] These calls, along with substantial political pressure from Congress, resulted in President Franklin D. Roosevelt issuing Executive Order No. 9066, as well as the Department of Justice classifying unnaturalized Italian Americans as "enemy aliens" under the Alien and Sedition Act. Thousands of Italians were arrested, and hundreds of Italians were interned in military camps, some for up to two years.[126] As many as 600,000 others were required to carry identity cards identifying them as "resident aliens." Thousands more on the West Coast were required to move inland, often losing their homes and businesses in the process. A number of Italian-language newspapers were forced to close.[127] Two books, Una Storia Segreta by Lawrence Di Stasi and Uncivil Liberties by Stephen Fox, as well as a movie, Prisoners Among Us, document these World War II developments.
On November 7, 2000, Bill Clinton signed the Wartime Violation of Italian American Civil Liberties Act.[125][128] This act ordered a comprehensive review by the attorney general of the United States of the treatment of Italian Americans during the Second World War. The findings concluded that
- The freedom of more than 600,000 Italian-born immigrants in the United States and their families was restricted during World War II by government measures that branded them "enemy aliens" and included requirements to carry identification cards, travel restrictions, and seizure of personal property.
- During World War II, more than 10,000 Italian Americans living on the West Coast were forced to leave their homes and prohibited from entering coastal zones. More than 50,000 were subjected to curfews.
- During World War II, thousands of Italian American immigrants were arrested, and hundreds were interned in military camps.
- Hundreds of thousands of Italian Americans performed exemplary service and thousands sacrificed their lives in defense of the United States.
- At the time, Italians were the largest foreign-born group in the United States, and today they are the fifth-largest immigrant group in the United States, numbering approximately 15 million.
- The impact of the wartime experience was devastating to Italian American communities in the United States, and its effects are still being felt.
- A deliberate policy kept these measures from the public during the war. Even today much information is still classified, the full story remains unknown to the public, and it has never been acknowledged in any official capacity by the United States government.
In 2010, California officially issued an apology to the Italian Americans whose civil liberties had been violated.[129]
Post–World War II period
[edit]
Italians continued to immigrate to the United States, and an estimated 600,000 arrived in the decades following the war. Many of the new arrivals had professional training or were skilled in various trades. After the end of World War II, a small number of Istrian Italians and Dalmatian Italians also emigrated to the United States during the Istrian-Dalmatian exodus, leaving their homelands, which were lost by Italy and annexed by Yugoslavia after the Treaty of Peace with Italy, 1947.[131] Notable Istrian-Dalmatian exiles who emigrated to the United States are Mario Andretti and Lidia Bastianich.[132][133]
The post-war period was a time of great social change for Italian Americans. Many aspired to a college education, which became possible for returning veterans through the GI Bill. Since the 1960s, a lot of people left Italy and went to North America (mostly), South America, and Europe. European migration was seasonal and permanent.[134] With better job opportunities and better educated, Italian Americans entered mainstream American life in great numbers. The Italian enclaves were abandoned by many who chose to live in other urban areas and in the suburbs. Many married outside of their ethnic group, most frequently with other ethnic Catholics, but increasingly also with those of diverse religious and ethnic backgrounds.[135][136] According to Dr. Richard D. Alba, director of the Center for Social and Demographic Analysis at the State University of New York at Albany, 8 percent of Americans of Italian descent born before 1920 had mixed ancestry, but 70 percent of them born after 1970 were the children of intermarriage. In 1985, among Americans of Italian descent under the age of 30, 72 percent of men and 64 percent of women married someone with no Italian background.[137] Numerous Italian Americans are people of color, including many people of mixed African-African and white Italian ancestry. Notable Black Italian-Americans include Pittsburgh Steeler running back Franco Harris.[138]
Italian Americans took advantage of the new opportunities that generally became available to all in the post-war decades. They made many significant contributions to American life and culture.

Numerous Italian Americans became involved in politics at the local, state, and national levels in the post-war decades. Those who became U.S. senators included John Pastore of Rhode Island, who was the first Italian American elected to the Senate in 1950; Pete Domenici, who was elected to the U.S. Senate from New Mexico in 1972 and served six terms; Patrick Leahy, who was elected to the U.S. Senate from Vermont in 1974 and served until 2023; and Alfonse D'Amato, who served as U.S. senator from New York from 1981 to 1999. Nancy Pelosi was both the first woman and the first Italian American Speaker of the House. Anthony Celebrezze served for five two-year terms as mayor of Cleveland, from 1953 to 1962 and, in 1962, President John F. Kennedy appointed him as United States Secretary of Health, Education, and Welfare (now the Department of Health and Human Services). Benjamin Civiletti served as the United States Attorney General during the last year and a half of the Carter administration, from 1979 to 1981. Frank Carlucci served as the United States Secretary of Defense from 1987 to 1989 in the administration of President Ronald Reagan.

Scores of Italian Americans became well known singers in the post-war period, including Frank Sinatra, Mario Lanza, Perry Como, Dean Martin, Tony Bennett, Frankie Laine, Bobby Darin, Julius La Rosa, Connie Francis, and Madonna. Italian Americans who hosted popular musical/variety TV shows in the post-war decades included Perry Como (1949–1967), piano virtuoso Liberace (1952–1956), Jimmy Durante (1954–1956), Frank Sinatra (1957–1958), and Dean Martin (1965–1974). Broadway, musical stars included Rose Marie, Carol Lawrence, Anna Maria Alberghetti, Sergio Franchi, Patti LuPone, Ezio Pinza, and Liza Minnelli.
In music composition, Henry Mancini and Bill Conti received numerous Academy Awards for their songs and film scores. Classical and operatic composers John Corigliano, Norman Dello Joio, David Del Tredici, Paul Creston, Dominick Argento, Gian Carlo Menotti, and Donald Martino were honored with Pulitzer Prizes and Grammy Awards.
Numerous Italian Americans became well known in movies, both as actors and directors, and many were Academy Award recipients. Movie directors included Frank Capra, Francis Ford Coppola, Michael Cimino, Vincente Minnelli, Martin Scorsese, and Brian De Palma.
Italian Americans were active in professional sports as players, coaches, and commissioners. Well-known professional baseball coaches in the post-war decades included Yogi Berra, Billy Martin, Tony La Russa, Tommy Lasorda, and Joe Torre. In professional football, Vince Lombardi set the standard of excellence for all coaches to follow. A. Bartlett Giamatti became president of the National Baseball League in 1986 and commissioner of Baseball in 1989. Paul Tagliabue was commissioner of the National Football League from 1989 to 2006.
In college football, Joe Paterno became one of the most successful coaches ever. Seven Italian American players won the Heisman Trophy: Angelo Bertelli of Notre Dame, Alan Ameche of Wisconsin, Gary Beban of UCLA, Joe Bellino of Navy, John Cappelletti of Penn State, Gino Torretta, and Vinny Testaverde of Miami.
In college basketball, a number of Italian Americans became well-known coaches in the post-war decades, including John Calipari, Lou Carnesecca, Rollie Massimino, Rick Pitino, Jim Valvano, Dick Vitale, Tom Izzo, Mike Fratello, Ben Carnevale, and Geno Auriemma.

Italian Americans became nationally known in other diverse sports. Rocky Marciano was the undefeated heavyweight boxing champion from 1952 to 1956; Ken Venturi won both the British and U.S. Open golf championships in 1956; Donna Caponi won the U.S. Women's Open golf championships in 1969 and 1970; Linda Frattianne was the woman's U.S. figure skating champion four years in a row, from 1975 to 1978, and world champion in 1976 and 1978; Willie Mosconi was a 15-time World Billiard champion; Eddie Arcaro was a 5-time Kentucky Derby winner; Mario Andretti was a 3-time national race car champion; Mary Lou Retton won the all-around gold medal in Olympic woman's gymnastics; Matt Biondi won a total of 8 gold medals in Olympic swimming; and Brian Boitano won a gold medal in Olympic men's singles figure skating.
Italian Americans founded many successful enterprises, both small and large, in the post-war decades, including Barnes & Noble, Tropicana Products, Zamboni, Transamerica, Subway, Mr. Coffee, and Conair Corporation. Other enterprises founded by Italian Americans were Fairleigh Dickinson University, the Eternal Word Television Network, and the Syracuse Nationals basketball team – later to become the Philadelphia 76ers. Robert Panara was a co-founder of the National Technical Institute for the Deaf and founder of the National Theater of the Deaf. Recognized as a pioneer in deaf culture studies in the United States, he was honored with a commemorative U.S. stamp in 2017.
Eight Italian Americans became Nobel Prize laureates in the post-war decades: Mario Capecchi, Renato Dulbecco, Riccardo Giacconi, Salvatore Luria, Franco Modigliani, Rita Levi Montalcini, Emilio G. Segrè, and Carolyn Bertozzi.
Italian Americans continued to serve with distinction in the military, with 4 Medal of Honor recipients in the Korean War and 11 in the Vietnam War,[139] including Vincent R. Capodanno, a Catholic chaplain.
At the close of the 20th century, 31 men and women of Italian descent were serving in the U.S. House and Senate, 82 of the 1,000 largest U.S. cities had mayors of Italian descent, and 166 college and university presidents were of Italian descent.[140] An Italian American, Antonin Scalia, was serving as a U.S. Supreme Court justice, who was later joined by Samuel Alito in 2006. More than two dozen Italian Americans were serving in the Catholic Church as bishops. Four—Joseph Bernardin, Justin Rigali, Anthony Bevilacqua, and Daniel DiNardo—had been elevated to Cardinals.
Italian Americans have served with distinction in all of America's wars, and over 30 have been awarded the Medal of Honor. A number of Italian Americans have served as top-ranking generals in the military, including Anthony Zinni, Raymond Odierno, Carl Vuono, and Peter Pace, the latter three having also been appointed Chief of Staff of their respective services. Over two dozen of Italian descent have been elected as state governors including, most recently, Paul Cellucci of Massachusetts, John Baldacci of Maine, Janet Napolitano of Arizona, and Donald Carcieri of Rhode Island.
Influence on American culture and society
[edit]
Italian Americans have influenced the American culture and society in a variety of ways, such as foods,[141][142] coffees, and desserts; wine production (in California and elsewhere in the United States); popular music, starting in the 1940s and 1950s and continuing into the present;[143] operatic, classical, and instrumental music;[144] jazz;[145] fashion and design;[146] cinema, literature, and Italianate architecture, in homes, churches, and public buildings; Montessori schools; Christmas crèches; fireworks displays;[147] and sports (e.g., bocce and beach tennis).
The historical figure of Christopher Columbus is commemorated on Columbus Day and is reflected in numerous monuments, city names, names of institutions, and the poetic name, "Columbia," for the United States itself. Italian American identification with the Genoese explorer, whose fame lay in his grand voyages departing Europe and crossing the Atlantic Ocean to make discoveries in the New World, playing an important role in American history and identity, but was of negligible significance to the history of Italy—typifying Italian Americans' limited sense of nationalism and generally loose attachment to Italy itself as a foreign country. This identification contrasts, for example, to the preoccupations of Irish Americans with the political situation in Ireland throughout the 20th century and American Jews' deep personal investment in the fate of Israel.[88]
Politics
[edit]In the 1930s, Italian Americans voted heavily Democratic.[148] Carmine DeSapio in the late 1940s became the first to break the Irish Catholic hold on Tammany Hall since the 1870s. By 1951, more than twice as many Italian American legislators as in 1936 served in the six states with the most Italian Americans.[149] Since 1968, voters have split about evenly between the Democratic (37 percent) and the Republican (36 percent) parties.[150] The U.S. Congress includes Italian Americans who are leaders in both the Republican and Democratic parties. In 2007, Nancy Pelosi (D-CA) became the first woman and Italian American Speaker of the United States House of Representatives. Former Republican New York City mayor Rudy Giuliani was a candidate for the U.S. presidency in the 2008 election, as was Colorado Congressman Tom Tancredo. Rick Santorum won many primaries in his candidacy for the 2012 Republican presidential nomination. In the 2016 election, Santorum and New Jersey governor Chris Christie ran for the Republican nomination, as did Ted Cruz and George Pataki, who both have a smaller amount of Italian ancestry. Mike Pompeo, American politician, diplomat, businessman, and attorney, served as the 70th United States secretary of state from 2018 to 2021. Ron DeSantis, governor of Florida since 2019, is of Italian ancestry.
Geraldine Ferraro was the first woman on a major party ticket, running for vice president as a Democrat in 1984. Two justices of the Supreme Court have been Italian Americans, Antonin Scalia and Samuel Alito. Both were appointed by Republican presidents, Scalia by Ronald Reagan and Alito by George W. Bush.
The Italian American Congressional Delegation currently includes 30 members of Congress who are of Italian descent. They are joined by more than 150 associate members, who are not Italian American but have large Italian American constituencies. Since its founding in 1975, the National Italian American Foundation (NIAF) has worked closely with the bicameral and bipartisan Italian American Congressional Delegation, which is led by co-chairs Rep. Bill Pascrell of New Jersey and Rep. Pat Tiberi of Ohio.
The NIAF hosts a variety of public policy programs, contributing to public discourse on timely policy issues facing the nation and the world. These events are held on Capitol Hill and other locations under the auspices of NIAF's Frank J. Guarini Public Policy Forum and its sister program, the NIAF Public Policy Lecture Series. NIAF's 2009 public policy programs on Capitol Hill featured prominent Italians and Italian Americans as keynote speakers, including Leon Panetta, director of the CIA, and Franco Frattini, minister of foreign affairs for the Republic of Italy.
By the 1890s, Italian Americans in New York City were mobilizing as a political force. They helped elect Fiorello La Guardia (a Republican) as mayor in 1933, and helped reelect him in 1937 and 1941. They rallied for Vincent R. Impellitteri (a Democrat) in 1950, and Rudolph W. Giuliani (a Republican) in 1989 (when he lost), and in 1993 and 1997 (when he won). All three Italian Americans aggressively fought to reduce crime in the city; each was known for his good relations with the city's powerful labor unions.[151] La Guardia and Giuliani have had the reputation among specialists on urban politics as two of the best mayors in American history.[152][153] Democrat Bill de Blasio, the third mayor of Italian ancestry, served as the 109th mayor of New York City for two terms, from 2014 to 2021. Mario Cuomo (a Democrat) served as the 52nd governor of New York for three terms, from 1983 to 1995. His son Andrew Cuomo was the 56th governor of New York and previously served as secretary of housing and urban development from 1997 to 2001 and as the attorney general of New York from 2007 to 2010.
However, in contrast to other ethnic groups, Italian Americans demonstrate a marked lack of ethnocentrism and long history of political individualism, eschewing ethnic bloc voting, preferring to vote on the basis of individual candidates and issues, embracing maverick political candidates over ethnic loyalties. Popular New York Mayor Fiorello La Guardia in fact underperformed among his own demographic; in 1941, La Guardia even lost the Italian vote to his Irish opponent William O'Dwyer. In 1965, when New York Democrats backed Mario Procaccino, an Italian-born candidate for city comptroller, Procaccino lost the Italian vote and won his election only because of support in Jewish voter precincts. In the 1973 New York City mayoral election, the son of Italian immigrants Mario Biaggi failed to unite Italian voters as an ethnic bloc the way his Jewish opponent Abraham Beame could do to win the Democratic primary.[88]
In the 1962 Massachusetts gubernatorial election, incumbent Italian American Governor John Volpe lost his re-election campaign by a razor-thin 0.2 percent—a final margin that could be more than sufficiently explained by Volpe polling only 51 percent among the state's significant population of Italian Americans, roughly half of whom voted for old-line Anglo-Saxon Protestant Endicott Peabody over a fellow ethnic.[88]
The pragmatic maverick streak of Italian American voters, reacting to individual candidates and circumstances, emerged clearly amid the urban race riots of the 1960s. Black Republican Edward Brooke won more than 40 percent of the Italian vote running for the U.S. Senate from Massachusetts. And a majority of Italian voters living in mostly white rural Upstate New York backed black Democratic nominee Basil A. Paterson for lieutenant governor of New York in 1970—but not Italian voters who lived in racially diverse metro New York City. In urban environments, race relations deteriorated severely over Italian American support for law and order policies against urban riots and crime. In the 1968 presidential election, independent George Wallace won 21 percent of the Italian vote in Newark, New Jersey, 29 percent of the Italian vote in Cleveland, Ohio, and more than 10 percent of the Italian American vote nationwide—compared to 8 percent among non-Southern Whites as a whole—presaging the rightward shift of Italian Americans away from the Democratic Party, first as Reagan Democrats, then ultimately realigning with the Republican Party.[88]
Economy
[edit]
Italian Americans have played a prominent role in the economy of the United States, and have founded companies of great national importance, such as Bank of America (by Amadeo Giannini in 1904), Qualcomm, Subway, Home Depot, and Airbnb among many others. Italian Americans have also made important contributions to the growth of the U.S. economy through their business expertise. Italian Americans have served as CEO's of numerous major corporations, such as the Ford Motor Company and Chrysler Corporation by Lee Iacocca, IBM Corporation by Samuel Palmisano, Lucent Technologies by Patricia Russo, the New York Stock Exchange by Richard Grasso, Honeywell Incorporated by Michael Bonsignore, and Intel by Paul Otellini. Economist Franco Modigliani was awarded the Nobel Prize in Economics "for his pioneering analyses of saving and of financial markets."[154] Economist Eugene Fama was awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 2013 for his contribution to the empirical analysis of portfolio theory, asset pricing, and the efficient-market hypothesis.
Social and economic conditions of Italian Americans
[edit]About two-thirds of America's Italian immigrants arrived during 1900–1914. Many were of agrarian backgrounds, with little formal education and industrial skills, who became manual laborers heavily concentrated in the cities. Others came with traditional Italian skills as tailors; barbers; bricklayers; stonemasons and stone cutters; marble, tile, and terrazzo workers; fishermen; musicians; singers; shoe makers and shoe repairers; cooks and bakers; carpenters; grape growers; wine makers; silk makers; and dressmakers and seamstresses. Others came to provide for the needs of the immigrant communities, notably doctors, dentists, midwives, lawyers, teachers, morticians, priests, nuns, and brothers. Many of the skilled workers found work in their specialty, first in the Italian enclaves and eventually in the broader society. Traditional skills were often passed down from father to son and from mother to daughter.
By the second generation, approximately 70 percent of the men had blue-collar jobs, and the proportion was down to approximately 50 percent in the third generation, according to surveys in 1963.[155] By 1987, the level of Italian American income exceeded the national average, and since the 1950s, it grew faster than any other ethnic group except the Jews.[156] By 1990, according to the U.S. census, more than 65 percent of Italian Americans were employed as managerial, professional, or white-collar workers. In 1999, the median annual income of Italian-American families was $61,300, while the median annual income of all American families was $50,000.[157]
A University of Chicago study[158] of 15 ethnic groups showed that Italian Americans were among those groups having the lowest percentages of divorced people, unemployed people, people on welfare, and people incarcerated. On the other hand, they were among those groups with the highest percentages of two-parent families, elderly family members still living at home, and families who eat together on a regular basis.
Science
[edit]
Italian Americans have been responsible for major breakthroughs in virtually all fields of science, including engineering, medicine, and physics. Physicist and Nobel Prize laureate Enrico Fermi was the creator of the world's first nuclear reactor, the Chicago Pile-1, and among the leading scientists involved in the Manhattan Project during World War II. One of Fermi's main collaborators, Franco Rasetti, was awarded the Charles Doolittle Walcott Medal by the National Academy of Sciences for his contributions to Cambrian paleontology. Federico Faggin developed the first microchip and microprocessor. Robert Gallo led research that identified a cancer-causing virus. Anthony Fauci in 2008 was awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom for his work on the AIDS relief program PEPFAR.[159] Astrophysicist Riccardo Giacconi was awarded the 2002 Nobel Prize in Physics for his contributions to the discovery of cosmic X-ray sources. Virologist Renato Dulbecco won the 1975 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his work on oncoviruses. Pharmacologist Louis Ignarro was co-recipient of the 1998 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for demonstrating the signaling properties of nitric oxide. Microbiologist Salvador Luria won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1969 for his contribution to major discoveries on the replication mechanism and the genetic structure of viruses. Physicist William Daniel Phillips in 1997 won the Nobel Prize in Physics for his contributions to laser cooling. Physicist Emilio Segrè discovered the elements technetium and astatine, and the antiproton, a subatomic antiparticle, for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1959. Nine Italian Americans, including a woman, have gone into space as astronauts: Wally Schirra, Dominic Antonelli, Charles Camarda, Mike Massimino, Richard Mastracchio, Ronald Parise, Mario Runco, Albert Sacco, and Nicole Marie Passonno Stott. Rocco Petrone was the third director of the NASA Marshall Space Flight Center, from 1973 to 1974.
Women
[edit]


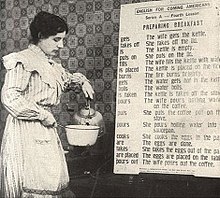
Italian women who arrived during the period of mass immigration had to adapt to new and unfamiliar social and economic conditions. Mothers, who had the task of raising the children and providing for the welfare of the family, commonly demonstrated great courage and resourcefulness in meeting those obligations, often under adverse living conditions. Their cultural traditions, which placed the highest priority on the family, remained strong as Italian immigrant women adapted to these new circumstances.
To assist the immigrants in the Little Italys, who were overwhelmingly Catholic, Pope Leo XIII dispatched a contingent of priests, nuns, and brothers of the Missionaries of St. Charles Borromeo and other orders. Among these was Sister Francesca Cabrini, who founded dozens of schools, hospitals, and orphanages. She was canonized as the first American saint in 1946.
Married women typically avoided factory work and chose home-based economic activities such as dressmaking, taking in boarders, and operating small shops in their homes or neighborhoods. Italian neighborhoods also proved attractive to midwives, women who trained in Italy before coming to America.[160] Many single women were employed in the garment industry as seamstresses, often in unsafe working environments. Many of the 146 who died in the Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire in 1911 were Italian American women. Angela Bambace was an 18-year-old Italian American organizer for the International Ladies Garment Workers Union in New York who worked to secure better working conditions and shorter hours for women workers in the garment industry.
The American scene in the 1920s featured a widespread expansion of women's roles, starting with the vote in 1920 and including new standards of education and employment for women and control of their own sexuality. "Flappers" raised the hemline and lowered the old restrictions in women's fashion. The Italian American media disapproved. It demanded the holding of the line regarding traditional gender roles in which men controlled their families. Many traditional patriarchal values prevailed among Southern European male immigrants, although some practices, such as the dowry, were left behind in Europe. The community spokesmen were shocked at the notion of a woman marking her secret ballot. They ridiculed flappers and proclaimed that feminism was immoral. They idealized an old male model of Italian womanhood. Mussolini was popular with readers and subsidized some papers, so when he expanded the electorate to include some women voting at the local level, the Italian American editorialists applauded him, arguing that the true Italian woman was, above all, a mother and a wife and, therefore, would be reliable as a voter on local matters, but only in Italy. Feminist organizations in Italy were ignored, as the editors purposely associated emancipation with Americanism and transformed the debate over women's rights into a defense of the Italian American community to set its own boundaries and rules.[161] The ethnic papers featured a woman's page that updated readers on the latest fabrics, color combinations, and accessories such as hats, shoes, handbags, and jewelry. Food was a major concern, and recipes were presented that adjusted to the availability of ingredients in the American market. Food supplies, which were limited in Italy by poverty and strict import controls, were abundant in America, so new recipes were needed.[162]
In the second and third generations, opportunities expanded as women were gradually accepted in the workplace and as entrepreneurs. Women also had much better job opportunities because they had a high school or sometimes college education and because they were willing to leave the Little Italys and commute to work.[163] During World War II, large numbers of Italian American women entered the workforce in factories providing war materiel, while others served as auxiliaries or nurses in the military services.
After World War II, Italian American women acquired an increasing degree of freedom in choosing a career and seeking higher levels of education. Consequently, the second half of the 20th century was a period in which Italian American women excelled in virtually all fields of endeavor. In politics, Geraldine Ferraro was the first woman vice presidential candidate, Ella Grasso was the first woman elected as a state governor, and Nancy Pelosi was the first woman Speaker of the House. In 1980, Mother Angelica (Rita Rizzo), a Franciscan nun, founded the Eternal Word Television Network (EWTN), a network viewed regularly by millions of Catholics. JoAnn Falletta was the first woman to become a permanent conductor of a major symphony orchestra (with both the Virginia Symphony Orchestra and the Buffalo Philharmonic Orchestra). Penny Marshall (Masciarelli) was one of the first women directors in Hollywood. Catherine DeAngelis, M.D., was the first woman editor of the Journal of the American Medical Association. Patricia Fili-Krushel was the first woman president of ABC Television. Bonnie Tiburzi was the first woman pilot in commercial aviation history. Patricia Russo was the first woman to become CEO of Lucent Technologies. Karen Ignagni has, since 1993, been the CEO of American Health Insurance Plans, an umbrella organization representing all major HMOs in the country. Nicole Marie Passonno Stott was one of the first women to go into space as an astronaut. Carolyn Porco, a world recognized expert in planetary probes, is the leader of the imaging science team for the Cassini probe, which orbited Saturn.
The National Organization of Italian American Women (NOIAW), founded in 1980, is an organization for women of Italian heritage committed to preserving Italian heritage, language, and culture by promoting and supporting the advancement of women of Italian ancestry.
Literature
[edit]



The works of a number of Italian American authors and poets, born of immigrant parents, were published in the first half of the 20th century. Pietro Di Donato, born in 1911, was a writer best known for his novel, Christ in Concrete, which was hailed by critics in the United States and abroad as a metaphor for the immigrant experience in America. Frances Winwar, born Francesca Vinciguerra in 1907 in Sicily, came to the United States at age 10. She is best known for her series of biographies of 19th-century English writers. She was also a frequent translator of classic Italian works into English and published several romantic novels set during historical events. John Ciardi, born in 1916, was primarily a poet. Among his works is a highly respected English-language rendition of Dante Alighieri's Divine Comedy. John Fante, born in 1909, was a novelist, short story writer, and screenwriter.
Later in the century, a growing number of books by recognized Italian American authors, such as Don DeLillo,[164] Paul Gallico (Poseidon Adventure), Gilbert Sorrentino, Gay Talese, Camille Paglia, and Mario Puzo (The Fortunate Pilgrim) found a place in mainstream American literature. Other notable 20th-century authors included Dana Gioia, executive director of the National Endowment for the Arts; John Fusco, author of Paradise Salvage; Tina DeRosa; and Daniela Gioseffi, winner of the John Ciardi Award for Lifetime Achievement in Poetry, and The American Book Award; and Josephine Gattuso Hendin (The Right Thing to Do). Poets Sandra (Mortola) Gilbert and Kim Addonizio were also winners of the John Ciardi Award for Lifetime Achievement in Poetry from Italian Americana, as was writer Helen Barolini and poet Maria Mazziotti Gillan.[165] These women have authored many books depicting Italian American women in a new light. Helen Barolini's The Dream Book: An Anthology of Writings by Italian American Women (1985) was the first anthology that pulled together the historic range of writing from the late 19th century to the 1980s. It exhibited the wealth of fiction, poetry, essays, and letters and paid special attention to the interaction of Italian American women with American social activism.[166] Italian American poets Lawrence Ferlinghetti and Gregory Corso played a prominent role in the Beat Generation. Ferlinghetti was also the co-founder of City Lights Bookstore, a San Francisco bookstore and publishing company that published much of the work of other Beat Generation writers.[167] Many of these authors' books and writings are easily found on the internet, as, for example, on an archive of contemporary Italian American authors, as well as in bibliographies online at Stonybrook University's Italian American Studies Department in New York[168] or at the Italian American Writers Association website.[169]
A scholarly literature has also emerged that critiques the literary output. Common themes include conflicts between marginal Italian American and mainstream culture, and tradition-bound immigrant parents opposed by their more assimilated children.[170] Mary Jo Bona provided the first full-length scholarly analysis of the literary tradition. She is especially interested in showing how authors portrayed the many configurations of family relationships, from the early immigrant narratives of journeying to a new world, through novels that stress intergenerational conflicts, to contemporary works about the struggle of modern women to form nontraditional gender roles.[171]
Among the scholars who have led the renaissance in Italian American literature are professors Richard Gambino, Anthony Julian Tamburri, Paolo Giordano, and Fred Gardaphé. The latter three founded Bordighera Press and edited From the Margin: An Anthology of Italian American Writing (Purdue University Press). At Brooklyn College, Dr. Robert Viscusi founded the Italian American Writers Association and is an author and American Book Award winner himself. As a result of the efforts of magazines like Voices in Italian Americana; Ambassador, a publication of the National Italian American Foundation; and Italian Americana, edited by Carla Simonini, Italian Americans have been reading more works of their own writers. A supplemental website at www.italianamericana.com to the journal Italian Americana, edited by novelist Christine Palamidessi Moore, also offers historical articles, stories, memoirs, poetry, and book reviews. Dana Gioia, was poetry editor of Italian Americana from 1993 to 2003, followed by poet Michael Palma, who also selects poems for Italian Americana's webpage supplement.[172] Lawrence Ferlinghetti, Daniela Gioseffi, and Paul Mariani, are among the internationally known authors who have been awarded the John Ciardi Award for Lifetime Achievement in Poetry during Michael Palma's tenure as poetry editor. Daniela Gioseffi, with Alfredo de Palchi, founded the Annual $2,000 Bordighera Poetry Prize[173] to further the names of Italian American poets in American literature. As of 1997, 12 books have been published in the bilingual series from Bordighera Press.[174]
In the field of academic cinema studies, Peter Bondanella, Peter Brunette, and Frank P. Tomasulo have made significant contributions to film scholarship as authors, editors, and educators.
Italian Americans have written not only about the Italian American experience but, indeed, the human experience. Some of the most popular inspirational books have been authored by Italian Americans—notably, those of Og Mandino, Leo Buscaglia, and Antoinette Bosco.[175] A series of inspirational books for children has been written by Tomie dePaola. Contemporary best-selling fiction writers include David Baldacci, Kate DiCamillo, Richard Russo, Adriana Trigiani, and Lisa Scottoline.
Religion
[edit]
The majority of Italian Americans are Catholics, although Catholic affiliation among Italian American adults has fallen from 89 percent in 1972 to 56 percent in 2010 (-33 percentage points).[176] By 1910, Italian Americans had founded 219 Catholic churches and 41 parochial schools, served by 315 priests and 254 nuns, 2 Catholic seminaries, and 3 orphanages.[177] Four hundred Italian Jesuit priests left Italy for the American West between 1848 and 1919. Most of these Jesuits left their homeland involuntarily, expelled by Italian nationalists in the successive waves of Italian unification that dominated Italy. When they came to the West, they ministered to Native Americans in the Northwest, Irish-Americans in San Francisco, and Mexican Americans in the Southwest. They also ran the nation's most influential Catholic seminary, in Woodstock, Maryland. In addition to their pastoral work, they founded numerous high schools and colleges, including Regis University, Santa Clara University, the University of San Francisco, and Gonzaga University.[178]

In some Sicilian American communities, primarily Buffalo and New Orleans, Saint Joseph's Day (March 19) is marked by parades and celebrations, including traditional "St. Joseph's tables," where meatless dishes are served for the benefit of the communities' poor. Columbus Day is also widely celebrated, as are the feasts of some regional Italian patron saints. In Boston's North End, the Italian immigrants celebrate the "Feast of all Feasts," Saint Anthony's Feast. Started in 1919 by Italian immigrants from Montefalcione, a small town near Naples, Italy, the feast is widely considered the largest and most authentic Italian religious festival in the United States. More than 100 vendors and 300,000 people attend the feast over a three-day period in August. San Gennaro (September 19) is another popular saint, especially among Neapolitans. Santa Rosalia (September 4), is celebrated by immigrants from Sicily. Immigrants from Potenza celebrate the San Rocco's Day (August 16) feast at the Potenza Lodge in Denver the third weekend of August. San Rocco is the patron saint of Potenza, as is San Gerardo. Many still celebrate the Christmas season with a Feast of the Seven Fishes. The Feast of the Assumption is celebrated in Cleveland's Little Italy on August 15. On this feast day, people will pin money on a Blessed Virgin Mary statue as a symbol of prosperity. The statue is then paraded through Little Italy to Holy Rosary Church. For almost 25 years, Cleveland Bishop Anthony Pilla participated in the parade and mass to celebrate his Italian heritage. Bishop Pilla retired in April 2006.
While most Italian American families have a Catholic background, about 19 percent self-identified as Protestant in 2010.[176] In the early 20th century, about 300 Protestant missionaries worked in urban Italian American neighborhoods. Some have joined the Episcopal Church, which still retains much of the Catholic liturgical form. Some have converted to evangelical churches. Fiorello La Guardia was raised Episcopalian; his father was Catholic, and his mother was from the small but significant community of Italian Jews. There is a small charismatic denomination, known as the Christian Church of North America, which is rooted in the Italian Pentecostal Movement that originated in Chicago in the early 20th century. A group of Italian immigrants in Trenton, New Jersey, and Wakefield, Massachusetts, built their own small Baptist chapel and converted to the Baptist denomination. The Church of Jesus Christ (Bickertonite), a denomination of the Latter Day Saint movement, which is headquartered in Monongahela, Pennsylvania, counts significant numbers of Italian Americans in its leadership and membership.[179] The town of Valdese, North Carolina, was founded in 1893 by a group of Italians of Waldensian religion, originally from the Cottian Alps in Italy.
Italian Jews
[edit]
The Jewish emigration from Italy was never of a magnitude that resulted in the formation of Italian Jewish communities in the United States. Religious Italian Jews integrated into existing Jewish communities without difficulty, especially in Sephardic communities, and those who were secular found Jewish secular institutions in the United States ready to welcome them. Despite their small numbers, Italian American Jews have had a great influence on American life,[180] starting with Lorenzo Da Ponte (born Emanuele Conegliano), Mozart's former librettist, opera impresario and the first professor of Italian at Columbia College in New York, where he lived from 1805 to his death in 1838.
From a religious point of view, the figure of greatest influence is Rabbi Sabato Morais, who, at the end of the 19th century, was the leader of the large Sephardic community of Philadelphia. In 1886, he became one of the founders of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America in New York, where he became its first dean. Two other Italian Jews achieved prominence in the United States in the first half of the 20th century: Giorgio Polacco was the principal conductor of the Metropolitan Opera House (1915–1917) and the Chicago Civic Opera (1921–1930), and Fiorello La Guardia was a member of the U.S. Congress (1917–1919 and 1923–1933) and a popular mayor of New York (1934–1945). A descendant on his mother's side of the great Italian rabbi Samuel David Luzzatto, La Guardia could address his constituency in both Italian and Yiddish.
Under Mussolini's Racial Laws of 1938, Italian Jews, who had lived in Italy for over two millennia, were stripped of most of their civil liberties. Finding refuge in the United States as a result of the fascist persecutions during the 1930s and 1940s, roughly 2,000 Italian Jews landed in America and continued their work in a wide range of fields.[181] Many achieved international importance, including Giorgio Levi Della Vida, Mario Castelnuovo-Tedesco, Vittorio Rieti, Bruno Rossi, Emilio Segre, Giorgio Cavaglieri, Ugo Fano, Robert Fano, Guido Fubini, Eugene Fubini, and Silvano Arieti. Of particular importance also are the contributions of the Italian Jewish women Maria Bianca Finzi-Contini, Bianca Ara Artom, and Giuliana Tesoro, who opened the fields of university and scientific research to Italian American women. After the war, four Italian American Jews received the Nobel Prize: Franco Modigliani, Emilio Segre, Salvador Luria, and Rita Levi Montalcini. Also of significance are the contributions of communication specialist Andrew Viterbi, journalist and writer Ken Auletta, and economist Guido Calabresi. The international recognition of the work of Primo Levi and other Italian-Jewish authors, such as Giorgio Bassani and Carlo Levi, has increased the interest in the United States in Italian Judaism, as demonstrated by the opening in 1998 of the Primo Levi Center of New York.[182]
Education
[edit]
During the era of mass immigration, rural families in Italy did not place a high value on formal education since they needed their children to help with chores as soon as they were old enough. For many, this attitude did not change upon arriving in America, where children were expected to help support the family as soon as possible.[183] This view toward education steadily changed with each successive generation. The 1970 census revealed that those under age 45 had achieved a level of education comparable to the national average,[184] and within six decades of their peak immigration year, Italian Americans as a whole had equaled the national average in educational attainment.[185] Presently, according to Census Bureau data, Italian Americans have an average high school graduation rate, and a higher rate of advanced degrees compared to the national average.[186] Italian Americans throughout the United States are well represented in a wide variety of occupations and professions, from skilled trades, to the arts, to engineering, science, mathematics, law, and medicine, and include a number of Nobel prize winners.[187]
There are two Italian international schools in the United States, La Scuola International[188] in San Francisco, and La Scuola d'Italia Guglielmo Marconi in New York City.[189]
Language
[edit]| Year | Speakers |
|---|---|
| 1910a | 1,365,110 |
| 1920a | 1,624,998 |
| 1930a | 1,808,289 |
| 1940a | 1,561,100 |
| 1960a | 1,277,585 |
| 1970a | 1,025,994 |
| 1980[190] | 1,618,344 |
| 1990[191] | 1,308,648 |
| 2000[192] | 1,008,370 |
| 2011[193] | 723,632 |
| ^a Foreign-born population only[194] | |
According to the Sons of Italy News Bureau, from 1998 to 2002 the enrollment in college Italian language courses grew by 30%, faster than the enrollment rates for French and German.[195] Italian is the fourth most commonly taught foreign language in U.S. colleges and universities behind Spanish, French, and German. According to the U.S. 2000 Census, Italian (including Sicilian) is the sixth most spoken language in the United States (tied with Vietnamese) after English with over 1 million speakers.[196]
As a result of the large wave of Italian immigration to the United States in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Italian and Sicilian were once widely spoken in much of the U.S., especially in northeastern and Great Lakes area cities like Buffalo, Rochester, Detroit, Chicago, Cleveland and Milwaukee, as well as San Francisco, St. Louis and New Orleans. Italian-language newspapers exist in many American cities, especially New York City, and Italian-language movie theatres existed in the U.S. as late as the 1950s. L'Idea is a bilingual quarterly published in Brooklyn since 1974. Arba Sicula (Sicilian Dawn) is a semiannual publication of the society of the same name, dedicated to preserving the Sicilian language. The magazine and a periodic newsletter offer prose, poetry and comment in Sicilian, with adjacent English translations.
Today, prizes like the Bordighera Annual Poetry Prize,[197] founded by Daniela Gioseffi, Pietro Mastrandrea and Alfredo di Palchi, with support from the Sonia Rraiziss-Giop Foundation and Bordighera Press, which publishes the winners in bilingual editions, have helped to encourage writers of the diaspora to write in Italian. Chelsea Books in New York City and Gradiva Press on Long Island have published many bilingual books due to the efforts of bilingual writers of the diaspora like Paolo Valesio,[198] Alfredo de Palchi,[199] and Luigi Fontanella. Dr. Luigi Bonaffini[200] of the City University of New York, publisher of The Journal of Italian Translation at Brooklyn College, has fostered Italian dialectic poetry throughout Italy and the U.S. Joseph Tusiani of New York and New York University,[201] a distinguished linguist and prize-winning poet born in Italy, paved the way for Italian works of literature in English and has published many bilingual books and Italian classics for the American audience, among them the first complete works of Michelangelo's poems in English to be published in the United States. All of this literary endeavor has helped to foster the Italian language, along with Italian opera, of course, in the United States. Many of these authors and their bilingual books are located throughout the internet.

Author Lawrence Distasi argues that the loss of spoken Italian among the Italian American population can be tied to U.S. government pressures during World War II. During World War II, in various parts of the country, the U.S. government displayed signs that read, "Don't Speak the Enemy's Language". Such signs designated the languages of the Axis powers, German, Japanese and Italian, as "enemy languages". Shortly after the Axis powers declared war on the U.S., many Italian, Japanese and German citizens were interned. Among the Italian Americans, those who spoke Italian, who had never become citizens and who belonged to groups that praised Benito Mussolini, were most likely to become candidates for internment. Distasi claims that many Italian language schools closed down in the San Francisco Bay Area within a week of the U.S. declaration of war on the Axis powers. Such closures were inevitable since most of the teachers in Italian languages were interned.
Despite previous decline, Italian and Sicilian are still spoken and studied by those of Italian American descent and it can be heard in various American communities, especially among older Italian Americans. The official Italian taught in schools is Standard Italian, which is based on 14th century literary Florentine.[202] However, the "Italian" with which Italian Americans are generally acquainted is often rooted in the Regional Italian and Italo-Dalmatian languages their immigrant ancestors brought from Italy to American, primarily southern Italian and Sicilian dialects of pre-unification Italy.[203]

Despite it being the fifth most studied language in higher education (college and graduate) settings throughout America,[204] the Italian language has struggled to maintain being an AP course of study in high schools nationwide. It was only in 2006 that AP Italian classes were first introduced, and they were soon dropped from the national curricula after the spring of 2009.[205] The organization which manages such curricula, the College Board, ended the AP Italian program because it was "losing money" and had failed to add 5,000 new students each year. Since the program's termination in the spring of 2009, various Italian organizations and activists have attempted to revive the course of study. Most notable in the effort is Margaret Cuomo, sister of New York Governor Andrew Cuomo. She provided the impetus for the program's birth in 2006 and is currently attempting to secure funding and teachers to reinstate the program. It is also worth noting that Italian organizations have begun fundraisers to revive AP Italian. Organizations such as the NIAF and Order Sons of Italy in America have made strides in collecting money, and are prepared to aid in the monetary responsibility any new AP Italian program would bring with it.
Web-based Italian organizations, such as ItalianAware,[206] have begun book donation campaigns to improve the status and representation of Italian and Italian American literature in the New York public libraries. According to ItalianAware, the Brooklyn Public Library is the worst offender in New York City.[207] It has 11 books pertaining to the Italian immigrant experience available for checkout, spread across 60 branches. That amounts to one book for every six branches in Brooklyn, which (according to ItalianAware) cannot supply the large Italian/Italian American community in the borough. ItalianAware aimed to donate 100 books to the Brooklyn Public Library by the end of 2010.
Italian American pidgin
[edit]Italian American pidgin or Italian American slang is a pidgin language thought to have developed in the early 1900s in American cities with a large Italian population, primarily New York and New Jersey. It soon spread to many Italian communities across cities and metropolitan areas in both the U.S. and Canada. It is not a language in its own right but is a mix of the various Italian dialects and American English.[208][209]
Cuisine
[edit]Italian Americans have profoundly influenced the eating habits of America. Italian American TV personalities, such as Mario Batali, Giada DeLaurentiis, Rachael Ray, Lidia Bastianich, and Guy Fieri have hosted popular cooking shows featuring Italian cuisine.
While heavily influenced by and sharing common dishes with Italian cuisine, especially the Neapolitan and Sicilian traditions of typical Italian immigrants to the United States, Italian American cuisine differs in several respects. The greater availability of meat in quantity led to new staples such as spaghetti and meatballs, while pizza evolved regionally into styles as diverse as Chicago-style deep dish and New York thin crust.
Folklore
[edit]
One of the most characteristic and popular of Italian American cultural contributions has been their feasts. Throughout the United States, wherever one may find an "Italian neighborhood" (often referred to as "Little Italy"), one can find festive celebrations such as the well-known Feast of San Gennaro in New York City, the unique Our Lady of Mount Carmel "Giglio" Feast in the Williamsburg section of Brooklyn, New York, Italian feasts involve elaborate displays of devotion to Jesus Christ and patron saints. On the weekend of the last Sunday in August, the residents of Boston's North End celebrate the "Feast of all Feasts" in honor of St. Anthony of Padua, which was started over 300 years ago in Montefalcione, Italy. Perhaps the most widely known is St. Joseph's feast day on March 19. These feasts are much more than simply isolated events within the year. Feast (Festa in Italian) is an umbrella term for the various secular and religious, indoor and outdoor activities surrounding a religious holiday. Typically, Italian feasts consist of festive communal meals, religious services, games of chance and skill and elaborate outdoor processions consisting of statues resplendent in jewels and donations. The celebration usually takes place over the course of several days, and is communally prepared by a church community or a religious organization over the course of several months.
Currently, there are more than 300 Italian feasts celebrated throughout the United States. Notable is Festa Italiana, held in Milwaukee every summer. These feasts are visited each year by millions of Americans from various backgrounds who come together to enjoy Italian music and food delicacies. In the past, as to this day, an important part of Italian American culture centers around music and cuisine.
TV and press
[edit]
Numerous American television personalities are of Italian descent. Talk-show hosts include Jay Leno, Jimmy Kimmel, Kelly Ripa, Maria Bartiromo, Adam Carolla, Neil Cavuto, Kelly Monaco, Jai Rodriguez, Annette Funicello, Victoria Gotti, Tony Danza, Giuliana DePandi, Giuliana Rancic, Bruno Cipriani.[210]
Italian American newspapers
[edit]Generoso Pope (1891–1950), the owner of a chain of Italian language newspapers in major cities, stands out as the epitome of the Italian American ethnic political broker. He bought Il Progresso Italo-Americano in 1928 for $2 million; he doubled its circulation to 200,000 in New York City, making it the largest Italian-language paper in the country. He purchased additional papers in New York and Philadelphia, which became the chief source of political, social, and cultural information for the community. Pope encouraged his readers to learn English, become citizens, and vote; his goal was to instill pride and ambition to succeed in modern America. A conservative Democrat who ran the Columbus Day parade and admired Mussolini, Pope was the most powerful enemy of anti-Fascism among Italian Americans. Closely associated with Tammany Hall politics in New York, Pope and his newspapers played a vital role in securing the Italian vote for Franklin D. Roosevelt's Democratic tickets. He served as chairman of the Italian Division of the Democratic National Committee in 1936, and helped persuade the president to take a neutral attitude over Italy's invasion of Ethiopia. He broke with Mussolini in 1941 and enthusiastically supported the American war effort. In the late 1940s Pope supported the election of William O'Dwyer as mayor in 1945 and Harry S. Truman as president. His business concerns continued to prosper under New York's Democratic administrations, and in 1946 he added the Italian-language radio station WHOM to his media holdings. In the early years of the Cold War, Pope was a leading anti-Communist and orchestrated a letter-writing campaign by his subscribers to stop the Communists from winning the Italian elections in 1948.[211]
Voters did not always vote the way editorials dictated, but they depended on the news coverage. At many smaller papers, support for Mussolini, short-sighted opportunism, deference to political patrons who were not members of the Italian-American communities, and the necessity of making a living through periodicals with a small circulation, generally weakened the owners of Italian-language newspapers when they tried to become political brokers of the Italian American vote.[212]
James V. Donnaruma purchased Boston's La Gazzetta del Massachusetts in 1905. La Gazzetta enjoyed a wide readership in Boston's Italian community because it emphasized detailed coverage of local ethnic events and explained how events in Europe affected the community. Donnaruma's editorial positions, however, were frequently at odds with the sentiments of his readership. Donnaruma's conservative views and desire for greater advertising revenue prompted him to court the favor of Boston's Republican elite, to whom he pledged editorial support in return for the purchase of advertising space for political campaigns. La Gazzetta consistently supported Republican candidates and policy positions, even when the party was proposing and passing laws to restrict Italian immigration. Nevertheless, voting records from the 1920s–1930s show that Boston's Italian Americans voted heavily for Democratic candidates.[213][214]
Carmelo Zito took over the San Francisco newspaper Il Corriere del Popolo in 1935. Under Zito, it became one of the fiercest foes of Mussolini's fascism on the West Coast. It vigorously attacked Italy's 1935 invasion of Ethiopia and its intervention in the Spanish Civil War. Zito helped form the Italian-American Anti-Fascist League and often attacked certain Italian prominenti like Ettore Patrizi, publisher of L'Italia and La Voce del Popolo. Zito's paper campaigned against alleged Italian pro-Fascist language schools of San Francisco.[215]
In 1909, Vincenzo Giuliano, an immigrant from Calabria, Italy and his wife Maria Oliva founded La Tribune Italiana d'America, known today as The Italian Tribune, which circulates throughout southeastern Michigan. A second newspaper founded by a Catholic order of priests, La Voce del Popolo also served the Metro Detroit community until the 1920s, when that newspaper merged with La Tribuna Italiana d'America. Upon Giuliano's death in the 1960s, his family continued the paper.
Organizations
[edit]Italian-American organizations include:
- Alpha Phi Delta
- American Italian Anti-Defamation League
- Columbus Citizens Foundation
- Italian American Congressional Delegation
- Italian American One Voice Coalition
- Italian-American Civil Rights League
- Italian-American National Union
- Italy–USA Foundation
- National Organization of Italian American Women
- Order Sons of Italy in America
- Unico National
- The Columbian Foundation
- American Relief for Italy, Inc (ARI)
In 1944, the creation of the American Relief for Italy, Inc (ARI) functioned as an umbrella organization until 1946. The ARI collected, shipped, and distributed over $10 million of relief materials donated by other Italian organizations and individuals from all over Italy. Catholic charities, labor unions, cultural clubs, and fraternal organizations all responded in helping to raise money for the ARI. These relief materials were donated to Italians in need and helped to provide humanitarian assistance. All remaining donations were distributed to Italian soldiers at war. This organization was one of the first steps in the lengthy process of political and economic stabilizations in postwar Italy.[217]
- American Committee on Italian Migration (ACIM)
Throughout the 1950s and the 1960s, the American Committee on Italian Migration (ACIM) was one of the largest, most active Italian American organizations in the United States. They gave assistance to Italian immigrants living in the United States threatened by political instability and provided recovery for those in need. Frequently, money and supplies were sent back home to those who were unable to migrate or were in the process of migrating to the United States. Most of these people were the women and children Italian men left behind in hopes of starting a new life in America. The ACIM grew rapidly with hundreds of thousands of members being both donors and beneficiaries.[217]
- National Catholic Welfare Conference (NCWC)
The National Catholic Welfare Conference (NCWC) worked with ACIM on legislative campaigns and immigration projects. In 1951, members from NCWC, ACIM, as well as other Italian Americans joined in efforts to create an organization that specifically benefited and focused on assisting Italian immigrants. After a vast effort in 1953, the Refugee Relief Act (RRA) was passed allowing the entrance of over two hundred thousand Italian immigrants into the United States. The RRA provided these Italian immigrants with many opportunities to start their new life in America. Job opportunities, a place to live, and proper education for immigrants children were provided.[217]
The National Italian American Foundation (NIAF) [218] – a nonpartisan, nonprofit organization headquartered in Washington, D.C. – works to represent Italian Americans, spread knowledge of the Italian language, foster U.S./Italy relations and connect the greater Italian American community. Additionally, two major Italian American fraternal and service organizations, Order Sons of Italy in America and Unico National, actively promote knowledge of Italian American history and culture.
The Italian Heritage and Culture Committee – NY, Inc. was founded in 1976, and has organized special events, concerts, exhibits and lectures celebrating Italian culture in New York City. Each year it focuses on a theme representative of the history and culture of Italy and Italian Americans.
The Italic Institute of America[219] is dedicated to fostering and preserving knowledge of the classical Italian heritage of American society, through the Latin language and Greco-Roman-Etruscan civilization, as well as five centuries of contributions to American society by Italians and their descendants.
Museums
[edit]
There are several museums in the United States, dedicated to Italian American culture:
- San Francisco, California: Museo ItaloAmericano
- Los Angeles, California: Italian American Museum of Los Angeles
- Chicago, Illinois: Casa Italia Chicago[220]
- New Orleans, Louisiana: American Italian Cultural Center[221]
- Albany, New York: American Italian Heritage Association and Museum[222]
- New York, New York: Italian American Museum[223]
- Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: History of Italian Immigration Museum (Filitalia Foundation)[224]
Discrimination and stereotyping
[edit]During the period of mass immigration to the United States, they were often victims of prejudice, economic exploitation, and sometimes even violence, particularly in the South. In the 1890s, more than 20 Italians were lynched.[225] The hostility was often directed toward the Southern Italians and Sicilians who began immigrating to the United States in large numbers after 1880.[226]
A journalist asked a West Coast construction boss if the Italian was a white man, to which the boss replied: "No sir, an Italian is a Dago".[227] This response reflected the xenophobic attitude of the time defining the idea of Whiteness in the United States. There was a social hierarchy within the various white American communities in which a different degrees of "whiteness" was associated with each group. Some European immigrants, such as Italians, were considered less white than the early European settlers and, therefore, were less accepted in American society.
Italian stereotypes abounded as a means of justifying the maltreatment of the immigrants. The print media greatly contributed to the stereotyping of Italians with lurid accounts of secret societies and criminality. Between 1890 and 1920, Italian neighborhoods were often depicted as violent and controlled by criminal networks. Two highly publicized cases illustrate the impact of these negative stereotypes:

In 1891, eleven Italian immigrants in New Orleans were lynched due to their alleged role in the murder of the police chief David Hennessy. This was one of the largest mass lynchings in U.S. history. The lynching took place after nine of the immigrants were tried for the murder and acquitted. Subsequently, a mob broke into the jail where they were being held and dragged them out to be lynched, together with two other Italians who were being held in the jail at the time, but had not been accused in the killing.

In 1920, two Italian immigrants, Nicola Sacco and Bartolomeo Vanzetti, were accused of robbery and murder in Braintree, Massachusetts. Many historians agree that they were given a very unfair and biased trial because of their anarchistic political beliefs and their Italian immigrant status. During the next few years, sporadic protests were held in major cities all around the world calling for their release, especially after Portuguese migrant Celestino Madeiros confessed to committing the crime absolving them of participation. The Supreme Court refused to upset the verdict, and Massachusetts Governor Alvan T. Fuller denied the men clemency. In spite of worldwide protests, Sacco and Vanzetti were eventually executed in 1927.
While the vast majority of Italian immigrants brought with them a tradition of hard work and were law-abiding citizens, as documented by police statistics of the early 20th century in Boston and New York City which show that Italian immigrants had an arrest rate no greater than that of other major immigrant groups,[228] a very small minority brought a very different custom. This criminal element preyed on the immigrants of the Little Italies, using intimidation and threats to extract protection money from the wealthier immigrants and shop owners, and were also involved in a multitude of other illegal activities. When the Fascists came to power in Italy, they made the destruction of the Mafia in Sicily a high priority. Hundreds fled to America in the 1920s and 1930s to avoid prosecution.
Prohibition, which went into effect in 1920, proved to be an economic windfall for those in the Italian American community already involved in illegal activities, and those who had fled from Sicily. This entailed smuggling liquor into the country, wholesaling it, and then selling it through a network of outlets. While other ethnic groups were also deeply involved in these illegal ventures, and the associated violence, Chicago mobster Al Capone became the most notorious figure of the Prohibition era. Though eventually repealed, Prohibition had a long-term effect as the spawning ground for later criminal activities.
In the 1950s, the scope of Italian American organized crime became well known though a number of highly publicized congressional hearings that followed a police raid on a top-level meeting of racketeers in Apalachin, New York. With advanced surveillance techniques, the Witness Protection Program, the Racketeer Influenced & Corrupt Organizations Act, and vigorous and sustained prosecution the power and influence of organized crime were greatly diminished in the decades that followed. Two Italian American prosecutors, Rudy Giuliani and Louis Freeh, were instrumental in bringing this about. Freeh was later appointed director of the FBI, while Giuliani would serve two terms as Mayor of New York City.
From the earliest days of the movie industry, Italians have been portrayed as violent criminals and sociopaths.[230] This trend has continued to the present day. The stereotype of Italian Americans is the standardized mental image which has been fostered by the entertainment industry, especially through commercially successful movies like The Godfather, Goodfellas, and Casino; and TV programs such as The Sopranos.[231] This follows a known pattern in which it is possible for the mass media to effectively create universally recognized, and sometimes accepted, stereotypes.[232]
A highly publicized protest from the Italian-American community came in 2001 when the Chicago-based organization AIDA (American Italian Defamation Association) unsuccessfully sued Time Warner for distribution of HBO's series The Sopranos.[233]
The DreamWorks animated film, Shark Tale, was widely protested by virtually all major Italian-American organizations as introducing the mob genre and negative stereotyping into a children's movie.[234] In spite of the protests, which started during its early production, the movie was produced and released in 2004.
In 2009, MTV launched a reality show, Jersey Shore,[235] which prompted severe criticism from Italian American organizations such as the National Italian American Foundation,[236] Order Sons of Italy in America, and Unico National for its stereotypical portrayal of Italian Americans.
In 2019, Made in Staten Island lasted just three episodes, also on MTV, before a public outcry from residents of the borough in general, and Italian-American residents therein in particular, forced the show's cancellation.
The effective stereotyping of Italian Americans as being associated with organized crime was shown by a comprehensive study of Italian American culture on film, conducted from 1996 to 2001 by the Italic Institute of America.[219] The findings showed that over two-thirds of the more than 2,000 films studied portray Italian Americans in a negative light. Further, close to 300 movies featuring Italian Americans as criminals have been produced since The Godfather, an average of nine per year.[237] According to the Italic Institute of America:
- The mass media has consistently ignored five centuries of Italian American history, and has elevated what was never more than a minute subculture to the dominant Italian American culture.[238]
In actuality, according to recent FBI statistics,[239] Italian American organized crime members and associates number approximately 3,000; and, given an Italian American population estimated to be approximately 18 million, the study concludes that only one in 6,000 is active in organized crime (0.007% of Italian-Americans).[229]
Communities
[edit]
Little Italies were, to a considerable extent, the result of Italophobia. The ethnocentrism and anti-Catholicism exhibited by the earlier Anglo-Saxon and northern European settlers helped to create an ideological foundation for fixing foreignness on urban spaces occupied by immigrants.[240] Communities of Italian Americans were established in most major industrial cities of the early 20th century, such as Baltimore, Maryland; New York City, New York; Newark, New Jersey; Boston, Massachusetts; Philadelphia, Pennsylvania; Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania; Hartford, Connecticut; Waterbury, Connecticut; New Haven, Connecticut; Providence, Rhode Island; St. Louis, Missouri; Chicago, Illinois; Cleveland, Ohio; Buffalo, New York; and Kansas City, Missouri. New Orleans, Louisiana was the first site of immigration of Italians into America in the 19th century, before Italy was a unified nation-state. This was before New York Harbor and Baltimore became the preferred destinations for Italian immigrants. In sharp contrast to the Northeast, most of the Southern states (with the exception of Central and South Florida and the New Orleans area) have relatively few Italian-American residents. During the labor shortage in the 19th and early 20th centuries, planters in the Deep South did attract some Italian immigrants to work as sharecroppers, but they soon left the extreme anti-Italian discrimination and strict regimen of the rural areas for the cities or other states. The state of California has had Italian-American residents since the 1850s. By the 1970s, gentrification of inner city neighborhoods and the arrival of new immigrant groups caused a sharp decline in the old Italian-American and other ethnic enclaves.[241] Many Italian Americans moved to the rapidly growing Western states, including Arizona, Colorado, Nevada, and California. Today, New York and New Jersey have the largest numbers of Italian Americans in the U.S. while smaller Northeastern cities such as Pittsburgh, Providence and Hartford have the highest percentage of Italian Americans in their metropolitan areas.
The New York-based daily newspaper Il Progresso Italo-Americano had a national audience and reflected the views of the leadership of the community. It was published 1880–1988.[242]
New York City
[edit]
New York City is home to the largest Italian-American population in the country and the second-largest Italian population outside of Italy. Several Little Italy enclaves exist in New York City, including Little Italy, Manhattan; the Lower East Side in general; Italian Harlem, Morris Park, Belmont, Bensonhurst, Howard Beach, Ozone Park, Carroll Gardens, Greenwich Village, Middle Village, Italian Williamsburg, Bay Ridge, and the South Shore of Staten Island. Historically, Little Italy on Mulberry Street in Manhattan extends as far south as Canal Street, as far north as Bleecker, as far west as Lafayette and as far east as the Bowery.[243] The neighborhood was once known for its large population of Italians.[243] Today, it consists of Italian stores and restaurants.[244] The Italian immigrants congregated along Mulberry Street in Manhattan's Little Italy to celebrate San Gennaro as the Patron Saint of Naples. The Feast of San Gennaro is a large street fair, lasting 11 days, that takes place every September along Mulberry Street between Houston and Canal Streets.[245] The festival is as an annual celebration of Italian culture and the Italian-American community. Today, much of the neighborhood has been absorbed and engulfed by Chinatown, as immigrants from China moved to the area. Arthur Avenue in the Belmont section of New York City's northernmost borough, The Bronx, is one of the many neighborhoods considered the Bronx's "Little Italy", with Morris Park, Pelham Bay, Throggs Neck, and other Bronx neighborhoods also serving as centers of Italian-American culture. Robert De Niro's directing debut, A Bronx Tale, takes place within Little Italy, however, it was largely filmed in Astoria, Queens.[246] The series Third Watch was initially based on Arthur Avenue, with the first episode referring to the firehouse as "Camelot", based on its location at the intersection of King Street and Arthur Avenue. The 1973 film The Seven-Ups, starring Roy Scheider, was filmed on Arthur Avenue and Hoffman Street. In 2003, a scene from the HBO series The Sopranos was shot in Mario's Restaurant. Leonard, of James Frey's A Million Little Pieces, grew up in this area. Much of the novel Underworld takes place near Arthur Avenue.[247] The author, Don DeLillo, himself grew up in that neighborhood.
Bensonhurst used to be heavily Italian-American, and it used to be considered the main "Little Italy" of Brooklyn. Since the late 1990s, most Italians have moved to Staten Island. The Italian-speaking community remains over 20,000 strong, according to the census of 2000. However, the Italian-speaking community is becoming "increasingly elderly and isolated, with the small, tight-knit enclaves they built around the city slowly disappearing as they give way to demographic changes".[248] Its main thoroughfare, 18th Avenue (also known as Cristoforo Colombo Boulevard) between roughly 60th Street and Shore Parkway, is lined with predominantly small, Italian family-owned businesses—many of which have remained in the same family for several generations. 86th Street is another popular local thoroughfare, lined by the arches of the elevated BMT West End Subway Line. The 18th Avenue Station was popularized in opening credits of Welcome Back, Kotter. Rosebank in Staten Island was another one of NYC's main areas of Italian immigrants since the 1880s, and their descendants have continued as its predominant ethnic group, exemplified by the location of the Garibaldi Memorial in the community. In recent years, the town has experienced an influx of other ethnic groups, including Eastern Europeans, various Latin nationalities as well as Asians, particularly from the Philippines. Today, the South Shore of Staten Island is the most heavily populated Italian area in the City of New York. Over 95% of the South Shore is Italian. The neighborhoods of the South Shore with large percentages of Italians are Huguenot, Annadale, Eltingville, and Tottenville. Howard Beach in the Queens is also home to a large Italian population.[249]
During the beginning of the Cold War, immigration into the United States from Italy was almost impossible. The American government did not want foreigners entering during an intense period of history, especially those immigrating to New York City. Americas were frightened that these immigrants could be terrorists, thus preventing Italians from gaining citizenship. As the Cold War continued, organization groups such as the Italian American Organization and the American Committee on Italian Migration (ACIM) started to form. They created vast efforts to provide assistance and aid to Italian immigrants coming into the United States. Throughout the Cold War, these organizations increased rapidly with many American Italian members as well as many new coming Italians. ACIM also took a leading role in directing the efforts of other Italian American and Catholic organizations that helped contribute to Italian immigration. These organizations provided new migrants with housing, clothing, access to job interviews, and education for children. Italians already living in America volunteered by making house visits to those immigrants who have just settled down in their new homes. These house visits made the intense and rigorous migration journey easier while allowing the Italian American community within New York City to grow. Immediately after the Cold War period, Italian Americans further consolidated and solidified their status as members of the American mainstream.[250]
Philadelphia
[edit]
Philadelphia's Italian American community is the second-largest in the United States. Italian Americans compose 21% of South Philadelphia's 163,000 people, and the area has numerous Italian stores and restaurants. Philadelphia is well known for its Italian Market in South Philadelphia. The Italian Market is the popular name for the South 9th Street Curb Market, an area of Philadelphia featuring many grocery shops, cafes, restaurants, bakeries, cheese shops, and butcher shops, many with an Italian influence. The "outdoor" market features bright, colorful metal awnings that cover the sidewalks where vendors of fruit, vegetables, fish, and housewares conduct business year round. Ground floor shops in traditional Philadelphia rowhouses line the street. Owners originally lived above their shops, and many still do.
South Philadelphia has produced many well-known Italian American popular singers and musicians, including: Tony Mottola (famous for the "Tony Mottola" or "Danger" Chord), Frankie Avalon, Bobby Rydell, Mario Lanza, Al Martino, Jim Croce, Fabian Forte, Joey DeFrancesco, Buddy DeFranco, Fred Diodati (lead singer of The Four Aces), Buddy Greco, Charlie Ventura, Eddie Lang, Joe Venuti, Mark Valentino and Vinnie Paz, Vincent "Jimmy Saunders" LaSpada.
Boston
[edit]
The North End in Boston since the early 20th century became the center of the Italian community of Boston. It is still largely residential and well known for its small, authentic Italian restaurants and for the first Italian cafe, Caffe Vittoria. The influx of Italian inhabitants has left a lasting mark on the area; many seminal Italian American.[251] Prince Pasta was begun by three Sicilian immigrants Gaetano LaMarco, Giuseppe Seminara, and Michele Cantella. Pastene was formed by Sicilian immigrant Luigi Pastene. Both companies have grown into million-dollar-a-year businesses, and continue to be successful to the present day. To fully understand the sheer size of the Italian immigrant population, one must look back at the groups that preceded them. The Irish, at their peak, numbered roughly 14,000 and the Jews numbered 17,000. The Italians, however, peaked at over 44,000.[251]
Newark
[edit]
In its heyday, Seventh Avenue in Newark was one of the largest Little Italy neighborhoods in the U.S., with a population of 30,000, in an area of less than a square mile. The center of life in the neighborhood was St. Lucy's Church, founded by Italian immigrants in 1891. Throughout the year, St. Lucy's and other churches sponsored processions in honor of saints that became community events. The most famous procession was the Feast of St. Gerard, but there were also great feasts for Our Lady of Mt. Carmel, Our Lady of Snow, the Assumption, and St. Rocco. Joe DiMaggio loved the restaurants of Seventh Avenue so much that he would take the New York Yankees to Newark to show them "real Italian food". Frank Sinatra had bread from Giordano's Bakery sent to him every week until his death, no matter where in the world he was. New York Yankees catcher Rick Cerone also grew up in the First Ward. One of the nation's largest Italian newspapers, The Italian Tribune, was founded on Seventh Avenue. Seventh Avenue produced stars such as Joe Pesci and Frankie Valli of the Four Seasons. Congressman Peter Rodino, Chairman of the House Judiciary Committee during its impeachment proceedings against Richard Nixon was a native of the First Ward as well. Seventh Avenue was notoriously devastated by urban renewal efforts during the 1950s. Eighth Avenue was obliterated by the city council, scattering the Italian American residents. Most of its businesses never recovered. The construction of Interstate 280 also served to cut the neighborhood off from the rest of the city. After the devastating urban renewal, some of the First Ward's Italians stayed in the neighborhood, while others migrated to other Newark neighborhoods like Broadway, Roseville and the Ironbound. [252]
Chicago
[edit]The neighborhood around Chicago's Taylor Street has been called the port of call for Chicago's Italian American immigrants.[253] Taylor Street's Little Italy was home to Hull House, an early settlement house, founded by Jane Addams and Ellen Starr in 1889. Chicago's Italian American experience begins with the mass migration from the shores of southern Italy, the Hull House experiment, the Great Depression, World War II, and the machinations behind the physical demise of a neighborhood by the University of Illinois in 1963.
Italian Americans dominated the inner core of the Hull House neighborhood, 1890s–1930s.[254] One of the first newspaper articles about Hull House (Chicago Tribune, May 19, 1890) is an invitation, written in Italian, to the residents of the Hull House neighborhood signed, "Le Signorine, Jane Addams and Ellen Starr".
The 1924 historic picture, Meet the "Hull House Kids", was taken by Wallace K. Kirkland Sr., one of the Hull House directors. It served as a poster for Jane Addams and the Hull House Settlement House. All twenty kids were first generation Italian Americans...all with vowels at the end of their names.
As suburbs grew in the post-World War II era, Chicago's Italian American population spread from the central city, such as to Elmwood Park. Harlem Avenue, "La Corsa Italia", is lined with Italian stores, bakeries, clubs and organizations. The Feast of our Lady of Mount Carmel, in nearby Melrose Park, has been a regular event in the area for more than one hundred years. The near-west suburbs of Melrose Park, Schiller Park, Franklin Park, River Grove, Norridge, Chicago Heights, and Harwood Heights are also home to many Italian Americans. West suburban Stone Park is home of Casa Italia, an Italian American cultural center.
Northwest of Chicago, the city of Rockford has a large population of Italian Americans. Other historical Italian American communities in Illinois include Peoria, Ottawa, Herrin, Quad Cities and the Metro East suburbs of Saint Louis, Missouri.
Milwaukee
[edit]Italians first came to Milwaukee, Wisconsin, in the late 19th century. Then in the 19th and 20th centuries large numbers of Italian immigrants began to come in mainly from Sicily and southern Italy. Brady Street, the historic Third Ward and the east side of Milwaukee is considered the heart of Italian immigration to the city, where as many as 20 Italian grocery stores once existed on Brady Street alone. Every year the largest Italian American festival in the United States, Festa Italiana, takes place in Milwaukee. Italian Americans number at around 16,992 in the city, but in Milwaukee County they number at 38,286.[255] There is also an Italian newspaper called The Italian Times printed by the Italian Community Center (ICC).
St. Louis
[edit]Italian immigrants from the northern Italian region of Lombardy came to St. Louis in the late 19th century and settled in the region called The Hill. As the city grew, immigrants from Southern Italy settled in a different neighborhood north of Downtown St Louis. Professional baseball players Joe Garagiola and his boyhood friend, Yogi Berra, grew up on The Hill. Americans of Italian descent in St. Louis have contributed to local cuisine, i.e. Imo's Pizza and toasted ravioli. As of 2021 there are approximately 2,000 native born Italians living in St. Louis, few of whom live in The Hill neighborhood. Italians today live mostly throughout the St. Louis metropolitan region. The Italian Community of St. Louis (Comunita' Italiana di St. Louis), an organization that promotes the Italian language and culture, has several popular events which include Carnevale[256] which occurs every February and Ferragosto which occurs each August. The St. Louis Italian Language Program also exists on the Hill at Gateway Science Academy on Fyler Avenue.[257]
Los Angeles
[edit]Los Angeles is home to the largest Italian American community in California (and on the West Coast), with 95,300 people identifying as Italian American.[258] San Pedro is Los Angeles's Little Italy, which is estimated to contain some 45,000 Italian-Americans. Most worked as fisherman during the first half of the 20th century. The traditional center of Los Angeles' Italian American community was the area north of the historic Los Angeles Plaza. It survived somewhat intact until the construction of Los Angeles Union Station, in 1939. The station was built in the center of Los Angeles' Old Chinatown, displacing half of the total Chinese community. The Chinese were allowed to relocate to Little Italy, where they quickly outnumbered the Italian community. Only a few relic-businesses survive, such as San Antonio Winery (the only winery, out of 92, to survive prohibition).[259] The Italian American Museum of Los Angeles opened in 2016 in the historic Italian Hall.[260] Lincoln Heights, northeast of Little Italy, also was a center of the Italian-American population in Los Angeles.
San Francisco
[edit]
According to the 1940 census, 18.5% of all European immigrants were Italian, the largest in the city. North Beach is San Francisco's Little Italy, and has historically been home to a large Italian American population. The American Planning Association (APA) has named North Beach as one of ten 'Great Neighborhoods in America'.[261]
Detroit
[edit]The first ethnic Italian in Detroit was Alphonse Tonty (Italian name: Alfonso Tonti), a Frenchman with an Italian immigrant father. He was the second-in-command of Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac, who established Detroit in 1701. Tonti's child, born in 1703, was the first ethnic European child born in Detroit. Tonti became the commander of the Detroit fort after Cadillac left to return to France.
In order to preserve the fur trade, the French administrators and the British administrators discouraged immigration, so the Italian population had slow growth. Growth in immigration increased after Detroit became a part of the United States and the Erie Canal had been constructed. Armando Delicato, author of Italians in Detroit, wrote that Italian immigration to Detroit "lagged behind other cities in the East".
In 1904 the City of Detroit had 900 Italians. In Metro Detroit there were several thousand ethnic Italians by 1900. The concentrations of the population lived in Eastern Market and east of the area presently known as Greektown. Of those Italians in 1900 most originated from Genoa, Lombardy, and Sicily. Some Italians stayed in Detroit temporarily before traveling onwards to mines in northern Michigan.
The increase in the automobile industry resulted in the increase of the Italian population in the 20th century. By 1925, the number of Italians in the City of Detroit increased to 42,000. The historical center of Detroit's Italian-American community was in an area along Gratiot Avenue, east of Downtown Detroit. During that period, Italian immigrants and their children lived throughout the City of Detroit, and several neighborhoods had concentrations of Italian immigrants. There were larger numbers of southern Italians than those from the north. Armando Delicato, author of Italians in Detroit, wrote that "Unlike many other American cities, no region of Italy was totally dominant in this area". Steve Babson, author of Working Detroit: The Making of a Union Town, wrote that "Many northern Italians, coming from an urban and industrialized society, had little in common with local Sicilians, who came from the rural and clannish south." In Detroit's history, within the crafts Italians concentrated on tileworking.
During World War II, Fort Wayne (Detroit) served as home to Italian prisoners of war (POWs) captured during the North African campaign. After Italy's surrender in September 1943, the POWs were given the opportunity to work as servants, cooks, and janitors. At the end of the war many chose to remain and settle in Detroit.
As of 1951, Detroit had about 150,000 Italians.
The National Italian American Foundation estimated that in 1990, Metro Detroit had 280,000 ethnic Italians. As of 2005 the closest remaining large Little Italy near Detroit was Via Italia in Windsor, Ontario and there was a group of remaining Italian shops and restaurants along Garfield Road in Clinton Township. In 2005 Delicato wrote that "Unlike some other national groups, like the Poles, who still look to Hamtramck, or the Mexicans, who have Mexicantown, Italian Detroiters no longer have a geographical center".
Cleveland
[edit]
Cleveland's Little Italy, also known as Murray Hill, is the epicenter of Italian culture in Northeast Ohio, a combined statistical area reporting 285,000 (9.9%)[262] Italian Americans.[263] Little Italy took root when Joseph Carabelli, immigrating in 1880, saw the opportunity for monument work in Cleveland's Lake View Cemetery and established what soon became the city's leading marble and granite works. Most fresco and mosaic work in Cleveland was accomplished by Italian artist immigrants.[264] Local Cleveland industrial billionaire John D. Rockefeller took a special liking to the Italian immigrants of the neighborhood and commissioned the building of the community center Alta House, named after his daughter Alta Rockefeller Prentice, in 1900. In 1906, Italian immigrant Angelo Vitantonio invented the first hand-crank pasta machine, which made pasta much easier to produce by eliminating the need to flatten and cut it by hand.[265] Some other famous Italian Americans from Northeast Ohio included Anthony J. Celebrezze (49th Mayor of Cleveland), Ettore "Hector" Boiardi (Chef Boyardee), Frank Battisti (Federal Judge), and Dean Martin, born Dino Paul Crocetti in Steubenville, Ohio.
Ohio's largest outdoor Italian American street festival, the Feast of the Assumption (Festa dell'assunzione), takes place the weekend of August 15 every year and draws over 100,000 people to the Little Italy neighborhood.[266] The festival is sponsored by the congregation of Holy Rosary Church, which was founded in 1892 with the current church built in 1905.
Kansas City
[edit]Attracted by employment in its growing railroad and meat packing industries, Italians primarily from Calabria and Sicily immigrated to Kansas City in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Kansas City's Calabrese mainly passed through the port of New York, sometimes stopping in industrial cities like Pittsburgh along the way, en route to their final destination in the Midwest. Meanwhile, Kansas City's Sicilian community generally came through the port of New Orleans, staying there for a decade or more before bringing their families north. In Kansas City, these communities settled close to one another, often overlapping: the Sicilians taking root in what is now known as the River Market and Columbus Park neighborhoods, and the Calabrese mainly settling in the adjacent "Old Northeast" area.
New Orleans
[edit]Economics in Louisiana and Sicily combined to bring about what became known as the Great Migration of thousands of Sicilians. The end of the Civil War allowed the freed men the choice to stay or to go, many chose to leave for higher paying jobs, which in turn led to a perceived scarcity of labor resources for the planters. Northern Italy enjoyed the fruits of modern industrialization, while southern Italy and Sicily suffered destitute conditions under the system of absentee landowners. The peasant was still essentially the serf in the system. Emigration not only offered peasants a chance to move beyond subsistence living, it also offered them a chance to pursue their own dreams of proprietorship as farmers or other business owners. On March 17, 1866, the Louisiana Bureau of Immigration was formed and planters began to look to Sicily as a possible solution to their labor needs. Steamship companies advertisements were very effective in recruiting potential workers. Three steamships per month were running between New Orleans and Sicily by September 1881 at a cost of only forty dollars per person.
In 1890 the ethnic Irish chief of police, David Hennessy was assassinated. Suspicion fell on Italians, whose growing numbers in the city made other whites nervous. The March 14, 1891 New Orleans lynchings were the largest ever mass lynchings in Louisiana history. The use of the term "mafia" by local media in relation to the murder is the first-known usage of the word in print.
Syracuse
[edit]
Italian immigrants first came to the area around Syracuse, New York (a city named for Siracusa, Sicily) in 1883 after providing labor for the construction of the West Shore Railroad. At first, they were quite transient and came and went, but eventually settled down on the Northside.[267] By 1899, the Italian immigrants were living on the Northside of the city in the area centered around Pearl Street.[268] The Italians all but supplanted the Germans in that area of the city and had their own business district along North State and North Salina Streets.[269] By September 2009, Syracuse's Little Italy district received millions of dollars of public and private investment for new sidewalks, streetscapes, landscaping, lighting and to set up a "Green Train" program, which trains men to work in green construction and renovation industries.[270] In recent years, the neighborhood is a mix of Italian shops, restaurants and businesses that cater to the area's South Asian and African population. Although the neighborhood is far less Italian than in past years, banners throughout the district still read Little Italy.[271] By 2010, demographics showed that 14.1% of the population in Syracuse was Italian descent.[272]
Providence
[edit]Federal Hill in Providence, Rhode Island, is best known for its Italian American community and abundance of restaurants. The first two decades of the 20th century witnessed heavy Italian American immigration into Federal Hill. Though the area today is more diverse, Federal Hill still retains its status as the traditional center for the city's Italian American community. The neighborhood features a huge square dedicated to Giuseppe Garibaldi, a monumental gateway arch decorated with La Pigna sculpture (a traditional Italian symbol of welcome, abundance, and quality) and a DePasquale Plaza used for outdoor dining. Providence's annual Columbus Day parade marches down Atwells Avenue.
Tampa-Ybor City
[edit]
The community of Ybor City in Tampa, Florida is a cigar-centric company town founded in 1885 and originally populated by a unique mix of Spanish, Cuban, Jewish, and Italian immigrants, with most of the Italians coming from a small group of villages in southwestern Sicily. At first, Italians found it difficult to find employment in the insular and guild-like cigar industry, which had moved to Tampa from Cuba and Key West and was dominated by Hispanic workers. Many founded businesses to serve cigar workers, most notably small grocery stores in the neighborhood's commercial district supplied by Italian-owned vegetable and dairy farms located on open land east of Tampa's city limits.[273] The immigrant cultures in town became better integrated as time went by; eventually, approximately 20% of the workers in the cigar industry were Italian Americans. The tradition of local Italian-owned groceries continued, however, and a handful of such businesses founded in the late 1800s were still operating into the 21st century.[274] Many descendants of Sicilian immigrants eventually became prominent local citizens, such as mayors Nick Nuccio and Dick Greco.
Birmingham
[edit]Birmingham, Alabama, was representative of smaller industrial centers. Most Italians in the early 20th century came to work in the burgeoning iron and coal industries. Dorothy L. Crim founded the Ensley Community House in the Italian district in 1912 at the behest of the Birmingham City Mission Board. From 1912 to 1969, Ensley House eased the often difficult transition to American life by providing direct assistance such as youth programs and day care services, social clubs, and 'Americanization' programs.[275]
San Diego
[edit]
Historically, Little Italy in San Diego was the home to Italian fishermen and their families. Many Italians moved to San Diego from San Francisco after the 1906 San Francisco earthquake in search of tuna and other deep-sea sport and commercial fish.[276] When Interstate 5 was constructed through Little Italy in the early 1970s, 35% of the neighborhood was destroyed and during the same time the California tuna industry was declining, which caused the neighborhood to suffer nearly 30 years of decline.[277] With the creation of the Little Italy Association in 1996, the neighborhood has gone through gentrification and has seen a renaissance as Community Benefit District specializing in Italian food, boutique shopping and maintenance that makes this shopping district the place to live in Downtown San Diego. Prior to gentrification, the neighborhood was mainly composed of low-density commercial businesses and single-family detached homes. Currently, the neighborhood is mainly composed of residential units, mostly mid-rises, high-rises, and lofts, with ground floor retail stores and a few commercial buildings.
West Virginia
[edit]Tens of thousands of Italians came to West Virginia during the late 1800s and early 1900s to work in the coal camps. As pick-and-shovel miners, Italians hold most of the state's coal production records. One Carmine Pellegrino mined 66 tons of coal by hand in a 24-hour period.[278] Italian miners created the pepperoni roll, a popular snack throughout the region. Many of these immigrants left for larger cities once they earned enough money, but some of their descendants remain, particularly in the north central counties. The communities of Clarksburg, Wheeling, and Bluefield each hold their own annual Italian Heritage Festival. Fairmont puts on a street festival every December that pays homage to the Feast of the Seven Fishes, an Italian tradition of eating seafood dishes on Christmas Eve instead of meat. The senior U.S. senator from West Virginia, Joe Manchin, is of Italian descent.
Arkansas
[edit]There was a historical trend of immigration of Italians into the U.S. state of Arkansas in the 19th and 20th centuries.
Austin Corbin, the owner of the Sunnyside Plantation in Chicot County, within the Arkansas Delta region, decided to employ Italians there during the post-Reconstruction period. The Mayor of Rome, Don Emanuele Ruspoli, connected to Corbin, found potential employees who originated in Emilia-Romagna, Marche, and Veneto, convincing them to go to Sunnyside. 98 families boarded the Chateau Yquem in Genoa with New Orleans as the destination. In November 1895, the ship docked in the United States, and the surviving passengers traveled onward to Sunnyside. The climate and drinking water conditions were difficult. A descendant of these Italians, Libby Borgognoni, stated that 125 of them died during the first year of operations. Corbin had misrepresented the nature of the plantation to the potential employees. Italians came to Sunnyside even after Corbin's death in 1896.
Italians later moved from the Arkansas Delta to the Ozarks, establishing Tontitown.[279]
Baltimore
[edit]Italians began to settle in Baltimore during the late 1800s. Some Italian immigrants came to the Port of Baltimore by boat. The earliest Italian settlers in Baltimore were sailors from Genoa, the capital city of the Italian region of Liguria, who arrived during the 1840s and 1850s. Later immigrants came from Naples, Abruzzo, Cefalù, and Palermo. These immigrants created the monument to Christopher Columbus in Druid Hill Park.[280] Many other Italians came by train after entering the country through New York City's Ellis Island. Italian immigrants who arrived by train would enter the city through the President Street Station. Because of this, Italians largely settled in a nearby neighborhood that is now known as Little Italy.
Little Italy comprises six blocks bounded by Pratt Street to the North, the Inner Harbor to the South, Eden Street to the East, and President Street to the West. Other neighborhoods where large numbers of Italians settled include Lexington, Belair-Edison, and Cross Street. Many settled along Lombard Street, which was named after the Italian town of Guardia Lombardi. The Italian community, overwhelmingly Roman Catholic, established a number of Italian American parishes such as St. Leo's Church and Our Lady of Pompeii Church. The Our Lady of Pompeii Church holds the annual Highlandtown Wine Festival, which celebrates Italian-American culture and benefits the Highlandtown community association.[281]
The August 2016 Central Italy earthquake affected Baltimore's Italian community, as many Baltimore Italian-Americans have friends or relatives living in Italy. Most Italians in Baltimore are of Southern or Central Italian descent, especially from Abruzzo, a region of Southern Italy close to the epicenter of the earthquake. St. Leo the Great Catholic Church in Little Italy held a vigil and sent prayers to the victims and survivors of the earthquake.[282]
Mississippi
[edit]Italians have settled in the state of Mississippi since colonial times, although numbers have increased over the years. Since the 18th and mainly the 19th century, Italian settlers have been located in cities and towns across Mississippi. In 1554, Mississippi began to have a real Italian presence, because of the Hernando de Soto expedition. The first Italians who visited Mississippi came in explorations conducted by the French and Spanish governments.
In the 19th century, many Italians entered the United States in New Orleans and traveled onwards to Mississippi.[283] Over 100 immigrants lived in Mississippi as the American Civil War started. In the late 19th century, Italian immigration increased in the United States, which made a tremendous impact on the area.[284] Some of them went to work in the so-called "Mississippi Delta" in the cotton plantations, and even helped the development of the blues music with their mandolins.
The late 19th century saw the arrival of larger numbers of Italian immigrants who left Italy seeking economic opportunities. Some Italians from Sicily settled as families along the Mississippi Gulf Coast in Biloxi, Ocean Springs, and Gulfport, preserving close ties with those in their homeland. They worked in the fishing and canning industries. Others were merchants, operating grocery stores, liquor stores, and tobacco shops. Biloxi's prosperous tourist industry in the early 20th century created opportunities for ambitious young (Italian) men ... Italians also settled in the Mississippi Delta. The first immigrants came there in the 1880s, working to repair levees and staying as hired farm laborers on plantations. Some of these families became peddlers selling goods to farmers. In 1895, the first Italians came to the Sunnyside Plantation, across the Mississippi River in the Arkansas Delta. That plantation would become the stopping off place for many Italian settlers along both sides of the river. They were mostly from central Italy and experienced in farm work. — Charles Reagan Wilson (University of Mississippi)[This quote needs a citation]
Denver
[edit]Large numbers of Italians first came to Colorado in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. Some settled in industrial Pueblo or in Welby, which was then a farming community, but the largest Italian community in twentieth century Colorado was in Northwest Denver, or as it was known at the time, "the North Side" or "North Denver."[285]
Italians first put down roots there because St. Patrick's Catholic Church, a largely Irish-descended congregation, already existed in the neighborhood. In 1894, the Italian community on the North Side formed its own Catholic church called Our Lady of Mt. Carmel.[285] The community remained strong through the early twentieth century, but in the decades after World War II, many Italian-Americans left Denver proper. Today, descendants of the old North Side Italian-American community are spread across metro Denver, particularly in its inner northwestern suburbs like Wheat Ridge, Westminster and Arvada.[286] The Sons of Italy's Denver-area lodge is on 32nd Avenue in Wheat Ridge.[287] Many Italian Americans without deep roots in Colorado have also settled in the Denver area and other parts of the state throughout the last decades of the twentieth century and in the new millennium.
Reminders of the old Italian community in Northwest Denver are few and far between today. Many of the remaining landmarks are on 38th Avenue. One is Gaetano's, a storied Italian American eatery on 38th Avenue and Tejon Street once owned by the Smaldone family, which was involved in bootlegging in Denver.[288] Many members of the Italian-American community in Northwest Denver could trace their roots to Potenza, a comune in Basilicata. A fraternal organization called the Potenza Lodge was founded in 1899 and still exists today on the corner of Shoshone Street and 38th Avenue.[289] Leprino Foods, a company founded by a Denver Italian-American which makes mozzarella cheese and other dairy products, has its global headquarters on 38th Avenue across Shoshone Street from the Potenza Lodge.[290]
Our Lady of Mt. Carmel is still important to some Italian-American families with roots in Northwest Denver, but there are Catholic churches with sizable Italian-American populations spread throughout the Denver area today.
Las Vegas
[edit]There is a significant Italian American community in Las Vegas.[291]

Demographics
[edit]
In the 2000 U.S. census, Italian Americans constituted the fifth largest ancestry group in America with about 15.6 million people, 5.6% of the total U.S. population.[4] As of 2006, the U.S. census estimated the Italian American population at 17.8 million persons, or 6% of the population,[292][293] constituting a 14% increase over the six-year period.
In 2010, the American Community Survey enumerated Americans reporting Italian ancestry at nearly 17.6 million, 5.8% of the U.S. population; in 2015, 17.3 million, 5.5% of the population. A decade thereafter, in 2020, the U.S. Census Bureau recorded slightly more than 16.5 million Americans reporting full or partial Italian ancestry, about 5.1% of the U.S. population.[294][295][296] As ancestry is self-reported, the decline in Italian identification in the 21st century may merely reflect growing Americanization and cultural assimilation of Italian Americans into the broader identity of White Americans, with younger generations increasingly intermixed with other European Americans: the number of Americans who reported being solely of Italian ancestry alone fell by 928,044—from 7,183,882 in 2010 to 6,652,806 in 2015 to 5,724,762 in 2020.[297][298][299] However, by contrast, the number of Americans who reported being of Italian ancestry mixed with another ancestry grew by 436,334—from 10,387,926 in 2010 to 10,632,691 in 2015 to 10,824,260 in 2020.[300][301][302]
U.S. states number and percentage Italian American in 2020[303][294][304][305]
| State | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| 78,547 | 1.61% | |
| 20,629 | 2.80% | |
| 297,383 | 4.15% | |
| 44,534 | 1.48% | |
| 1,414,190 | 3.59% | |
| 275,803 | 4.85% | |
| 590,721 | 16.54% | |
| 81,036 | 8.37% | |
| 27,731 | 3.95% | |
| 1,222,217 | 5.76% | |
| 234,113 | 2.23% | |
| 30,019 | 2.11% | |
| 54,112 | 3.08% | |
| 726,216 | 5.71% | |
| 180,628 | 2.70% | |
| 63,176 | 2.01% | |
| 62,266 | 2.14% | |
| 90,775 | 2.03% | |
| 200,407 | 4.30% | |
| 76,133 | 5.68% | |
| 291,816 | 4.83% | |
| 825,642 | 12.01% | |
| 452,303 | 4.53% | |
| 124,817 | 2.23% | |
| 53,122 | 1.78% | |
| 204,254 | 3.34% | |
| 38,075 | 3.59% | |
| 49,349 | 2.57% | |
| 158,170 | 5.22% | |
| 137,322 | 10.13% | |
| 1,353,075 | 15.23% | |
| 46,352 | 2.21% | |
| 2,320,549 | 11.89% | |
| 334,430 | 3.20% | |
| 8,767 | 1.15% | |
| 715,494 | 6.13% | |
| 69,023 | 1.75% | |
| 154,010 | 3.69% | |
| 1,430,006 | 11.18% | |
| 172,852 | 16.34% | |
| 153,895 | 3.02% | |
| 10,732 | 1.22% | |
| 152,739 | 2.26% | |
| 523,680 | 1.83% | |
| 86,754 | 2.75% | |
| 45,447 | 7.28% | |
| 332,213 | 3.90% | |
| 255,671 | 3.40% | |
| 77,548 | 4.29% | |
| 200,205 | 3.45% | |
| 18,338 | 3.15% | |
| 16,549,022 | 5.07% |
U.S. states with over 10% people of Italian ancestry
[edit]- Rhode Island 18.9%[306]
- Connecticut 18.7%[307]
- New Jersey 16.8%[308]
- New York 15.93%[309]
- Massachusetts 13.9%[310]
- Pennsylvania 12.2%[311]
- New Hampshire 10.7%[312]
- Delaware 10.1%[312]
U.S. communities with the most residents of Italian ancestry
[edit]The top 20 U.S. communities with the highest percentage of people claiming Italian ancestry are:[313]
- Fairfield, New Jersey 50.3%
- Johnston, Rhode Island 49.5%
- North Branford, Connecticut 43.9%
- East Haven, Connecticut 43.6%
- Hammonton, New Jersey 43.2%
- Ocean Gate, New Jersey 42.6%
- East Hanover, New Jersey 41.3%
- North Haven, Connecticut 41.2%
- Cedar Grove, New Jersey 40.8%
- Wood-Ridge, New Jersey 40.6%
- North Providence, Rhode Island 38.9%
- Dunmore, Pennsylvania 38.9%
- Newfield, New Jersey 38.8%
- Saugus, Massachusetts 38.5%
- Jenkins, Pennsylvania 38.4%
- West Pittston, Pennsylvania 37.9%
- Old Forge, Pennsylvania 37.8%
- Lowellville, Ohio 37.5%
- Hughestown, Pennsylvania 37.5%
- Prospect, Connecticut 37.5%
U.S. places named for Italian Americans
[edit]- Busti, New York (Town and village name)
Socioeconomic Status/Demographics
[edit]In 2023 Italian Americans had a Per Capita Income of $55,349, significantly higher than $43,313 which is the Per Capita Income for the Total Population and higher than $50,675 for all White Americans. Italian American Males and Females had median earnings of $80,234 and $63,952, respectively. This is significantly higher than $63,975 and $52,370 for the Total Population. Italian Americans had a Median Household Income of $94,003, significantly higher than the Total Population and a household size that was smaller than the Total Population.
In terms of education, Italian Americans are generally much more educated than the Total Population. 96.2% of Italian Americans have attained a High School graduate and 46.1% have attained a Bachelor's degree or higher.
52.1% of Italian Americans work in Management, business, science, and arts occupations, but the community also has a large population working in Sales and office occupations.[314]
Notable people
[edit]See also
[edit]- Sicilian Americans
- List of Italian-American neighborhoods
- Little Italys in the United States
- History of Italians in Baltimore
- History of Italian Americans in Boston
- History of Italian Americans in Metro Detroit
- History of Italians in Mississippi
- Italians in New Orleans
- Italians in New York City
- History of Italian Americans in Philadelphia
- Utah Italians
- Tontitown, Arkansas
- Valdese, North Carolina
- List of Italian-American actors
- List of Italian Americans in sports
- Order Sons of Italy in America
- Italian-American cuisine
- American Mafia
- Italy–USA Foundation, based in Rome
- Italy–United States relations,
- Italian diaspora, worldwide
- Anti-Italianism, worldwide
- Italophilia
References and notes
[edit]- ^ a b "Races and Ethnicities USA 2020". United States census. September 21, 2023. Retrieved October 21, 2023.
- ^ "AMERICAN ITALIAN SLANG WORDS". LETS LEARN SLANG. June 15, 2021.
- ^ "American-Italian dictionary". americanitalian.net.
- ^ a b Brittingham, Angela, and G. Patricia De La Cruz (2004). Ancestry: 2000 Archived 2004-12-04 at the Library of Congress Web Archives Washington, D.C.: U.S. Dept. of Commerce, Economics and Statistics Administration, U.S. Census Bureau.
- ^ a b c Annual Report of the Immigration and Naturalization Service 1966 (PDF). Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office. June 1967. pp. 55–58. Retrieved July 13, 2022.
- ^ a b "Table 1: Italian Immigration To The United States By Years". Mtholyoke.edu. Archived from the original on November 4, 2020. Retrieved October 7, 2017.
- ^ Wepman, Dennis (2008). Immigration. Infobase Publishing. p. 171. ISBN 978-1-4381-0810-0.
- ^ a b Mangione, Jerre and Ben Morreale, La Storia: Five Centuries of the Italian American Experience, Harper Perennial, 1992
- ^ Frank J. Cavaioli, "Patterns of Italian immigration to the United States" Catholic Social Science Review 13 (2008): 213-229 at p. 220.
- ^ "Who Was Shut Out?: Immigration Quotas, 1925-1927". History Matters.
- ^ Pellegrino A D'Acierno (October 1, 1998). The Italian American Heritage: A Companion to Literature and Arts. Routledge.
- ^ Andrew F. Rolle, The immigrant upraised: Italian adventurers and colonists in an expanding America (Oklahoma UP, 1968) pp. 3–15.
- ^ Though the modern state of Italy had yet to be established, the Latin equivalent of the term Italian had been in use for natives of the region since antiquity. See Pliny the Elder, Letters 9.23.
- ^ Greene, George Washington (1837). The Life and Voyages of Verrazzano. Cambridge University: Folsom, Wells, and Thurston. p. 13. Retrieved August 18, 2017 – via Google Books.
- ^ a b Martone, Eric (2016). Italian Americans: The History and Culture of a People. ABC-CLIO. p. 504. ISBN 978-1-6106-9995-2.
- ^ "Universalis cosmographia secundum Ptholomaei traditionem et Americi Vespucii alioru[m]que lustrationes". Archived from the original on January 9, 2009. Retrieved September 8, 2014.
- ^ a b "Henri de Tonti (1649–1704)". Encyclopedia of Arkansas. 2011. Retrieved December 6, 2019.
- ^ a b HMdb.org, "Henri de Tonti Historical Marker", Natchitoches Parish, Louisiana. Retrieved August 9, 2009.
- ^ "Peter Caesar Alberti". Archived from the original on September 14, 2015. Retrieved June 2, 2011.
- ^ Memorials of the Huguenots in America, by Ammon Stapleton, page 42
- ^ "Biography of George Wythe". Archived from the original on May 28, 2019. Retrieved October 7, 2017.
- ^ Arthur, Stanley Clisby; Huchet de Kernion, George Campbell (1998). Old families of Louisiana. Gretna, Louisiana: Pelican Pub. Co. ISBN 1565544560. OCLC 44521358.
- ^ a b Williams, T. Harry (1955). P.G.T. Beauregard: Napoleon in Gray. Louisiana State University Press. ISBN 0-8071-0831-6. LCCN 55-7362.
- ^ Bartlett, John Russell (1860). Records of the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, in New England: 1741-1756. A. C. Greene and brothers, state printers. p. 340.
- ^ New York Historical Society (1896). Publication Fund Series. New York Historical Society. p. 430.
- ^ Harper's Magazine. Harper's Magazine Company. 1882. p. 493.
- ^ Prominent Families of New York (PDF). The New York Historical Company. 1898. Retrieved May 26, 2021.
- ^ Andrew F. Rolle, The immigrant upraised: Italian adventurers and colonists in an expanding America (U of Oklahoma Press, 1968).
- ^ Filippo Mazzei, The Virginia Gazette, 1774. Translated by a friend and neighbor, Thomas Jefferson:
Translated by Jefferson as follow:Tutti gli uomini sono per natura egualmente liberi e indipendenti. Quest'eguaglianza è necessaria per costituire un governo libero. Bisogna che ognuno sia uguale all'altro nel diritto naturale.
All men are by nature equally free and independent. Such equality is necessary in order to create a free government.
All men must be equal to each other in natural law - ^ "About". Department of Modern Languages and Literatures, College of William and Mary. Archived from the original on October 5, 2013. Retrieved June 17, 2019.
- ^ "Bellini Colloquium". William & Mary. Retrieved May 11, 2021.
- ^ "BostonFamilyHistory.com – The Place to Meet Your Past". Bostonhistorycollaborative.com. Archived from the original on October 4, 2013. Retrieved August 10, 2014.
- ^ http://article/italians-in-america-band-leaders-a173703 [dead link]
- ^ "History of the Directors".
- ^ "Pise, Charles Constantine", in John Julian (1907/1957), A Dictionary of Hymnology, reprint, New York: Dover, Vol. 2, p. 1687.
- ^ "Pise, Charles Constantine", in Catholic Encyclopedia (1913), New York: Robert Appleton Company.
- ^ "TROTTI, Samuel Wilds - Biographical Information". bioguide.congress.gov.
- ^ "The Transcontinental Railroad". Archives.gov. Retrieved October 7, 2017.
- ^ "Día de la Raza – Viva Cuernavaca". universaldomainexchange.com. Retrieved December 2, 2018.
- ^ House Resolution 269, dated 11 June 2002, written and sponsored by Rep. Vito Fossella.
- ^ Vincent A. Lapomarda, "Higher Education", in The Italian American Experience: An Encyclopedia, ed. Salvatore LaGumina (New York: Garland, 2000), p.286.
- ^ Rosanne Martorella, "Science", in The Italian American Experience: An Encyclopedia, ed. Salvatore LaGumina (New York: Garland, 2000), p.583.
- ^ NATIONAL ITALIAN AMERICAN FOUNDATION Archived 2013-05-20 at the Wayback Machine - Italian American Contributions.
- ^ Images: A Pictorial History of Italian Americans. New York, 1986, p.26
- ^ Belfiglio, Valentino J. (Spring–Summer 1978). "Italians and the American Civil War". Italian Americana. 4 (2): 164. JSTOR 41330626. Retrieved December 21, 2022.
- ^ Mack Smith, Denis, Garibaldi, Prentice-Hall, 1969, pp. 69–70
- ^ "APPENDIX A: Italian Immigration to the United States in the Last Twenty Years". Center for Migration Studies Special Issues. 7 (2): 101–118. March 1989. doi:10.1111/j.2050-411x.1989.tb00597.x. ISSN 2050-411X.
- ^ Mark Choate, Emigrant Nation: The making of Italy abroad. (Harvard University Press, 2008).
- ^ "Italian Immegration to the United States by Years". Mount Holyoke College. Archived from the original on October 25, 2020. Retrieved July 29, 2023.
- ^ Nelli (1980) p 545.
- ^ Thomas J. Archdeacon, Becoming American: An Ethnic History (Free Press, 1983), p. 139 online
- ^ Luciano J. Iorizzo, Italian immigration and the impact of the padrone system (1980) p. 160
- ^ "Italian". Library of Congress. Retrieved January 6, 2020.
- ^ Alfred T. Banfield, ""The padrone, the sojourners, and the settlers: a preface to the 'little Italics' of Maine." Maine Historical Society Quarterly (1992) Vol. 31 Issue 3/4, pp 114-141.
- ^ James Ciment; John Radzilowski (2015). American Immigration: An Encyclopedia of Political, Social, and Cultural Change: An Encyclopedia of Political, Social, and Cultural Change. Routledge. p. 109. ISBN 978-1-317-47716-7.
- ^ Michael Burgan (2009). Italian Immigrants. Infobase Publishing. p. 29. ISBN 978-1-4381-0359-4.
- ^ Humbert S. Nelli, Italians in Chicago, 1880-1930 : a study in ethnic mobility (1970) pp. 18, 59.
- ^ Robert Higgs, "Race, Skills, and Earnings: American Immigrants in 1909" Journal of Economic History 31#2 (1971), pp. 420-428, table on p. 426 online
- ^ Robert A. Orsi, The Madonna of 115th Street: faith and community in Italian Harlem, 1880-1950 (Yale UP, 1985), pp. 156-160.
- ^ Orsi, 168-71, 204-207.
- ^ Nelli, Italians in Chicago, p. 203-204.
- ^ Glynn, Irial. "Emigration Across the Atlantic: Irish, Italians and Swedes compared, 1800–1950". European History Online. Retrieved October 7, 2017.
- ^ Michael Burgan and Robert Asher, Italian Immigrants (2004) p. 32
- ^ "Digital History". Digitalhistory.uh.edu. Retrieved October 7, 2017.
- ^ Bill Cribbs. "IMMIGRANTS FROM ITALY – Article from 1895". Genealogybuff.com. Retrieved August 10, 2014.
- ^ Staff (May 31, 1896) "Little Italy in New-York" The New York Times p.32
- ^ a b Moses, Paul (2015). An Unlikely Union: The Love-Hate Story of New York's Irish and Italians. New York University Press. p. 90.
- ^ John W. Briggs, An Italian Passage: Immigrants to Three American Cities, 1890-1930 (Yale University Press, 1978)
- ^ Gambino, Richard (1977). Vendetta: A True Story of the Worst Lynching in America, the Mass Murder of Sicilian Americans in New Orleans in 1891, the Vicious Motivations Behind it, and the Tragic Repercussions and Stereotypes that Linger to This Day. Doubleday. ISBN 0-385-12273-X.
- ^ Egolf, B; Lasker, J; Wolf, S; Potvin, L (1992). "The Roseto effect: a 50-year comparison of mortality rates". Am J Public Health. 82 (8): 1089–92. doi:10.2105/ajph.82.8.1089. PMC 1695733. PMID 1636828.
- ^ "Tontitown (Washington County) - Encyclopedia of Arkansas". Encyclopediaofarkansas.net. Retrieved October 7, 2017.
- ^ "Waldensians - NCpedia". Ncpedia.org. Retrieved October 7, 2017.
- ^ Crissouli (January 10, 2012). "That Moment in Time: CLARE CHATTER". Thatmomentintime-crissouli.blogspot.com. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ The Stone Carvers: Master Craftsmen of Washington National Cathedral, Marjorie Hunt, Smithsonian Books, November 1999
- ^ Giacomo Puccini's La Fanciulla del West. 100th Anniversary of World Premiere.
- ^ "Francesco Fanciulli". www.marineband.marines.mil. Retrieved May 11, 2021.
- ^ Eric Martone, ed. Italian Americans: the history and culture of a people (ABC-CLIO, 2016) pp 65–68.
- ^ Holli, Melvin G. (1999). The American Mayor. University Park: PSU Press. ISBN 0-271-01876-3.
- ^ Michael Miller Topp, "The Transnationalism of the Italian-American Left: The Lawrence Strike of 1912 and the Italian Chamber of Labor of New York City." Journal of American Ethnic History (1997): 39-63.
- ^ Philip V. Cannistraro, and Gerald Meyer, eds. The lost world of Italian American radicalism: politics, labor, and culture (Greenwood, 2003).
- ^ Iorizzo, Luciano J.; Mondello, Salvatore (1971). The Italian-Americans. New York, New York: Twayne Publishers. p. 100.
- ^ Baily, Samuel L. (1999). Immigrants in the Lands of Promise: Italians in Buenos Aires and New York City, 1870 - 1914. Ithaca, New York: Cornell University Press. pp. 207–208. ISBN 0-8014-3562-5.
- ^ McDonald, Robert Alexander Fyfe (1915). Adjustment of School Organization to Various Population Groups. Contributions to Education. Vol. 75. New York City, New York: Teachers College, Columbia University. pp. 72–73.
- ^ Ministero Degli Affari Esteri Commissariato dell'Emigrzione (1907). "Diploma d'onore" [Honorary Award]. Bollettino dell'Emigrazione (in Italian) (18). Rome, Italy: Tipografia Nazionale de G. Bertero E. C. Via Umbria: 282–283. Retrieved January 31, 2017.
- ^ Christopher M. Sterba, Good Americans: Italian and Jewish immigrants during the First World War (2003)
- ^ Mangione, Jerre and Ben Morreale, "La Storia – Five Centuries of the Italian American Experience", pg. 340
- ^ James Ciment, The Home Front Encyclopedia: Vol.I (2007) p.341
- ^ a b c d e f Sowell, Thomas (1981). "Chapter 5: The Italians". Ethnic America: A History. New York: Basic Books. ISBN 0-465-02075-5.
- ^ Beaman, Middleton (July 1924). "Current Legislation: The Immigration Act of 1924". American Bar Association Journal. 10 (7). American Bar Association: 490–492. JSTOR 25709038.
- ^ "Immigration". Statistical Abstract of the United States: 1931 (PDF) (53rd ed.). Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of Foreign and Domestic Commerce. August 1931. pp. 103–107. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 29, 2021. Retrieved October 23, 2021.
- ^ "History of Italian Immigration". Mtholyoke.edu. Archived from the original on October 14, 2017. Retrieved August 16, 2016.
- ^ U.S. Department of Commerce, Statistical Abstract of the United States: 1930 (1930) pp 99-100.
- ^ "Who Was Shut Out?: Immigration Quotas, 1925-1927". historymatters.gmu.edu. Retrieved August 16, 2016.
- ^ Michael Perino, The Hellhound of Wall Street: How Ferdinand Pecora's Investigation of the Great Crash Forever Changed American Finance (Penguin Press, 2010).
- ^ Bonfils, Marie (March 8, 2016). "The Reckoning, Pecora for the Public".
- ^ While not a Communist Party member, "no elected politician has ever symbolized the Left in Congress more consistently than Vito Marcantonio." Gerald Meyer (1989). Vito Marcantonio: Radical Politician, 1902-1954. SUNY Press. pp. 1–2. ISBN 978-0-7914-0082-1.
- ^ Salvatore J. LaGumina, ed., The Italian American Experience: An Encyclopedia(1999) pp 480–486.
- ^ "Luigi Del Bianco: About Luigi". Luigimountrushmore.com. Archived from the original on February 22, 2013. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ Mangione, Jerre and Ben Morreale, "La Storia – Five Centuries of the Italian American Experience", pg. 176–177
- ^ "Making American Farmers of Italian Immigrants: Successful Experiments in Building Up Colonies to Till the Soil, Though States Give Insufficient Encouragement" (PDF). The New York Times. December 4, 1910.
- ^ Donna R. Gabaccia, "Ethnicity in the Business World: Italians in American Food Industries," The Italian American Review 6#2 (1997/1998): 1–19.
- ^ Salvatore J. LaGumina, "Reflections of an Italian-American Worker." Journal of Ethnic Studies 3.2 (1975): 65-77 online.
- ^ Roberto M. Dainotto (2015) The Mafia: A Cultural History pp. 7-44
- ^ Davidf Critchley, The origin of organized crime in America: The New York City Mafia, 1891–1931 (Routledge, 2008).
- ^ Dominic J. Capeci, "Al Capone: Symbol of a Ballyhoo Society." Journal of Ethnic Studies 2.4 (1975): 33–46.
- ^ John Patrick Diggins, Mussolini and Fascism: The View From America (Princeton UP, 1972) pp. 58-60, 66, 68, 143.
- ^ Peter R. D'Agostino, Rome in America: Transnational Catholic Ideology from the Risorgimento to Fascism (U. of North Carolina Press, 2004) pp. 256–258.
- ^ Stefano Luconi, "Fascism and Italian-American Identity Politics." Italian Americana 33#1(2015), pp. 6–24. online, quoting p. 7
- ^ Fraser M. Ottanelli, " 'Mussolini's Column': Fascist Memorials and the Politics of Italian American Identity in Chicago." Italian American Review 12.1 (2022): 86-107.
- ^ "Enrico Fermi, architect of the nuclear age, dies". Autumn 1954. Archived from the original on November 17, 2015. Retrieved November 2, 2015.
- ^ "Gentile". National Aviation Hall of Fame. Retrieved December 21, 2020.
- ^ Johnson, Richard Riley (1995). Twenty Five Milk Runs (And a few others): To Hell's Angels and back. Victoria, Canada: Trafford Publishing. p. 4. ISBN 1-4120-2501-X. Retrieved October 30, 2009.
- ^ Taylor, David A. "During World War II, the U.S. Saw Italian-Americans as a Threat to Homeland Security". smithsonianmag.com. Retrieved May 26, 2021.
- ^ "Why America Targeted Italian-Americans During World War II". history.com. January 14, 2019. Retrieved May 26, 2021.
- ^ Di Stasi, Lawrence (2004). Una Storia Segreta: The Secret History of Italian American Evacuation and Internment during World War II. Heyday Books. ISBN 1-890771-40-6.
- ^ Fox, Stephen (2000). Uncivil liberties: Italian Americans under siege during World War II ([Rev.] ed.). [Parkland, Fla.]: Universal Publishers/Upublish.com. ISBN 978-1-58112-754-6.
- ^ "Prisoners Amoung [sic] Us Italian American Identity and WWII". youtube.com. November 8, 2016. Archived from the original on December 11, 2021. Retrieved May 26, 2021.
- ^ Luconi, "Fascism and Italian-American Identity Politics," p. 15.
- ^ Tirabassi, Maddalena (1984–1985). "Enemy Aliens or Loyal Americans?: the Mazzini Society and the Italian-American Communities". Rivista di Studi Anglo-Americani (4–5): 399–425.
- ^ Morrow, Felix (June 1943). "Washington's Plans for Italy". Fourth International. 4 (6): 175–179. Retrieved December 9, 2018.
- ^ Marton, Eric. "Italian Americans: The History and Culture of a People." Page 148. Quote Vice President Nelson Rockefeller: "I think of the 1.5 million Americans of Italian descent who made up ten per cent of the armed might of the United States in World War II, and many of these men you have met in years still well remembered."
- ^ "Jan 14, 2019 Why America Targeted Italian-Americans During World War II". history.com. January 14, 2019. Retrieved May 26, 2021.
- ^ "Biagio M. Corvo, 74, Intelligence Officer During World War II". New York Times. June 7, 1994. Retrieved April 2, 2021.
- ^ "American National Biography Online". Anb.org. Retrieved October 7, 2017.
- ^ a b "Prisoner's Among Us" (PDF). National Italian American Foundation. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 6, 2017.
- ^ "A Review of the Restrictions on Persons of Italian Ancestry During World War II" (PDF). US DOJ. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 9, 2007.
- ^ Branca-Santos, Paula (Spring 2001). "Injustice Ignored: The Internment of Italian - Americans during World War II". Pace International Law Review. 13 (1): 151. doi:10.58948/2331-3536.1207. S2CID 153416867.
- ^ "Text of H.R. 2442 (106th): Wartime Violation of Italian American Civil Liberties Act (Passed Congress/Enrolled Bill version) - GovTrack.us". GovTrack.us. Retrieved August 16, 2016.
- ^ Chawkins, Steve (August 23, 2010). "State apologizes for mistreatment of Italian residents during WWII". Los Angeles Times. ISSN 0458-3035. Retrieved August 16, 2016.
- ^ "10 Greatest Race Car Drivers of All Time". carophile.org. May 7, 2015. Retrieved April 9, 2017.
- ^ "Il Giorno del Ricordo" (in Italian). February 10, 2014. Retrieved October 16, 2021.
- ^ "L'eredità dell'esilio: vip e debiti" (in Italian). February 16, 2019. Retrieved December 16, 2022.
- ^ "Al lavoro con... Lidia Matticchio Bastianich" (in Italian). November 23, 2020. Retrieved December 16, 2022.
- ^ Buliga, Ana Laura. "Causes and Effects of the Migratory Italian Waves in the 19Th - 20Th Centuries." Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Brasov, Series VII: Social Sciences & Law, vol. 9 (58), no. 2, July 2016, pp. 53–60. EBSCOhost,
- ^ Moquin, Documentary History (1974) pp 401–32
- ^ Candeloro (1984) pp 266–68
- ^ Collins, Glenn (February 11, 1985). "THE FAMILY;A NEW LOOK AT INTERMARRIAGE IN THE U.S. (Published 1985)". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved February 6, 2021.
- ^ "John Gennari (Author of the book "Flavor and Soul: Italian America at Its African American Edge")". We the Italians. Retrieved May 19, 2023.
- ^ Aldo E. Salerno, "Medal of Honor Winners", in The Italian American Experience: An Encyclopedia, ed. Salvatore LaGumina (New York: Garland, 2000), pp. 365–68.
- ^ "Italian American Contributions". March 9, 2015. Archived from the original on March 9, 2015.
- ^ Andrew F. Smith (May 1, 2007). The Oxford Companion to American Food and Drink. Oxford University Press. p. 501. ISBN 978-0-19-530796-2.
- ^ Fred L. Gardaphe (2004). Leaving Little Italy: Essaying Italian American Culture. SUNY Press. p. 138. ISBN 978-0-7914-5917-1.
- ^ "'Amore': Italian-American Singers In The 20th Century". Npr.org. Retrieved October 7, 2017.
- ^ Geoffrey S. Cahn, "Composers, Classical", in The Italian American Experience: An Encyclopedia, ed. Salvatore LaGumina (New York: Garland, 2000), p. 141.
- ^ Luciano J. Iorizzo, "Jazz", in The Italian American Experience: An Encyclopedia, ed. Salvatore LaGumina (New York: Garland, 2000), p. 314.
- ^ "Italian Influence on American Glamour". Life In Italy. May 31, 2012. Retrieved October 7, 2017.
- ^ "1893 Zambelli, Grucci and Italian American fireworks predominance". Milestons of the Italian American Experience. Archived from the original on October 25, 2015. Retrieved May 13, 2015.
- ^ See Rudolph, J. Vecoli (1996). "The Coming Of Age Of Italian Americans: 1945-1974", Ethnicity 1978 5(2) 119-147; and Stefano Luconi, "Machine Politics and the Consolidation of the Roosevelt Majority: The Case of Italian Americans in Pittsburgh and Philadelphia". Journal of American Ethnic History. 15 (2): 32–59.
- ^ Lubell, Samuel (1956). The Future of American Politics (2nd ed.). Anchor Press. p. 70. OL 6193934M.
- ^ "NIAF. Two Days of Italian/American Affairs". I-italy.org. October 14, 2007. Archived from the original on February 16, 2015. Retrieved September 2, 2010.
- ^ Salvatore J. LaGumina, "New York City Italian American Mayors, La Guardia, Impellitteri, and Giuliani: Comparisons, Contrasts and Curiosities", Proceedings of the American Italian Historical Association, Nov 2000, Vol. 33, pp 24–44
- ^ Sam Roberts (April 18, 2008), "The Giuliani Years: History; La Guardia's Legacy Is Formidable, but it May Be Surpassed", The New York Times
- ^ Thomas Kessner, Fiorello H. LaGuardia and the Making of Modern New York (1989)
- ^ Press Release, Nobel Prize Organisation, 15 October 1985
- ^ Nelli, Humbert S. (1980). "Italians". In Thernstrom, Stephan; Orlov, Ann; Handlin, Oscar (eds.). Harvard Encyclopedia of American Ethnic Groups. Harvard University Press. pp. 545–560. ISBN 0-674-37512-2. OCLC 1038430174.
- ^ Frank M. Sorrentino; Jerome Krase (2000). The Review of Italian American Studies. Lexington Books. p. 259. ISBN 978-0-7391-0159-9.
- ^ "A Profile of Today's Italian Americans: A Report Based on the Year 2000 Census" (PDF). Order of the Sons of Italy in America. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 27, 2011. Retrieved July 21, 2011.
- ^ Comparative Study of Fifteen Ethnic Groups, University of Chicago Study, 1994
- ^ "Fauci: The Virus Hunter". PBS (Special Documentary). 2021.
- ^ Vecchio (2006)
- ^ Bénédicte Deschamps, "The Italian-American Press and the "Woman Question", 1915–1930," Studi Emigrazione (June 2003) 40#150, pp 303–314.
- ^ Elizabeth Zanoni, "'Per Voi, Signore: Gendered Representations of Fashion, Food, and Fascism in Il Progresso Italo-Americano during the 1930s." Journal of American Ethnic History (2012) 31#3 pp 33-71. online [dead link]
- ^ Worrall, Janet E. (2001). "Labor, Gender, and Generational Change in a Western City". Western Historical Quarterly. 32 (4): 437–467. doi:10.2307/3650801. JSTOR 3650801.
- ^ see Italian Americana, Vol. 29, no. 2, Summer 2011 for five articles about DeLillo's work
- ^ "Contemporary Italian American Writing". ItalianAmericanWriters.com. Retrieved September 3, 2010.
- ^ Helen Barolini, ed. The Dream Book: An Anthology of Writings by Italian American Women, (1995)
- ^ "City Lights Books". Citylights.com. Archived from the original on January 28, 2015. Retrieved September 3, 2010.
- ^ "Introduction on an Annotated Bibliography". Italianstudies.org. Retrieved September 3, 2010.
- ^ "Bibliography". Iawa.net. Retrieved September 3, 2010.
- ^ Josephine Gattuso Hendin, "The New World of Italian American Studies". American Literary History, Volume 13, Number 1, Spring 2001, pp. 141–157
- ^ Mary Jo Bona, Claiming a Tradition: Italian American Women Writers (1999)
- ^ Italian Americana, Volumes 12-21, nos. 1–2
- ^ "Contemporary Italian American Writing – Bordighera Poetry Prize". ItalianAmericanWriters.com. Archived from the original on January 15, 2013. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ "Bordighera Press". Bordighera Press. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ "Antoinette Bosco's Home Page". Antoinettebosco.com. Retrieved August 10, 2014.
- ^ a b "An Italian American Mystery". nineteensixty-four.blogspot.com. Center for Applied Research in the Apostolate (CARA) at Georgetown University. July 8, 2011. Retrieved May 31, 2021.
- ^ The Catholic Encyclopedia, Vol. 8, 1910
- ^ Gerald McKevitt BROKERS OF CULTURE, ITALIAN JESUITS IN THE AMERICAN WEST, 1848–1919 (Stanford University Press, 2007). See review of book by John T. McGreevy ("Off A Distant Land") in AMERICA, 7, May 2007, 30–31.
- ^ Form, William (2000). "Italian Protestants: Religion, Ethnicity, and Assimilation". Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion. 39 (3): 307–320. doi:10.1111/0021-8294.00026. JSTOR 1387816.
- ^ Jack Nusan Porter, "Italian American Jews," in The Italian American Experience: An Encyclopedia, ed. Salvatore J. LaGumina (New York: Garland, 2000), pp.302–303.
- ^ "The Italian Jewish Exiles in America. An Overview by Gianna Pontecorboli". Centro Primo Levi New York. Retrieved May 31, 2021.
- ^ "Centro Primo Levi New York". Retrieved March 3, 2024.
- ^ Franco, J. Philip di (1988). The Italian Americans (1. print. ed.). New York: Chelsea House Publishers. pp. 37–38. ISBN 0-87754-886-2.
- ^ Vecoli (1978)
- ^ Chavez, Linda (March 25, 2011). "Hispanic population booms". Florida Today. Melbourne, Florida. pp. 9A.
- ^ United States Census Bureau. "US demographic census". Archived from the original on February 12, 2020. Retrieved April 15, 2008.
- ^ "Nobel Prize Winners of Italian Descent". Italiansrus.com. Retrieved September 3, 2010.
- ^ "La Scuola, the only Italian Immersion School in San Francisco, receives recognition as the first and only Italian Accredited School on the west coast!". La Scuola International School. Archived from the original on January 10, 2019. Retrieved January 10, 2019.
- ^ "About la scuola Archived 2015-06-23 at the Wayback Machine." La Scuola d'Italia Guglielmo Marconi. Retrieved on May 2, 2015.
- ^ "Appendix Table 2. Languages Spoken at Home: 1980, 1990, 2000, and 2007". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved August 6, 2012.
- ^ "Detailed Language Spoken at Home and Ability to Speak English for Persons 5 Years and Over--50 Languages with Greatest Number of Speakers: United States 1990". United States Census Bureau. 1990. Retrieved July 22, 2012.
- ^ "Language Spoken at Home: 2000". United States Bureau of the Census. Archived from the original on February 12, 2020. Retrieved August 8, 2012.
- ^ "Detailed Languages Spoken at Home by English-Speaking Ability for the Population 5 Years and Over: 2011" (PDF). census.gov. US Census Bureau. p. 3. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 8, 2019.
- ^ "Mother Tongue of the Foreign-Born Population: 1910 to 1940, 1960, and 1970". United States Census Bureau. March 9, 1999. Retrieved August 6, 2012.
- ^ "Sons of Italy News Bureau" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on December 22, 2009.
- ^ "Language Use and English-Speaking Ability: 2000" (PDF). 2003. Retrieved September 3, 2010.
- ^ "The Bordighera Poetry Prize". Italianamericanwriters.com. Archived from the original on January 15, 2013. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ "Faculty". Columbia.edu. February 22, 1999. Archived from the original on June 24, 2010. Retrieved September 3, 2010.
- ^ "Contemporary Italian American Writing — Alfredo de Palchi". ItalianAmericanWriters.com. Retrieved September 3, 2010.
- ^ "Italian Dialect Poetry". Userhome.brooklyn.cuny.edu. Retrieved September 3, 2010.
- ^ "Joseph Tusiani – Biography". Siba3.unile.it. Archived from the original on July 16, 2011. Retrieved September 3, 2010.
- ^ Italian Americans entry (in Italian) in the Enciclopedia Treccani
- ^ Nosowitz, Dan (November 5, 2015). "How Capicola Became Gabagool: The Italian New Jersey Accent, Explained". Atlas Obscura. Retrieved June 14, 2019.
- ^ "Languages Spoken and Learned in the United States". Vistawide.com. Retrieved September 3, 2010.
- ^ Pilon, Mary (May 10, 2010). "Italian Job: Get Back on AP Exam". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved September 3, 2010.
- ^ "ItalianAware-Home". January 31, 2019. Archived from the original on January 31, 2019. Retrieved March 3, 2024.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ "Literature Donations". Italianaware.com. Archived from the original on July 13, 2011. Retrieved September 3, 2010.
- ^ "AMERICAN ITALIAN SLANG WORDS". LETS LEARN SLANG. June 15, 2021.
- ^ "American-Italian dictionary". americanitalian.net.
- ^ "Famous Italian American TV Personalities". Life in Italy. November 19, 2015. Archived from the original on June 23, 2021. Retrieved May 15, 2021.
- ^ Philip V. Cannistraro, "Generoso Pope and the Rise of Italian American Politics, 1925-1936", in Italian Americans: New Perspectives in Italian Immigration and Ethnicity, edited by Lydio F. Tomasi, (1985) pp 264–288.
- ^ Luconi, Stefano (2001). "Generoso Pope and Italian-American Voters in New York City". Studi Emigrazione. 38 (142): 399–422.
- ^ Deschamps, Benedicte; Luconi, Stefano (2002). "The Publisher of the Foreign-Language Press as an Ethnic Leader? The Case of James V. Donnaruma and Boston's Italian-American Community in the Interwar Years". Historical Journal of Massachusetts. 30 (2): 126–143.
- ^ Eula, Michael J. (2001). "Ethnicity and Newark's 'Italian Tribune', 1934–1980". Italian Americana. 19 (1): 23–35.
- ^ Deschamps, Bénédicte (2001). "Opposing Fascism in the West: The Experience of 'Il Corriere Del Popolo' in San Francisco in the Late 1930s". Proceedings of the American Italian Historical Association. 34: 109–123.
- ^ "National Headquarters – Order Sons and Daughters of Italy in America". OSIA.
- ^ a b c Battisti, Danielle (2012). "The American Committee on Italian Migration, Anti-Communism, and Immigration Reform". Journal of American Ethnic History. 31 (2): 11–40. doi:10.5406/jamerethnhist.31.2.0011. ISSN 0278-5927. JSTOR 10.5406/jamerethnhist.31.2.0011.
- ^ "Home". The National Italian American Foundation. Retrieved March 3, 2024.
- ^ a b "Italic Institute of America". Italic.org. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ Casa Italia Chicago http://casaitaliachicago.org/
- ^ American Italian Cultural Center http://americanitalianculturalcenter.com/
- ^ American Italian Heritage Association and Museum https://americanitalianmuseum.org/
- ^ Italian American Museum https://www.italianamericanmuseum.org
- ^ History of Italian Immigration Museum http://filitaliainternational.com/museum-main Archived July 3, 2020, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Italian - Under Attack - Immigration...- Classroom Presentation - Teacher Resources - Library of Congress". Loc.gov. Retrieved October 7, 2017.
- ^ Pitroso, Giulio (2022). "Una prospettiva regionalista su "Italian Diaspora" e "Anti-Italianism" in Australia e negli Stati Uniti A regionalist perspective on "Italian Diaspora" and "Anti-Italianism" in Australia and in the United States". Nazioni e Regioni (19–20): 119–138. doi:10.15162/2282-5681/1683. ISSN 2282-5681.
- ^ Jacobson, Mathew Frye (1998). Whiteness of a Different Color: European Immigrants and the Alchemy of Race. Harvard University Press. p. 56.
- ^ Italiansclevelandmemory.org p. 123 Archived February 20, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b Gambino, Megan. "What is The Godfather Effect?". .smithsonianmag.com. Retrieved May 26, 2021.
- ^ Bertellini, Giorgio (2004). "Black Hands and White Hearts: Italian Immigrants as 'Urban Racial Types' in Early American Film Culture". Urban History. 31 (3): 375–399. doi:10.1017/s0963926805002427. S2CID 145365445.
- ^ Schuppe, Jonathan (December 16, 2000). "Essex officials tell 'The Sopranos': Fuhgeddabout filming around here". The Star-Ledger. Archived from the original on February 6, 2009. Retrieved July 31, 2008.
- ^ Campbell, R., Media and Culture: An Introduction to Mass Communication, St. Martin's Press, New York, p. 1998
- ^ "And They Came To Chicago: The Italian American Legacy". Modiomedia.com. December 1, 1958. Retrieved September 3, 2010.
- ^ Vicki Vasilopoulos (February 29, 2004). "O.K., What About Sharks Is So Italian? - New York Times". The New York Times. Retrieved August 10, 2014.
- ^ Joshua Rhett Miller (November 25, 2009). "Italian-American Groups Ask MTV To Cancel 'Jersey Shore'". Fox News. Retrieved October 9, 2011.
- ^ https://www.niaf.org/niaf_event/national-italian-american-foundation-official-statement-mtvs/
- ^ "Italian Culture on Film, Image Research Project, Italic Institute of America". Italic.org. Archived from the original on August 23, 2012. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ "Hollywood vs Italians", The Italic Way, a publication of the Italic Institute of America, Vol XXVII, 1997
- ^ "FBI — Italian/Mafia". Fbi.gov. Archived from the original on May 24, 2014. Retrieved August 10, 2014.
- ^ Gabaccia, Donna R. (2006). "Global Geography of 'Little Italy': Italian Neighbourhoods in Comparative Perspective". Modern Italy. 11 (1): 9–24. doi:10.1080/13532940500489510. S2CID 56372320.
- ^ Krase, Jerome (2007). "Seeing Ethnic Succession in Little and Big Italy". Proceedings of the American Italian Historical Association. 37: 155–171.
- ^ Guido Rossi, "Il progresso Italo-Americano and its portrayal of Italian-American Servicemen (1941-1945)." Nuova Rivista Storica (2023) 107#2 pp. 759-787.
- ^ a b "Little Italy | Italy". Lifeinitaly.com. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ "The Official Website for New York City's Little Italy District". Little Italy NYC. Archived from the original on September 4, 2017. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ "Little Italy New York City". Italian-link.com. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ "A Bronx Tale (1993)". IMDb.com. Retrieved October 7, 2017.
- ^ On page 234 of the novel, an old, infirm character easily walks from the main character's old house to Arthur Avenue.
- ^ Santos, Fernanda (January 6, 2009). "For Italians in Brooklyn, Voices on Streets Have Changed". The New York Times. Retrieved August 22, 2009.
- ^ Lemire, Jonathan (September 22, 2002). "'Small town' has big pride - & image woes: The Howard Beach story". Daily News. New York. Archived from the original on June 5, 2011. Retrieved January 17, 2010.
- ^ Battisti, Danielle. "The American Committee on Italian Migration, Anti-Communism, and Immigration Reform." Leatherby Libraries, Board of Trustees of the University of Illinois Press, 2012.
- ^ a b "Little Italy- Boston". Italianaware.com. August 23, 1927. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ "The Vanishing of the First Ward, Newark's Original Little Italy". September 7, 2020.
- ^ "Stories from Chicago's Little Italy". Taylor Street Archives. Archived from the original on December 28, 2018. Retrieved September 3, 2010.
- ^ Candeloro, Dominic (September 18, 2013). "Rundown of Chicago Italian Neighborhoods and churches: There was never just ONE Little Italy in Chicago". Retrieved March 17, 2023.
- ^ "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved August 10, 2014.
- ^ "Carnevale in St. Louis". stlouisitalians.com. Retrieved March 29, 2020.
- ^ "St Louis Italian Language Program on The Hill". stlouisitalians.com. Retrieved March 30, 2020.
- ^ "Italians in Los Angeles: Guide to a Diverse Community". italianlosangeles.org.
- ^ "Exploring The Remains of L.A.'s Little Italy". Kcet. July 10, 2013.
- ^ "The Italian American Museum of Los Angeles – IAMLA". iamla.org.
- ^ "North Beach: Authentic Character Is Intact 150 Years Later". American Planning Association. October 2, 2007. Retrieved October 16, 2007.
- ^ "American FactFinder - Results". factfinder2.census.gov. United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 12, 2020. Retrieved October 7, 2017.
- ^ "Order Sons of Italy in America® – Home". Osia.org. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ "Encyclopedia of Cleveland History:ITALIANS". Ech.cwru.edu. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ "crank pasta « International Housewares Association Blog". Housewares.org. November 15, 2010. Archived from the original on November 24, 2012. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ "Feast of the Assumption – Profile of Cleveland's Feast of the Assumption in Little Italy". Tripsavvy. Cleveland.about.com. September 6, 2012. Archived from the original on April 3, 2013. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ "North Salina Street Historic District, Syracuse City". The Gombach Group, 2010. Retrieved October 23, 2010.
- ^ "Syracuse: Among the Babies, "Bambinos", "Kinters" and Pickininies of Syracuse". The Syracuse Sunday Herald. Syracuse, NY. October 29, 1899.
- ^ "New York, Syracuse". Atlantis, 2010. Retrieved November 3, 2010.
- ^ Dunbar, Alex (September 25, 2009). "Syracuse's Little Italy at a Tipping Point". Syracuse, NY: Barrington Broadcasting Group, LLC. Archived from the original on July 19, 2011. Retrieved October 23, 2010.
- ^ "LITTLE ITALY, SYRACUSE, NEW YORK". August 21, 2014. Retrieved March 17, 2023.
- ^ "Syracuse, New York". CityData, 2010. Retrieved October 22, 2010.
- ^ Mormino, Gary (1987). The Immigrant World of Ybor City: Italians and Their Latin Neighbors in Tampa, 1885-1985. Gainesville, Florida: University Press of Florida. ISBN 0-8130-1630-4.
- ^ Jaden Hair (July 9, 2009). "Meat market inspires loyalty". TBO.com. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ Hubbs, G. Ward. "A Settlement House in Ensley's Italian District". Alabama Heritage. 2005 (75): 32–40.
- ^ Quinney, Kimber M.; Cesarini, Thomas J. (October 20, 2007). San Diego's Little Italy. Arcadia Publishing. p. 1. ISBN 978-0-7385-4780-0.
- ^ Little Italy History Archived 2010-04-15 at the Wayback Machine. The Little Italy Association. Retrieved on 2007-10-16.
- ^ Coughlin, Jovina (May 31, 2013). "West Virginia's Little Italy Communities". Jovina Cooks. Retrieved December 10, 2019.
- ^ "IX. Italians of the North and Italians of the South". The Real Italians. New York: Columbia University Press. December 31, 1942. pp. 69–75. doi:10.7312/sfor94080-009. ISBN 978-0-231-89689-4.
- ^ LaGumina, Salvatore John (2000). The Italian American experience: an encyclopedia. New York: Garland Pub. ISBN 978-0-203-80114-7. OCLC 560063238.
- ^ Carlsen, J.; Getz, D. (2006). "Strategic planning for a regional wine festival: The Margaret River Wine Region Festival". In Jack Carlsen; Stephen Charters (eds.). Global wine tourism: research, management and marketing. Wallingford: CABI. pp. 209–224. doi:10.1079/9781845931704.0209. ISBN 978-1-84593-170-4.
- ^ Wilner, John (December 1964). "Some Advanced Technical Features of the New WBAL-TV Facilities". IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting. BC-10 (2): 54–66. doi:10.1109/tbc.1964.265831. ISSN 0018-9316.
- ^ Anderson, Hattie (September 1923). "The Panhandle-Plains Historical Society". The Mississippi Valley Historical Review. 10 (2): 182–185. doi:10.2307/1902735. ISSN 0161-391X. JSTOR 1902735.
- ^ Jones, Dee. "August Derleth Papers". University of Southern Mississippi (Finding aid). doi:10.18785/fa.dg0264.
- ^ a b Wiberg, Ruth Eloise. (1995). Rediscovering Northwest Denver: its history, its people, its landmarks. Niwot, CO: University Press of Colorado. ISBN 0-585-03049-9. OCLC 42329582.
- ^ "Honors Thesis: Community and Transit in Northwest Denver". www.linkedin.com. Retrieved December 10, 2020.
- ^ "Welcome to the Denver Lodge #2075". Order Sons and Daughters of Italy in America Denver Lodge 2075. Retrieved December 10, 2020.
- ^ Boyle, Grace (August 28, 2013). "Gaetano's Celebrating Its Rebirth and Paying Homage to the Smaldones After More than 60 Years". Eater Denver. Retrieved December 10, 2020.
- ^ "Potenza Lodge". www.potenzalodge.com. Retrieved December 10, 2020.
- ^ "About Leprino, Dairy Industry Leader since 1950". Leprino Foods. Retrieved December 10, 2020.
- ^ Simich, Jerry L.; Wright, Thomas C. (March 7, 2005). The Peoples Of Las Vegas: One City, Many Faces. University of Nevada Press. ISBN 978-0-87417-651-3.
- ^ "Total Ancestry Reported - Universe: Total Ancestry Categories Tallied for People with One or More Ancestry Categories Reported", American Community Survey, U.S. Census Bureau, 2006. Retrieved March 19, 2010.
- ^ "Selected Population Profile in the United States, Total population" Archived 2020-02-12 at archive.today, American Community Survey, U.S. Census Bureau, 2006. Retrieved March 19, 2010.
- ^ a b "Table B04006 - People Reporting Ancestry - 2020 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 13, 2022. Retrieved July 13, 2022.
- ^ "Table B04006 - People Reporting Ancestry - 2015 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 13, 2022. Retrieved July 13, 2022.
- ^ "Table B04006 - People Reporting Ancestry - 2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 13, 2022. Retrieved July 13, 2022.
- ^ "Table B04004 - People reporting single ancestry - 2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 14, 2022. Retrieved July 13, 2022.
- ^ "Table B04004 - People reporting single ancestry - 2015 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 14, 2022. Retrieved July 13, 2022.
- ^ "Table B04004 - People reporting single ancestry - 2020 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 13, 2022. Retrieved July 13, 2022.
- ^ "Table B04005 - People reporting multiple ancestries - 2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 13, 2022. Retrieved July 13, 2022.
- ^ "Table B04005 - People reporting multiple ancestries - 2015 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 13, 2022. Retrieved July 13, 2022.
- ^ "Table B04005 - People reporting multiple ancestries - 2020 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 13, 2022. Retrieved July 13, 2022.
- ^ "Table B04006 - People Reporting Ancestry - 2020 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates, All States". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 17, 2022. Retrieved July 16, 2022.
- ^ "Italian American Population in All 50 States". Niaf.org. Archived from the original on October 9, 2008. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ 2010 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates: "Selected Social Characteristics in the United States"
- ^ "Uscensus2010data.com". www.uscensus2010data.com. January 27, 2012. Archived from the original on February 26, 2014. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ "Uscensus2010data.com". www.uscensus2010data.com. January 27, 2012. Archived from the original on February 26, 2014. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ "Uscensus2010data.com". www.uscensus2010data.com. January 27, 2012. Archived from the original on February 26, 2014. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ "New York Archives". Archived from the original on February 6, 2022. Retrieved February 6, 2022.
- ^ "Uscensus2010data.com". www.uscensus2010data.com. January 27, 2012. Archived from the original on February 26, 2014. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ "Uscensus2010data.com". www.uscensus2010data.com. January 27, 2012. Archived from the original on February 26, 2014. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ a b "Selected Social Characteristics in the United States: 2013 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates (DP02)". U.S. Census Bureau American Factfinder. Archived from the original on December 29, 2014. Retrieved December 29, 2014.
- ^ "Welcome to the most Italian place in the United States. It's in New Jersey". Italian American Studies Association. Retrieved December 20, 2021.
- ^ "Explore Census Data". data.census.gov. Retrieved December 29, 2024.
Bibliography
[edit]- Alba, Richard D. Italian Americans: Into the twilight of ethnicity (Prentice Hall, 1985) online
- Bona, Mary Jo. Claiming a Tradition: Italian American Women Writers (1999)
- Bonomo Albright, Carol and Christine Palamidessi Moore, ed. American Woman, Italian Style (Fordham Press, 2011).
- Chiaricati, Federico. "Sons of our race! Help your motherland! Buy Italian! Italian propaganda through food ads among Italian American ethnic communities at the turn of the century." History of Retailing and Consumption 8.1 (2022): 49-68. online
- Connell, William J. and Fred Gardaphé, eds., Anti-Italianism: Essays on a Prejudice (2010)
- Connell, William J. and Stanislao Pugliese, eds., The Routledge History of Italian Americans (2018)
- Cordasco, Francesco. The Italians; social backgrounds of an American group (1974)online
- Cosco, Joseph P. Imagining Italians: The Clash of Romance and Race in American Perceptions, 1880-1910 (State University of New York Press, 2012) online.
- Krajewski, Andrew T., Daniel DellaPosta, and Diane Felmlee. "Vertical organizations, flat networks: Centrality and criminal collaboration in the Italian-American Mafia." Social Networks 68 (2022): 127-138.
- D'Acierno, Pellegrino A., ed. The Italian American Heritage: A Companion to Literature and Arts (Routledge, 2021) online.
- D'Agostino, Peter R. Rome in America: Transnational Catholic Ideology from the Risorgimento to Fascism (2004).
- Dainotto, Roberto M. The Mafia: A Cultural History (2015)
- De Ville, John. "Italians in the United States." The Catholic Encyclopedia (1910) vol 8 online
- Diggins, John P. Mussolini and Fascism: The View from America (1972)
- Dore, Grazia. "Some Social and Historical Aspects of Italian Emigration to America" Journal of Social History, 2#2 (1968), pp. 95–122 online
- Diner, Hasia R. Hungering for America: Italian, Irish, and Jewish Foodways in the Age of Migration (2001). 292 pp.
- Fasce, Ferdinando (2009). "Singing at Work: Italian Immigrants and Music during the Epoch of World War I". Italian Americana. 27: 133–48.
- Fox, Stephen, The unknown internment: an oral history of the relocation of Italian Americans during World War II, (1990).
- Gallo, Patrick. Old Bread, New Wine: A Portrait of the Italian-Americans (1981)
- Gans, Herbert J. Urban Villagers (1982), sociological study online
- Gems, Gerald R. Sport and the Shaping of Italian-American Identity. (Syracuse University Press, 2013) 312 pp.
- Giordano, Paolo A. and Anthony Julian Tamburri, eds. Italian Americans in the Third Millennium : Social Histories and Cultural Representations. New York: American Italian Historical Association, 2009.
- Giordano, Ralph G. "Italian Culture in America The Immigrants 1880 to 1930 From Discrimination to Assimilation" (Academica Press 2023).
- Giordano, Ralph G., "Italian Culture in America How a Founding Father Introduced Italian Art, Architecture, Food, Wine, and Liberty to the American People" (Academica 2020).
- Giovinazzo, William, Italianità: The Essence of Being Italian and Italian-American" Dark River, an imprint of Bennion Kearny, 2018. Italianità: The Essence of Being Italian and Italian-American | Book
- Glynn, Irial: Emigration Across the Atlantic: Irish, Italians and Swedes compared, 1800-1950 , European History Online, Mainz: Institute of European History, 2011, retrieved: June 16, 2011.
- Gardaphe, Fred L. Italian Signs, American Streets: The Evolution of Italian American Narrative (1996)
- Johnson, Colleen Leahy, and Colleen L. Johnson. Growing up and growing old in Italian-American families (Rutgers University Press, 1985)
- Lagumina, Salvatore J. et al. eds. The Italian American Experience: An Encyclopedia (2000) [
- Landry, Harral, ed. To See the Past More Clearly: The Enrichment of the Italian Heritage, 1890-1990 (1994) Austin: Nortex Press
- Leone, Castaldo. Italians in America (2001) Milanostampa, S.p.A.: Mockingbird Press
- Lombardo, Robert M. "Chicago's Little Sicily", Journal of the Illinois State Historical Society Volume: 100. Issue: 1. 2007.
- Luconi, Stefano. From Paesani to White Ethnics: The Italian Experience in Philadelphia (2001)
- Luconi, Stefano (2012). "Contested Loyalties: World War II and Italian Americans' Ethnic Identity". Italian Americana. 30: 151–67.
- Luconi, Stefano. "Food as a Terrain for Identity Construction and Ethnic Confrontation among Italian Americans in the United States." Journal of American Studies of Turkey 60 (2023): 17-42. online
- Maddalena, Marinari. Unwanted: Italian and Jewish Mobilization against Restrictive Immigration Laws, 1882–1965 (2020) excerpt
- Mangione, Jerre and Ben Morreale, La Storia: Five Centuries of the Italian American Experience. New York: Harper Perennial, 1992.
- Martone, Eric, ed. Italian Americans: the history and culture of a people (ABC-CLIO, 2016) online
- Nelli, Humbert S. From immigrants to ethnics : the Italian Americans (Oxford University Press, 1983) online
- Nelli, Humbert S. "Italians", in Stephan Thernstrom, ed. Harvard Encyclopedia of American Ethnic Groups. (Harvard University Press, 1980). ISBN 0-674-37512-2. pp 545–60.
- Nelli, Humbert S. The Business of Crime: Italians and Syndicate Crime in the United States (1981) online
- Nelli, Humbert S. "The Italian padrone system in the United States" Labor History (1964) 5:2, 153–167, DOI: 10.1080/00236566408583942
- Parati, Graziella, and Anthony Julian Tamburri, eds. The Cultures of Italian Migration: Diverse Trajectories and Discrete Perspectives. Cranberry, NJ: Fairleigh Dickinson University Press; 2011.
- Pecorini, Alberto (1909). "The Italian as an Agricultural Laborer". Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science. 33 (2): 156–166. doi:10.1177/000271620903300216. JSTOR 1011573. S2CID 151953455.
- Pozzetta, George. "Italian Americans." in Gale Encyclopedia of Multicultural America, edited by Thomas Riggs, (3rd ed., vol. 2, Gale, 2014), pp. 505–522. online
- Reppetto, Thomas A. American Mafia : a history of its rise to power (2004), scholarly history online
- Rolle, Andrew F. The immigrant upraised: Italian adventurers and colonists in an expanding America (Oklahoma UP, 1968)
- Rolle, Andrew. The Italian Americans (1980) psychohistory
- Ruberto, Laura E. and Joseph Sciorra, eds. New Italian Migrations to the United States: Vol. 1: Politics and History since 1945 (University of Illinois Press, 2017). xvi, 201 pp
- Seguin, Charles, and Sabrina Nardin. (2022) "The Lynching of Italians and the Rise of Antilynching Politics in the United States." Social Science History 46.1 (2022): 65-91. online
- Serra, Ilaria. The Imagined Immigrant: Images of Italian Emigration to the United States Between 1890 and 1924 (2009)
- Soresina, Marco. "Italian emigration policy during the Great Migration Age, 1888–1919: the interaction of emigration and foreign policy." Journal of Modern Italian Studies 21.5 (2016): 723–746.
- Sterba, Christopher M. Good Americans: Italian and Jewish Immigrants During the First World (2003)
- Thomas, Teresa Fava. "Arresting the Padroni problem and Rescuing the White Slaves in America: Italian Diplomats, Immigration Restrictionists & the Italian bureau 1881-1901." Altreitalia Riviste 192 Tesi 194 (2010) 40: 57–82. online
- Tommasi, L.F. (ed.), Italian Americans: New perspectives in Italian emigration and ethnicity (1985)
- Vecchio, Diane C. Merchants, Midwives, and Laboring Women: Italian Migrants in Urban America (2006).
- Vecoli, Rudolph J (1978). "The Coming of Age of Italian Americans: 1945–1974". Ethnicity. 5 (2): 119–147.
Localities
[edit]- Barton, Josef J. Peasants and Strangers: Italians, Rumanians, and Slovaks in an American City, 1890-1950 (1975). about Cleveland, Ohio online
- Briggs, John W. An Italian Passage: Immigrants to Three American Cities (Yale UP, 1978) on Utica NY, Rochester NY, and Kansas City, MO, 1890–1930. online
- Candeloro, Dominic. "Suburban Italians" in Melvin G. Holli and Peter Jones, eds. Ethnic Chicago (1984) pp 239–68 online
- Candeloro, Dominic. Chicago's Italians: Immigrants, Ethnics, Americans. (Arcadia Publishing, 2003).
- Cinel, Dino. From Italy to San Francisco: The Immigrant Experience (1982)
- Cinotto, Simone. The Italian American Table: Food, Family, and Community in New York City. (University of Illinois Press, 2013)
- Cinotto, Simone. Soft Soil, Black Grapes: The Birth of Italian Winemaking in California, (New York University Press, 2012)
- Critchley, David F. The origin of organized crime in America: The New York City Mafia, 1891–1931 (Routledge, 2008).
- DeBlasio, Donna M., and Martha I. Pallante. "Becoming Italian American in the Nation's Heartland: The Immigrant Experience in Ohio's Mahoning Valley." Italian Americana 40.2 (2022): 99–125.
- Delicato, Armando, Italians in Detroit. (2005).
- Demarco, William M. Ethnics and Enclaves: Boston's Italian North End (1981)
- Fichera, Sebastian. Italy on the Pacific: San Francisco's Italian Americans. New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2012.
- Guglielmo, Thomas A. White on Arrival: Italians, Race, Color, and Power in Chicago, 1890-1945 (2003)
- Jackson, Jessica Barbata. "Before the Lynching: Reconsidering the Experience of Italians and Sicilians in Louisiana, 1870s-1890s". Louisiana History (2017). 58#3: 300–338. online
- Juliani, Richard N. The Social Organization of Immigration: The Italians in Philadelphia (1980) excerpt and text search
- Juliani, Richard N. Priest, Parish, and People: Saving the Faith in Philadelphia's Little Italy (2007)
- Lassonde, Stephen. "Learning and earning: Schooling, juvenile employment, and the early life course in late nineteenth-century New Haven." Journal of Social History (1996): 839-870. online
- Lassonde, Stephen. Learning to Forget: Schooling and Family Life in New Haven's Working Class, 1870-1940 (Yale UP 2005) a major scholarly study focused on Italian Americans
- ProQuest Dissertations Publishing, 1994. 9523192; PhD dissertation version of Lassonde, online, 1994)
- Luconi, Stefano. The Italian-American Vote in Providence, R.I., 1916-1948 (2005)
- Luconi, Stefano. From paesani to white ethnics: The Italian experience in Philadelphia (SUNY Press, 2001) online.
- Kobler, John. Capone: the life and world of Al Capone (1971) online, on Chicago.
- Mormino, Gary. "The Immigrant World of Ybor City: Italians and Their Latin Neighbors in Tampa, 1885–1985". Gainesville: University Press of Florida. (1987)
- Nelli, Humbert S. Italians in Chicago, 1880–1930: A Study in Ethnic Mobility (2005) online
- Orsi, Robert A. The Madonna of 115th Street: Faith and Community in Italian Harlem, 1880–1950. (Yale UP, 1985) online 3rd ed. 2010
- Ottanelli, Fraser M. " 'Mussolini's Column': Fascist Memorials and the Politics of Italian American Identity in Chicago." Italian American Review 12.1 (2022): 86–107.
- Puleo, Stephen (2007). The Boston Italians: A Story of Pride, Perseverance, and Paesani, from the Years of the Great Immigration to the Present Day. Boston: Beacon Press. ISBN 978-0-8070-5036-1.
- Smith, Tom. "The Crescent City Lynchings: The Murder of Chief Hennessy, the New Orleans 'Mafia' Trials, and the Parish Prison Mob" (The Lyons Press, 2007). online
- Stanger-Ross, Jordan. Staying Italian: Urban Change and Ethnic Life in Postwar Toronto and Philadelphia (2010).
- Vecoli, Rudolph J. "The Formation of Chicago's" Little Italies"." Journal of American Ethnic History 2.2 (1983): 5-20. online
- Veronesi, Gene. Italian Americans and Their Communities of Cleveland (1977) Ohio city; online
- Whyte, William Foote. Street Corner Society: The Social Structure of an Italian Slum (University of
Chicago Press, 1943) focus on gangs in "Cornerville" (Boston's North End).
- Yans-McLaughlin, Virginia. Family and Community: Italian Immigrants in Buffalo, 1880–1930. (1982) online.
Memory and historiography
[edit]- Agnoletto, Stefano. "Ethnicity Versus Structural Factors in North American History: The Case Study of the Italian Economic Niches." Studia Migracyjne-Przeglad Polonijny 40.1 (151) (2014): 161–181. online
- Alba, Richard D. "The twilight of ethnicity among Americans of European ancestry: The case of Italians." in Celebrating 40 Years of Ethnic and Racial Studies (Routledge, 2019). 50-74. online[permanent dead link]
- Alba, Richard D. Italian Americans: Into the twilight of ethnicity (2023) online.
- Bushman, Claudia L. America discovers Columbus: how an Italian explorer became an American hero (1992) online
- Cannistraro, Philip, and Richard Juliani, ed. Italian-Americans: The Search for a Usable Past. (The American Italian Historical Association, 1989).
- Cordasco, Francesco. Italians in the United States : an annotated bibliography of doctoral dissertations completed at American universities, with a handlist of selected published bibliographies, related reference materials, and guide books for Italian emigrants (1981) online
- Cordasco, Francesco. Italian Americans : a guide to information sources (Gale 1978) online
- D'acierno, Pellegrino. "Cinema Paradiso: The Italian American Presence in American Cinema." in The Italian American Heritage (Routledge, 2021). 563-690. abstract
- Friedman-Kasaba, Kathie. Memories of migration: Gender, ethnicity, and work in the lives of Jewish and Italian women in New York, 1870-1924 (State University of New York Press, 2012).
- Gabaccia, Donna. "Italian American Women: A Review Essay," Italian Americana 12#1 (1993): 38–61.
- Gabaccia, Donna R. "Italian Immigrant Women in Comparative Perspective." The Review of Italian American Studies (2000): 391-405 online.
- Gardaphe, Fred. L. The Art of Reading Italian Americana, New York: Bordighera Press, 2011.
- Gardaphe, Fred L. Leaving Little Italy: Essaying Italian American Culture (SUNY Press, 2003).
- Giordano, Paolo A. and Anthony Julian Tamburri, eds. "Beyond the Margin: Essays on Italian Americana" (1998).
- Gravano, Alan J., and Alexandra de Luise. "The Italian American Studies Association at Fifty-Five: 1966–2021." Diasporic Italy 1 (2021): 103-123. online
- Hobbie, Margaret. Italian American Material Culture: A Directory of Collections, Sites, and Festivals in the United States and Canada (1992).
- Kosta, Ervin B. "Becoming Italian, becoming American: Ethnic affinity as a strategy of boundary making." Ethnic and Racial Studies 42.5 (2019): 801-819.
- Krase, Jerome, ed. The Status of Interpretation in Italian American Studies (Forum Italicum, (2011) online[permanent dead link].
- Luconi, Stefano, "Is Italian-American History an Account of the Immigrant Experience with the Politics Left Out? Some Thoughts on the Political Historiography about Italian Americans", in Italian Americans in the Third Millennium: Social Histories and Cultural Representations, ed. Paolo A. Giordano and Anthony Julian Tamburri, 55–72. (New York: American Italian Historical Association, 2009).d=103874809
- Luconi, Stefano. "Whiteness and Ethnicity in Italian-American Historiography." in The Status of Interpretation in Italian American Studies: Proceedings of the first Forum in Italian American Criticism [FIAC] (Forum Italicum Publishing, 2011). Online[dead link]
- Meyer, Gerald. "Theorizing Italian American History: The Search for an Historiographical Paradigm." in The Status of Interpretation in Italian American Studies (2011): 164+. Online[dead link]
- Ottanelli, Fraser M. " 'Mussolini's Column': Fascist Memorials and the Politics of Italian American Identity in Chicago." Italian American Review 12.1 (2022): 86–107.
- Pozzetta, George E. "From Immigrants to Ethnics: The State of Italian-American Historiography." Journal of American Ethnic History 9#1 (1989): 67–95. Online
- Rossi, Guido. "Il progresso Italo-Americano and its portrayal of Italian-American Servicemen (1941-1945)." Nuova Rivista Storica (2023), 107#2 pp. 759–787.
- Simms, Norman. "The Italian-American Image During the Twentieth Century." The Histories 5.1 (2019): 4+ online
- Tamburri, Anthony Julian, Paolo A. Giordano, Fred L. Gardaphé, eds. From the Margin: Writings in Italian Americana (2000, 2nd ed.)
- Tamburri, Anthony Julian. To Hyphenate or not to Hyphenate: the Italian/American Writer: Or, An "Other" American? (1991)
- Tamburri, Anthony Julian. Re-viewing Italian Americana: Generalities and Specificities on Cinema (2011)
- Tamburri, Anthony Julian. Re-reading Italian Americana: Specificities and Generalities on Literature and Criticism (2014)
- Wirth, Christa. Memories of Belonging: Descendants of Italian Migrants to the United States, 1884-Present (Brill, 2015) online review
Primary sources
[edit]- Albright, Carol Bonomo, and Christine Palamidessi Moore, eds. American Woman, Italian Style: Italian Americana's Best Writings on Women (Fordham Univ Press, 2011) online.
- Bonomo Albright, Carol and Joanna Clapps Herman, eds. Wild Dreams (Fordham Press, 2008). Stories, memoirs, poems by and about Italian Americans. online
- Ciongoli, A. Kenneth, and Jay Parini, eds. Beyond The Godfather: Italian American Writers on the Real Italian American Experience (University Press of New England, 1997) online
- Gesualdi, Louis J. ed. The Italian/American Experience: A Collection of Writings (2012) online
- Moquin, Wayne, ed. A Documentary History of Italian Americans (1974) online
External links
[edit]- La Gazzetta Italiana - The Italian American Voice
- Italian American Digital Project Archived March 14, 2015, at the Wayback Machine
- National Italian American Foundation
- "Immigration -> Italian." Library of Congress.
- "Italian Immigration." Digital History, University of Houston
- Italian American Museum, New York Archived August 18, 2019, at the Wayback Machine
- Italy Revisited (photo archives)
- Taylor Street Archives
- ItalianImmigrants.org 1855 through 1900
- "Italian". Chicago Foreign Language Press Survey. Chicago Public Library Omnibus Project of the Works Progress Administration of Illinois. 1942 – via Newberry Library. (Selected short newspaper articles, translated into English, 1855–1938).
- The Italian Americans Archived June 29, 2019, at the Wayback Machine - PBS documentary
- "Italian American Stereotypes in U.S. Advertising" (PDF). The Order Sons of Italy in America. 2003. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 26, 2016.
- Cannato, Vincent J. (October 9, 2015). "How America became Italian". The Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved October 6, 2020.
- Immigration History Research Center (IHRC), University of Minnesota






