Demographics of Timor-Leste
| Demographics of Timor-Leste | |
|---|---|
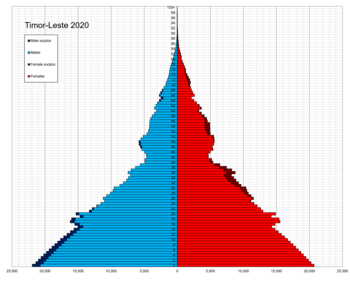 Population pyramid of Timor-Leste in 2020 | |
| Population | 1,445,006 (2022 est.) |
| Growth rate | 2.15% (2022 est.) |
| Birth rate | 30.94 births/1,000 population (2022 est.) |
| Death rate | 5.61 deaths/1,000 population (2022 est.) |
| Life expectancy | 69.92 years |
| • male | 68.25 years |
| • female | 71.7 years |
| Fertility rate | 4.21 children born/woman (2022 est.) |
| Infant mortality rate | 33.69 deaths/1,000 live births |
| Net migration rate | -3.82 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2022 est.) |
| Age structure | |
| 0–14 years | 38.29% |
| 15–64 years | 56.38% |
| 65 and over | 5.33% |
| Sex ratio | |
| Total | 1 male(s)/female (2022 est.) |
| At birth | 1.07 male(s)/female |
| Under 15 | 1.06 male(s)/female |
| 65 and over | 0.79 male(s)/female |
| Nationality | |
| Nationality | Timorese |

This is a demography of the population of Timor-Leste including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
Vital statistics
[edit]UN estimates
[edit]Registration of vital events is in Timor-Leste not complete. The Population Department of the United Nations prepared the following estimates. Population estimates account for under numeration in population censuses.[1]
| Mid-year population (thousands) | Live births (thousands) | Deaths (thousands) | Natural change (thousands) | Crude birth rate (per 1000) | Crude death rate (per 1000) | Natural change (per 1000) | Total fertility rate (TFR) | Infant mortality (per 1000 live births) | Life expectancy (in years) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 415 | 18 | 15 | 3 | 43.4 | 35.9 | 7.5 | 6.61 | 274.2 | 29.05 |
| 1951 | 418 | 18 | 14 | 4 | 43.7 | 34.2 | 9.5 | 6.59 | 271.8 | 29.30 |
| 1952 | 423 | 19 | 14 | 4 | 43.9 | 33.4 | 10.5 | 6.56 | 268.5 | 29.62 |
| 1953 | 427 | 19 | 14 | 5 | 44.2 | 32.9 | 11.2 | 6.54 | 265.8 | 29.89 |
| 1954 | 432 | 19 | 14 | 5 | 44.4 | 32.5 | 11.9 | 6.51 | 262.8 | 30.20 |
| 1955 | 437 | 20 | 14 | 5 | 44.6 | 32.1 | 12.5 | 6.48 | 259.7 | 30.52 |
| 1956 | 443 | 20 | 14 | 6 | 44.8 | 31.8 | 13.0 | 6.45 | 256.7 | 30.83 |
| 1957 | 449 | 20 | 14 | 6 | 45.1 | 31.6 | 13.5 | 6.42 | 254.0 | 31.12 |
| 1958 | 455 | 21 | 14 | 6 | 45.3 | 31.3 | 14.0 | 6.39 | 251.3 | 31.40 |
| 1959 | 462 | 21 | 14 | 7 | 45.5 | 31.1 | 14.4 | 6.36 | 248.6 | 31.70 |
| 1960 | 469 | 21 | 14 | 7 | 45.7 | 30.6 | 15.1 | 6.32 | 244.3 | 32.20 |
| 1961 | 476 | 22 | 14 | 7 | 45.7 | 30.2 | 15.5 | 6.27 | 241.1 | 32.57 |
| 1962 | 483 | 22 | 14 | 8 | 45.7 | 29.9 | 15.9 | 6.22 | 237.9 | 32.95 |
| 1963 | 491 | 22 | 15 | 8 | 45.6 | 29.5 | 16.1 | 6.16 | 235.4 | 33.26 |
| 1964 | 499 | 23 | 15 | 8 | 45.5 | 29.2 | 16.3 | 6.08 | 232.5 | 33.60 |
| 1965 | 507 | 23 | 14 | 9 | 45.2 | 28.3 | 16.9 | 6.01 | 226.4 | 34.36 |
| 1966 | 516 | 23 | 14 | 9 | 44.9 | 27.6 | 17.2 | 5.93 | 221.2 | 35.00 |
| 1967 | 525 | 23 | 14 | 9 | 44.5 | 26.9 | 17.6 | 5.86 | 215.3 | 35.73 |
| 1968 | 535 | 24 | 14 | 9 | 44.1 | 26.3 | 17.7 | 5.79 | 211.5 | 36.23 |
| 1969 | 544 | 24 | 14 | 10 | 43.6 | 25.8 | 17.8 | 5.72 | 207.8 | 36.71 |
| 1970 | 554 | 24 | 14 | 10 | 43.1 | 25.3 | 17.8 | 5.66 | 204.3 | 37.17 |
| 1971 | 564 | 24 | 14 | 10 | 42.4 | 24.6 | 17.7 | 5.58 | 200.2 | 37.72 |
| 1972 | 574 | 24 | 14 | 10 | 41.6 | 24.0 | 17.6 | 5.49 | 195.8 | 38.32 |
| 1973 | 584 | 24 | 14 | 10 | 40.7 | 23.2 | 17.5 | 5.39 | 190.7 | 38.99 |
| 1974 | 592 | 24 | 15 | 9 | 39.8 | 25.0 | 14.8 | 5.29 | 200.8 | 36.88 |
| 1975 | 600 | 23 | 24 | − 0 | 39.1 | 39.8 | −0.7 | 5.19 | 241.2 | 24.83 |
| 1976 | 610 | 23 | 23 | 0 | 38.3 | 37.9 | 0.4 | 5.12 | 229.8 | 25.96 |
| 1977 | 619 | 23 | 24 | −1 | 37.9 | 39.9 | −2.0 | 5.09 | 242.6 | 24.43 |
| 1978 | 628 | 24 | 27 | − 4 | 37.9 | 43.8 | −5.9 | 5.09 | 266.9 | 21.84 |
| 1979 | 635 | 24 | 27 | − 2 | 38.3 | 42.3 | −3.9 | 5.14 | 258.8 | 22.53 |
| 1980 | 642 | 25 | 21 | 3 | 39.0 | 33.6 | 5.4 | 5.22 | 203.3 | 28.45 |
| 1981 | 649 | 27 | 21 | 6 | 41.3 | 32.5 | 8.8 | 5.53 | 193.5 | 29.57 |
| 1982 | 655 | 27 | 21 | 7 | 41.6 | 31.3 | 10.3 | 5.56 | 183.4 | 30.82 |
| 1983 | 662 | 28 | 20 | 7 | 41.9 | 30.6 | 11.3 | 5.59 | 177.0 | 31.64 |
| 1984 | 671 | 28 | 19 | 9 | 42.2 | 28.4 | 13.7 | 5.61 | 161.5 | 33.75 |
| 1985 | 682 | 29 | 19 | 9 | 42.4 | 28.5 | 13.9 | 5.65 | 161.4 | 33.80 |
| 1986 | 694 | 29 | 19 | 10 | 42.5 | 28.1 | 14.5 | 5.67 | 157.4 | 34.34 |
| 1987 | 708 | 30 | 19 | 11 | 42.5 | 26.7 | 15.7 | 5.68 | 148.7 | 35.64 |
| 1988 | 723 | 31 | 19 | 11 | 42.5 | 26.6 | 15.8 | 5.72 | 148.4 | 35.75 |
| 1989 | 740 | 31 | 14 | 17 | 42.3 | 19.1 | 23.3 | 5.76 | 144.4 | 44.55 |
| 1990 | 758 | 32 | 14 | 18 | 42.2 | 18.7 | 23.5 | 5.81 | 142.6 | 44.95 |
| 1991 | 773 | 32 | 14 | 18 | 41.8 | 18.4 | 23.3 | 5.84 | 140.8 | 44.99 |
| 1992 | 784 | 33 | 14 | 19 | 41.6 | 17.5 | 24.1 | 5.87 | 134.2 | 46.28 |
| 1993 | 795 | 33 | 13 | 20 | 41.2 | 16.8 | 24.4 | 5.88 | 128.5 | 47.25 |
| 1994 | 807 | 33 | 13 | 20 | 40.9 | 16.1 | 24.8 | 5.91 | 123.6 | 48.25 |
| 1995 | 819 | 33 | 13 | 20 | 40.6 | 16.3 | 24.3 | 5.94 | 123.5 | 48.02 |
| 1996 | 831 | 34 | 13 | 20 | 40.2 | 15.8 | 24.4 | 5.94 | 118.7 | 48.82 |
| 1997 | 843 | 34 | 13 | 21 | 39.9 | 15.4 | 24.5 | 5.96 | 114.2 | 49.52 |
| 1998 | 855 | 34 | 13 | 21 | 39.6 | 15.7 | 23.9 | 5.96 | 115.1 | 49.12 |
| 1999 | 867 | 34 | 16 | 19 | 39.4 | 18.0 | 21.4 | 5.97 | 118.0 | 45.70 |
| 2000 | 878 | 35 | 9 | 26 | 39.1 | 10.2 | 28.9 | 5.98 | 77.0 | 58.57 |
| 2001 | 893 | 35 | 9 | 26 | 39.1 | 9.9 | 29.2 | 6.01 | 73.3 | 59.36 |
| 2002 | 910 | 36 | 9 | 27 | 39.0 | 9.6 | 29.4 | 6.02 | 69.7 | 60.15 |
| 2003 | 927 | 36 | 9 | 27 | 38.3 | 9.3 | 29.0 | 5.95 | 66.5 | 60.87 |
| 2004 | 946 | 36 | 9 | 27 | 37.6 | 9.1 | 28.5 | 5.85 | 63.1 | 61.63 |
| 2005 | 969 | 35 | 9 | 27 | 36.5 | 8.8 | 27.7 | 5.71 | 59.8 | 62.33 |
| 2006 | 995 | 35 | 8 | 27 | 35.4 | 8.5 | 26.9 | 5.56 | 56.7 | 63.07 |
| 2007 | 1 019 | 35 | 8 | 26 | 34.2 | 8.3 | 25.9 | 5.40 | 53.9 | 63.72 |
| 2008 | 1 043 | 35 | 8 | 26 | 33.2 | 8.1 | 25.1 | 5.23 | 51.4 | 64.33 |
| 2009 | 1 066 | 35 | 9 | 26 | 32.3 | 8.0 | 24.3 | 5.04 | 49.2 | 64.85 |
| 2010 | 1 088 | 34 | 9 | 26 | 31.4 | 8.0 | 23.4 | 4.85 | 47.3 | 65.30 |
| 2011 | 1 113 | 34 | 9 | 25 | 30.7 | 7.9 | 22.8 | 4.66 | 45.7 | 65.70 |
| 2012 | 1 138 | 34 | 9 | 25 | 29.8 | 7.7 | 22.1 | 4.44 | 44.1 | 66.08 |
| 2013 | 1 162 | 34 | 9 | 25 | 29.1 | 7.6 | 21.5 | 4.27 | 42.6 | 66.44 |
| 2014 | 1 185 | 34 | 9 | 25 | 28.4 | 7.6 | 20.9 | 4.09 | 41.2 | 66.79 |
| 2015 | 1 206 | 33 | 9 | 24 | 27.7 | 7.5 | 20.2 | 3.90 | 39.8 | 67.14 |
| 2016 | 1 225 | 33 | 9 | 24 | 27.0 | 7.3 | 19.7 | 3.74 | 38.5 | 67.45 |
| 2017 | 1 243 | 33 | 9 | 24 | 26.5 | 7.2 | 19.3 | 3.60 | 37.3 | 67.75 |
| 2018 | 1 262 | 33 | 9 | 24 | 25.9 | 7.0 | 18.9 | 3.45 | 36.2 | 68.02 |
| 2019 | 1 280 | 33 | 9 | 24 | 25.5 | 6.9 | 18.6 | 3.34 | 35.2 | 68.27 |
| 2020 | 1 300 | 33 | 9 | 24 | 25.3 | 6.8 | 18.4 | 3.25 | 34.2 | 68.48 |
| 2021 | 1 321 | 33 | 10 | 23 | 24.9 | 7.2 | 17.7 | 3.15 | 33.4 | 67.74 |
Fertility and Births
[edit]Total Fertility Rate (TFR) and Crude Birth Rate (CBR):[2]
| Year | CBR (Total) | TFR (Total) | CBR (Urban) | TFR (Urban) | CBR (Rural) | TFR (Rural) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2003 | 52.1 | 7.8 | 50.5 | 7.4 | ||
| 2009–2010 | 33.2 | 5.7 (5.1) | 33.1 | 4.9 (4.2) | 33.2 | 6.0 (5.4) |
| 2016 | 26.8 | 4.2 (3.5) | 28.4 | 3.5 (3.0) | 26.2 | 4.6 (3.8) |
Fertility rate by municipality
[edit]Aileu Municipality and Ainaro Municipality have the highest fertility rate with 5.5 children per woman, followed by Ermera Municipality with 5.4 children per woman.[3]
| Municipality | Fertility rate in 2004 | Fertility rate in 2010 | Fertility rate in 2015 | Decline between 2004 and 2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dili | 6.7 | 5.3 | 3.9 | |
| Liquiçá | 7.1 | 6.2 | 5.1 | |
| Covalima | 7.0 | 5.6 | 4.7 | |
| Manufahi | 7.3 | 5.6 | 4.9 | |
| Manatuto | 6.7 | 5.6 | 4.6 | |
| Aileu | 8.4 | 7.0 | 5.5 | |
| Lautém | 7.7 | 6.4 | 5.2 | |
| Bobonaro | 6.9 | 5.9 | 4.7 | |
| Baucau | 6.9 | 5.8 | 4.7 | |
| Viqueque | 6.3 | 5.3 | 4.6 | |
| Ermera | 8.2 | 6.9 | 5.4 | |
| Ainaro | 8.3 | 6.4 | 5.5 | |
| Oecusse (SAR) | 6.9 | 5.2 | 4.2 | |
| 7.2 | 5.9 | 4.7 |
Between 2014/15, around 43.5% of the births occurred in a health facility, up from 36.3% in 2010/11. This percentage varies widely from 77.5% in Dili Municipality to only 15.1% of all births in Ermera Municipality.
Life expectancy at birth
[edit]Average life expectancy at age 0 of the total population.[4]
| Period | Life expectancy in Years |
Period | Life expectancy in Years |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1950–1955 | 30.0 | 1985–1990 | 46.5 |
| 1955–1960 | 32.5 | 1990–1995 | 50.5 |
| 1960–1965 | 35.0 | 1995–2000 | 57.0 |
| 1965–1970 | 37.5 | 2000–2005 | 61.5 |
| 1970–1975 | 40.0 | 2005–2010 | 66.4 |
| 1975–1980 | 31.2 | 2010–2015 | 67.7 |
| 1980–1985 | 39.9 |
Population pyramids
[edit]| Age group | Male | Female | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 601 112 | 582 531 | 1 183 643 | 100 |
| 0-4 | 77 896 | 72 410 | 150 306 | 12.70 |
| 5-9 | 80 377 | 75 705 | 156 082 | 13.19 |
| 10-14 | 80 721 | 75 548 | 156 269 | 13.20 |
| 15-19 | 69 839 | 67 033 | 136 872 | 11.56 |
| 20-24 | 52 759 | 54 244 | 107 003 | 9.04 |
| 25-29 | 45 486 | 47 464 | 92 950 | 7.85 |
| 30-34 | 35 934 | 36 461 | 72 395 | 6.12 |
| 35-39 | 24 245 | 24 645 | 48 890 | 4.13 |
| 40-44 | 29 097 | 26 779 | 55 876 | 4.72 |
| 45-49 | 25 044 | 22 274 | 47 318 | 4.00 |
| 50-54 | 18 661 | 16 776 | 35 437 | 2.99 |
| 55-59 | 14 436 | 12 867 | 27 303 | 2.31 |
| 60-64 | 13 864 | 14 516 | 28 380 | 2.40 |
| 65-69 | 14 611 | 16 427 | 31 038 | 2.62 |
| 70-74 | 8 949 | 9 204 | 18 153 | 1.53 |
| 75-79 | 4 862 | 5 009 | 9 961 | 0.84 |
| 80-84 | 2 399 | 2 798 | 5 197 | 0.44 |
| 85+ | 1 932 | 2 281 | 4 213 | 0.36 |
| Age group | Male | Female | Total | Percent |
| 0-14 | 238 994 | 223 663 | 462 657 | 39.09 |
| 15-64 | 329 365 | 323 059 | 652 334 | 55.11 |
| 65+ | 32 753 | 35 809 | 68 562 | 5.79 |
| Age Group | Male | Female | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 642 639 | 618 768 | 1 261 407 | 100 |
| 0–4 | 86 042 | 78 681 | 164 723 | 13.06 |
| 5–9 | 84 950 | 76 259 | 161 209 | 12.78 |
| 10–14 | 82 088 | 75 015 | 157 103 | 12.45 |
| 15–19 | 75 602 | 71 942 | 147 544 | 11.70 |
| 20–24 | 60 513 | 60 703 | 121 216 | 9.61 |
| 25–29 | 46 777 | 50 239 | 97 016 | 7.69 |
| 30–34 | 40 344 | 42 718 | 83 062 | 6.58 |
| 35–39 | 28 909 | 30 013 | 58 922 | 4.67 |
| 40–44 | 24 228 | 23 965 | 48 193 | 3.82 |
| 45–49 | 27 718 | 25 146 | 52 864 | 4.19 |
| 50–54 | 21 620 | 19 325 | 40 945 | 3.25 |
| 55–59 | 16 674 | 15 419 | 32 093 | 2.54 |
| 60–64 | 14 583 | 14 712 | 29 295 | 2.32 |
| 65-69 | 11 764 | 12 441 | 24 205 | 1.92 |
| 70-74 | 9 187 | 9 388 | 18 575 | 1.47 |
| 75-79 | 6 452 | 6 789 | 13 241 | 1.05 |
| 80+ | 5 188 | 6 013 | 11 201 | 0.89 |
| Age group | Male | Female | Total | Percent |
| 0–14 | 253 080 | 229 955 | 483 035 | 38.29 |
| 15–64 | 356 968 | 354 182 | 711 150 | 56.38 |
| 65+ | 32 591 | 34 631 | 67 222 | 5.33 |
Median age
[edit]In 2015 the median age of the population was 19.6 years old. The population living in rural areas is slightly younger (19.0) compared to the population living in urban areas (20.6). Ainaro Municipality has the lowest median age with 17.3 years, while Dili Municipality has the highest median age with 21.2 years.[7]
CIA World Factbook demographic statistics
[edit]
The following demographic statistics are from the CIA World Factbook[8]
Population
[edit]
- 1,242,000 (2017)
Birth rate
[edit]- 33.4 births/1,000 population (2017 est.)
Death rate
[edit]- 5.9 deaths/1,000 population (2017 est.)
Population growth rate
[edit]- 2.36% (2017 est.)
Net migration rate
[edit]- -3.9 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2017 est.)
Infant mortality rate
[edit]- total: 35.1 deaths/1,000 live births (2017 est)
Life expectancy at birth
[edit]- total population: 68.4 years
- male: 66.8 years
- female: 70.1 years (2017 est.)
Total fertility rate
[edit]- 4.97 children born/woman (2017 est)
Nationality
[edit]- noun: East Timorese
- adjective: East Timorese
- Austronesian (Malayo-Polynesian), Papuan, small Chinese particularly Cantonese people and Europeans particularly Portuguese people descent.
- Roman Catholic 97.6% (2015 est.)
- Protestant/Evangelical 2% (2015 est.)
- Islam 0.2% (2015 est.)
- Other 0.2% (2015 est.)
- Tetum (official), Portuguese (official), Indonesian (constitutionally defined as a 'working language') and English (constitutionally defined as a 'working language').
- Note: There are a total of about 16 indigenous languages, of which Tetum, Galole, Mambae, and Kemak are spoken by significant numbers of people. The Tetum language is partially influenced by European languages, particularly Portuguese, a legacy of Portuguese rule.
- definition: age 15 and over can read and write
(2015 est.)total population male female
After achieving independence, Timor-Leste had a high illiteracy rate, with 55% of women and 46% of men illiterate. Approximately 18% of the adult population had achieved secondary education and approximately 1.4% of them had an academic degree or achieved other higher education, nearly all of whom resided in urban areas, primarily the capital Dili. Attempts to improve education services face challenges in the form of a lack of educated and experienced teachers. Continuing high fertility rates also translates to greater strains on the government to increase education budgets. The United Nations (UN) has assisted in rebuilding the education system increasing the number of teachers and rehabilitating many schools, leading to a rapid increase in school enrollment. However, problems remain as the quality of education was deemed secondary to the need to increase enrollment in Timor-Leste.
Another problem faced in increasing the education levels includes the economic conditions of the population. With high proportions of the population living below the poverty line and large households with many children, the direct costs of schooling is significant for families. Lack of monetary resources to send children to school imposes greater difficulty in increasing enrollment rates in schools. In addition, parents may be disillusioned with the poor quality of education and thus may not even be interested to send their children to schools. Much remains to be done to establish a new curriculum and support it with texts and learning materials to improve the quality of education. The variety of language spoken also means a large number of children do not speak the language of instruction – Portuguese – and this causes them to be marginalised. Many teachers do not speak Portuguese.
The inaccessibility of schools with proper facilities adds to the problem of providing adequate education to the population. Schools are located far away from homes and, coupled with the poor conditions of schools, may inhibit the early enrollment of children or lead to early drop-outs. Schools in rural areas face substantial lack of facilities to render them safe. As for the schools in urban areas, significant urban migration has meant that the supply of schools in urban areas have not managed to keep up with the increasing demand; leading to overcrowding in urban schools.
Besides the problems faced at the level of the individual households and the schools, problems in the governance and management of education are also significant impediments to raising education levels in Timor-Leste. The lack of qualified personnel in critical positions within the education ministry has meant that overall policy making, planning and management functions are restricted. Management of schools at the district level is often under-qualified due to the lack of formal training. Today therefore, Timor-Leste faces many challenges in increasing the literacy rates of their people.
At the end of Portuguese rule, literacy was at 5%.[9] Timor-Leste's adult literacy rate in 2010 was 58.3%, up from 37.6% in 2001.[10] By 2021 it was 68% among adults, and 84% among those aged 15–24, being slightly higher among women than men.[11]: 27
Education
[edit]
Timor-Leste's adult literacy rate in 2010 was 58.3%, up from 37.6% in 2001.[10] At the end of Portuguese rule, literacy was at 5%.[12] By 2021 it was 68% among adults, and 84% among those aged 15-24, being slightly higher among women than men.[11]: 27 More girls than boys attend school, although some drop out upon reaching puberty.[11]: 25 Primary schools exist throughout the country, although the quality of materials and teaching is often poor. Secondary schools are generally limited to municipal capitals. Education takes up 10% of the national budget.[11]: 27
As of 2016 22% of working age women (15-49) and 19% of working age men had no education, 15% of women and 18% of men had some primary education, 52% of women and 51% of men had some secondary education, and 11% of women and 12% of men had higher education. Overall, 75% of women and 82% of men were literate.[13]: 2
The country's main university is the National University of East Timor. There are also four colleges.[14]
Since independence, both Indonesian and Tetum have lost ground as media of instruction, while Portuguese has increased: in 2001 only 8.4% of primary school and 6.8% of secondary school students attended a Portuguese-medium school; by 2005 this had increased to 81.6% for primary and 46.3% for secondary schools.[15] Indonesian formerly played a considerable role in education, being used by 73.7% of all secondary school students as a medium of instruction, but by 2005 Portuguese was used by most schools in Baucau, Manatuto, as well as the capital district.[15] Portugal provides support to about 3% of the public schools in Timor-Leste, focused on those in urban areas, further encouraging the use of the Portuguese language.[11]: 28
The Philippines has sent Filipino teachers to Timor-Leste to teach English, so as to facilitate a program between the two countries, under which deserving East Timorese nationals with English language skills will be granted university scholarships in the Philippines.[15]
The Human Rights Measurement Initiative (HRMI)[16] finds that Timor-Leste is fulfilling only 84.5% of what it should be fulfilling for the right to education based on the country's level of income.[17] HRMI breaks down the right to education by looking at the rights to both primary education and secondary education. While taking into consideration Timor-Leste income level, the nation is achieving 90.6% of what should be possible based on its resources (income) for primary education but only 78.4% for secondary education.[17]
References
[edit]- ^ United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs Population Division (2022). "World Population Prospects 2022 Demographic indicators by region, subregion and country, annually for 1950-2100" (XLS (91MB)). United Nations Population Division. 27 (Online ed.). New York: United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. rows 8789:8860, cols M,X,AE,S,AH,S,AA,AV,AI. Archived from the original on 2022-08-09.
- ^ "MEASURE DHS: Demographic and Health Surveys".
- ^ http://www.statistics.gov.tl/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/2015-Census-Fertility-Report12.pdf [bare URL PDF]
- ^ "World Population Prospects - Population Division - United Nations". esa.un.org. Retrieved 2018-08-26.
- ^ "Population by Age & Sex". Statistics Timor-Leste General Directorate of Statistics. Statistics Timor-Leste. Retrieved 29 January 2020.
- ^ "UNSD — Demographic and Social Statistics".
- ^ 2015 Timor-Leste Population and Housing Census – Data Sheet
- ^ "East & Southeast Asia :: TIMOR-LESTE". CIA The World Factbook. 11 April 2023.
- ^ Roslyn Appleby (30 August 2010). ELT, Gender and International Development: Myths of Progress in a Neocolonial World. Multilingual Matters. p. 92. ISBN 978-1-84769-303-7.
- ^ a b "National adult literacy rates (15+), youth literacy rates (15–24) and elderly literacy rates (65+)". UNESCO Institute for Statistics.
- ^ a b c d e "Timor-Leste Country Report 2022". Bertelsmann Stiftung. 2022. Retrieved 2 May 2022.
- ^ Roslyn Appleby (30 August 2010). ELT, Gender and International Development: Myths of Progress in a Neocolonial World. Multilingual Matters. p. 92. ISBN 978-1-84769-303-7.
- ^ "Timor-Leste 2016 Demographic and Health Survey Key Findings" (PDF). General Directorate of Statistics. 2018. Retrieved 30 May 2022.
- ^ Robinson, Geoffrey (2010). If You Leave Us Here, We Will Die: How Genocide Was Stopped in East Timor. Princeton: Princeton University Press. p. 72.
- ^ a b c "Table 5.7 – Profile Of Students That Attended The 2004/05 Academic Year By Rural And Urban Areas And By District". Direcção Nacional de Estatística. Archived from the original on 14 November 2009.
- ^ "Human Rights Measurement Initiative – The first global initiative to track the human rights performance of countries". humanrightsmeasurement.org. Retrieved 31 March 2022.
- ^ a b "Timor-Leste - HRMI Rights Tracker". rightstracker.org. Retrieved 31 March 2022.
External links
[edit]- Fernandes, Ajito; Prabawa, Titi Susilowati; Therik, Wilson M. A. (April 2022). "The Livelihood of Chinese Migrants in Timor-Leste". Social Sciences. 11 (4): 157. doi:10.3390/socsci11040157. ISSN 2076-0760.

